FastAPI入门:demo、路径参数、查询参数
demo
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/")
async def root():return {"message": "Hello World"}
在终端运行
fastapi dev main.py
结果如下:
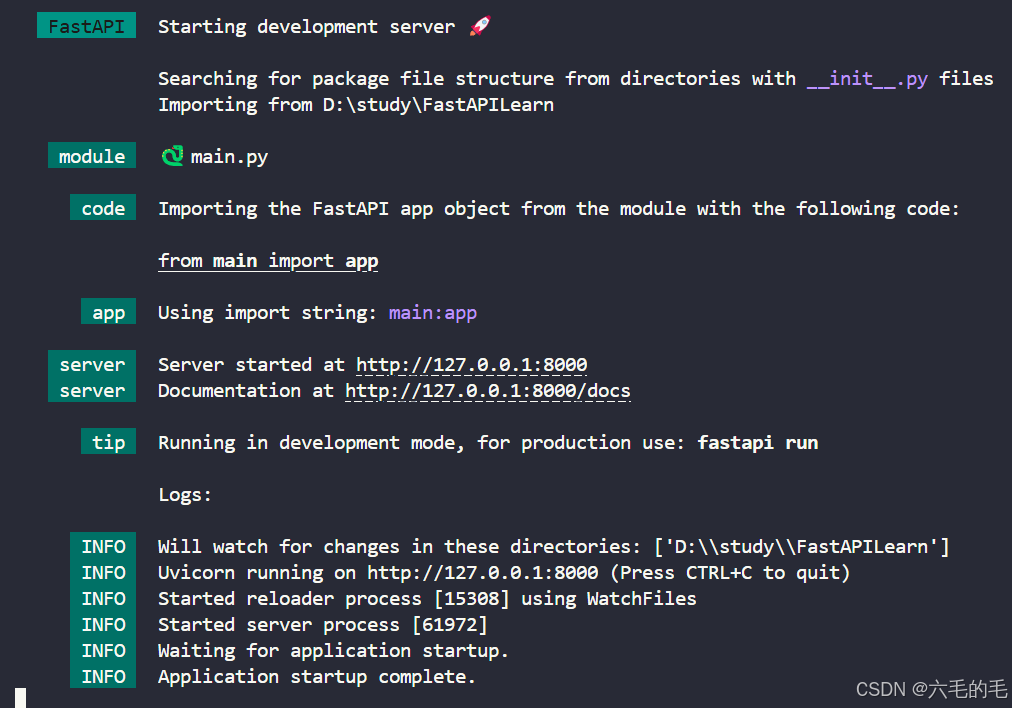
打开http://127.0.0.1:8000:
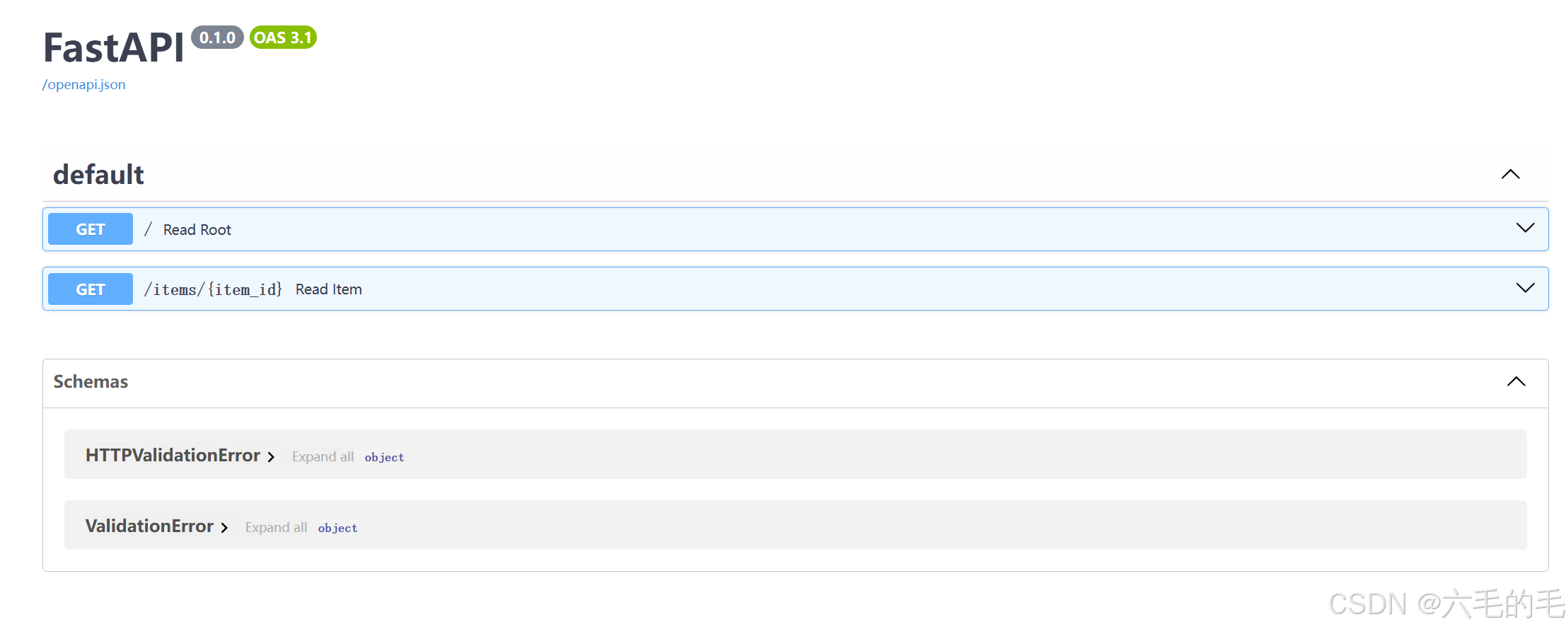
交互式API文档:位于http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs
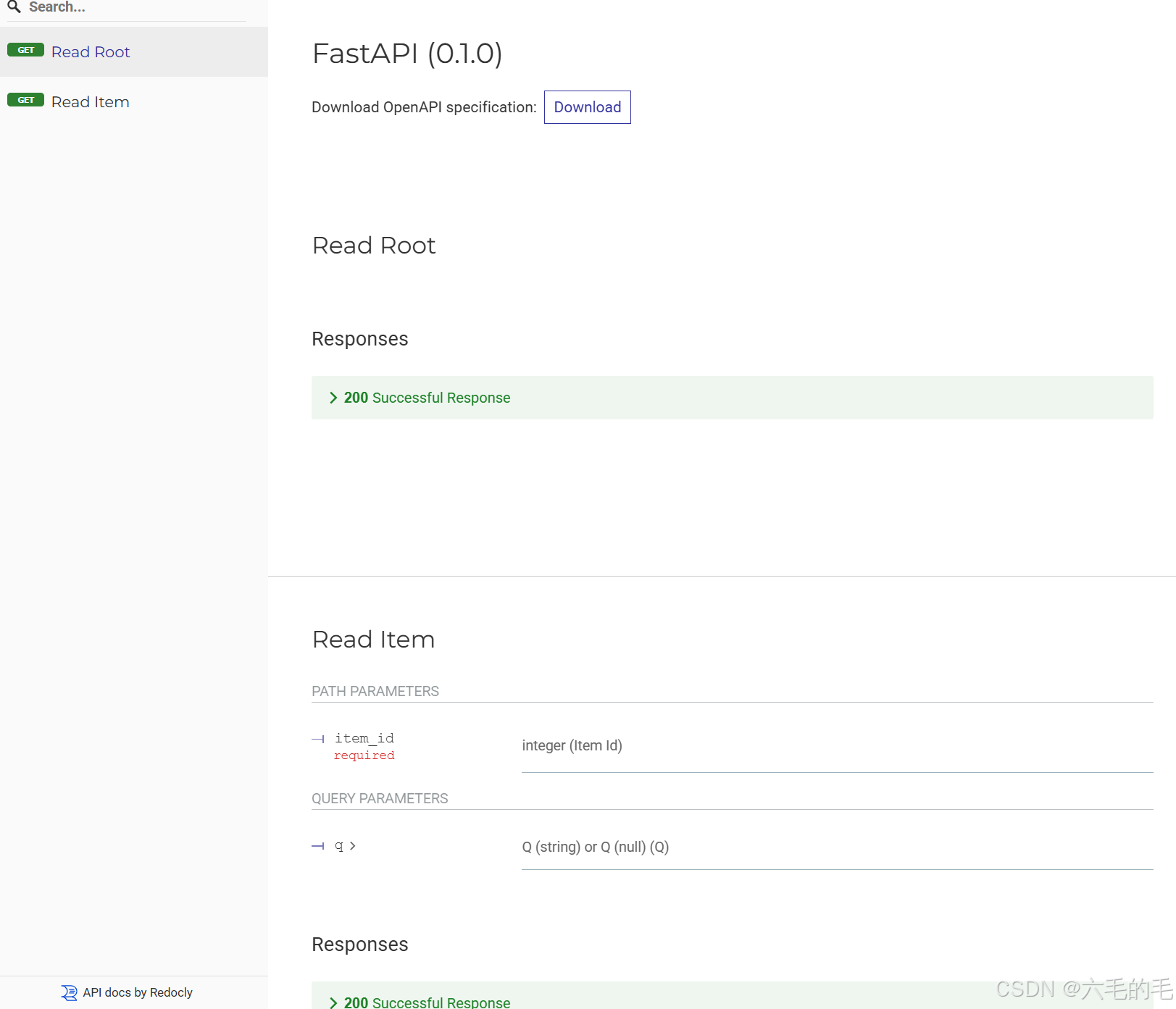
可选的API文档:位于http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc
路径参数
FastAPI 支持使用 Python 字符串格式化语法声明路径参数(变量)
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id):return {"item_id": item_id}
这段代码把路径参数 item_id 的值传递给路径函数的参数 item_id
路径有顺序之分。例如要使用 /users/me 获取当前用户的数据。然后还要使用 /users/{user_id},通过用户 ID 获取指定用户的数据。
由于路径操作是按顺序依次运行的,因此,一定要在 /users/{user_id} 之前声明 /users/me
预设值
路径操作可以使用 Python 的 Enum 类型接收预设的路径参数
class ModelName(str, Enum):# 多重继承,继承str和Enumalexnet = "alexnet"resnet = "resnet"lenet = "lenet"
包含路径的路径参数
在结尾加上:path表示匹配的是路径
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/files/{file_path:path}")
async def read_file(file_path: str):return {"file_path": file_path}
查询参数
声明的参数不是路径参数时,路径操作函数会把该参数自动解释为查询参数。
可选参数
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: str | None = None, short: bool = False):item = {"item_id": item_id}if q:item.update({"q": q})if not short:item.update({"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"})return item
将参数默认值设为None即声明可选参数.不声明默认值均为必选参数
布尔类型参数
FastAPI 会按照以下规则进行转换:
转换为 True 的值:
“true” (不区分大小写)
“True”
“TRUE”
“1”
“yes”
“on”
转换为 False 的值:
“false” (不区分大小写)
“False”
“FALSE”
“0”
“no”
“off”
参数不存在时 (使用默认值 False)
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: str | None = None, short: bool = False):item = {"item_id": item_id}if q:item.update({"q": q})if not short:item.update({"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"})return item
多个路径和查询参数
FastAPI 可以识别同时声明的多个路径参数和查询参数。而且声明查询参数的顺序并不重要。
FastAPI 通过参数名进行检测:
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/users/{user_id}/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(user_id: int, item_id: str, q: str | None = None, short: bool = False
):item = {"item_id": item_id, "owner_id": user_id}if q:item.update({"q": q})if not short:item.update({"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"})return item
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/1/items/4?q=4&short=0

