Kotlin - 协程结构化并发Structured Concurrency
前言
Kotlin的Project Lead,Roman Elizarov的一片文章https://elizarov.medium.com/structured-concurrency-722d765aa952介绍了Structured Concurrency发展的背景。相对Kotlin1.1时代,后来新增的Structured Concurrency理念,也就是我们现在所熟悉的协程版本所具备的特性,解决了各种复杂业务场景下,例如协程嵌套、异步等等使用方式时所面临的生命周期管理问题。本文通过梳理源码来试图理解Structured Concurrency的具体含义和实现原理。
概念理解
常见的业务场景如下:
suspend fun loadAndCombine(name1: String, name2: String): Image { val deferred1 = async { loadImage(name1) }val deferred2 = async { loadImage(name2) }return combineImages(deferred1.await(), deferred2.await())
}deferred1和deferred2都是异步执行的,最终需要将二者的执行结果合并后返回。而如果此时其中一个loadImage执行异常,或者主动取消,很难去通知另一个LoadImage及时停止执行,释放资源。
或者如下场景:
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {printLog("launch1")
launch {delay(20000)printLog("launch1-1")}printLog("launch1 done")cancel()}在外层的launch执行到最后,希望cancel内部所有的子协程。在没有Structrued Concurrency特性的时候,要实现这种逻辑需要类似使用线程时的处理方式。而Structrued Concurrency特性可以让我们在cancel外层协程时,自动cancel其里面所有的子协程。
这就是所谓的对协程生命周期的管理。为了能够将所有协程的生命周期完全管理起来,Kotlin使用了CoroutineScope。
Coroutines are always related to some local scope in your application, which is an entity with a limited life-time, like a UI element.
CoroutineScope相当于圈定了一个空间,所有的协程都在这个空间里面执行。这样所有协程的声明周期就可以通过CoroutineScope来进行管理了。
实现原理
我们知道每个launch都是一个Job。Job和CoroutineScope的关系如下:
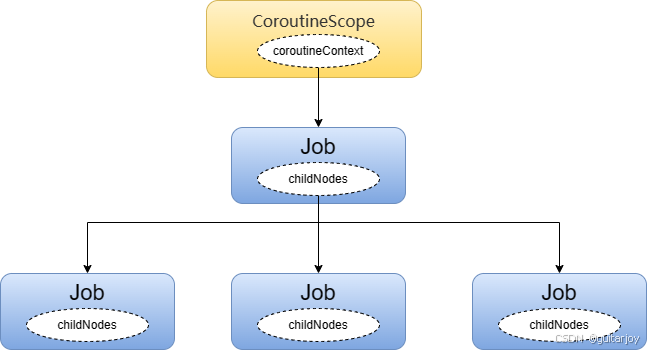
再次根据这个例子,看这种关系如何实现的:
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {printLog("launch1")
launch {delay(20000)printLog("launch1-1")}printLog("launch1 done")cancel()}
首先看新建CoroutineScope(Job())
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\CoroutineScope.ktpublic fun CoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineScope =ContextScope(if (context[Job] != null) context else context + Job())internal class ContextScope(context: CoroutineContext) : CoroutineScope {override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext = context// CoroutineScope is used intentionally for user-friendly representationoverride fun toString(): String = "CoroutineScope(coroutineContext=$coroutineContext)"
}
CoroutineScope本身是一个接口,这里的CoroutineScope不是构造函数,而是一个顶层函数。这里有两个关注点:
context[Job]和context + Job()
所有的Job、CoroutineDispatcher都继承于CoroutineContext。因此CoroutineScope函数的参数我们可以新建一个Job(), 也可以传一个CoroutineDispatcher。以Job()为例,看下其实现:
public interface Job : CoroutineContext.Element {/**
* Key for [Job] instance in the coroutine context.
*/public companion object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<Job>Job继承于CoroutineContext.Element,
public interface Element : CoroutineContext {/**
* A key of this coroutine context element.
*/public val key: Key<*>public override operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E? =@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")if (this.key == key) this as E else nullpublic override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =operation(initial, this)public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext =if (this.key == key) EmptyCoroutineContext else this}注意这里的get函数,其返回值取决于key。key在哪里赋值的?
Job也是一个接口,其Job()也是一个顶层函数:
public fun Job(parent: Job? = null): CompletableJob = JobImpl(parent)internal open class JobImpl(parent: Job?) : JobSupport(true), CompletableJob {JobImp继承JobSupport,而JobSupport是Job的具体实现
public open class JobSupport constructor(active: Boolean) : Job, ChildJob, ParentJob {final override val key: CoroutineContext.Key<*> get() = Job可以看到key的实际值为Job。
所以,如果CoroutineScope(...)的参数传入的是Job(), 则context[Job]返回的是Job。
那context + Job()代表什么呢?
在CoroutineContext的接口声明里看到了plus操作符重载:
public operator fun plus(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext =if (context === EmptyCoroutineContext) this else // fast path -- avoid lambda creation
context.fold(this) { acc, element ->val removed = acc.minusKey(element.key)if (removed === EmptyCoroutineContext) element else {// make sure interceptor is always last in the context (and thus is fast to get when present)val interceptor = removed[ContinuationInterceptor]if (interceptor == null) CombinedContext(removed, element) else {val left = removed.minusKey(ContinuationInterceptor)if (left === EmptyCoroutineContext) CombinedContext(element, interceptor) elseCombinedContext(CombinedContext(left, element), interceptor)}}}是将两个CoroutineContext合并成了CombinedContext。CombinedContext本身也是一个CoroutineContext。
综上, 在新建CoroutineScope的时候,如果传入了一个Job,则使用这个Job,如果没有传入Job(可能传入一个CoroutineDispatcher),则新建一个Job。然后将Job赋值给ContextScope的coroutineContext成员变量。
如此一来,一个新建的CoroutineScope就关联了一个顶层的Job。
使用launch创建一个协程:
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\Builders.common.ktpublic fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) elseStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)return coroutine
}
首先,launch是CoroutineScope的扩展函数,也就是说只能在CoroutineScope内创建协程。newCoroutineContext(context):
public actual fun CoroutineScope.newCoroutineContext(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext {val combined = foldCopies(coroutineContext, context, true)val debug = if (DEBUG) combined + CoroutineId(COROUTINE_ID.incrementAndGet()) else combinedreturn if (combined !== Dispatchers.Default && combined[ContinuationInterceptor] == null)
debug + Dispatchers.Default else debug
}这里context是EmptyCoroutineContext,coroutineContext是刚才CoroutineScope(Job())传入的顶层Job。经过foldCopies后,返回的combined可以看做是顶层Job的封装。在return语句中可以看到debug(即顶层Job)加上了debug + Dispatchers.Default,这就是为什么默认会运行在Dispatchers.Default线程的原因。
创建了newContext后,如果start.isLazy会构建LazyStandaloneCoroutine,否则构建StandaloneCoroutine。start是协程的执行方式,默认为立即执行,也可以懒加载执行。具体见kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\CoroutineStart.kt
这里构建的是默认的StandaloneCoroutine
private open class StandaloneCoroutine(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
active: Boolean
) : AbstractCoroutine<Unit>(parentContext, initParentJob = true, active = active) {override fun handleJobException(exception: Throwable): Boolean {handleCoroutineException(context, exception)return true}
}parentContext参数传入的是刚才构建的newContext,也就是顶层Job。initParentJob默认值为true。接着看下他的继承类AbstractCoroutine:
public abstract class AbstractCoroutine<in T>(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
initParentJob: Boolean,
active: Boolean
) : JobSupport(active), Job, Continuation<T>, CoroutineScope {init {/*
* Setup parent-child relationship between the parent in the context and the current coroutine.
* It may cause this coroutine to become _cancelling_ if the parent is already cancelled.
* It is dangerous to install parent-child relationship here if the coroutine class
* operates its state from within onCancelled or onCancelling
* (with exceptions for rx integrations that can't have any parent)
*/if (initParentJob) initParentJob(parentContext[Job])}AbstractCoroutine继承了JobSupport、Job,也就是说,StandaloneCoroutine实际上是构造了一个Job。看下这里的initParentJob(parentContext[Job]),parentContext是刚才传进来的顶层Job的封装newContext,这里取出其Job传进initParentJob
protected fun initParentJob(parent: Job?) {
assert { parentHandle == null }if (parent == null) {
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandlereturn}
parent.start() // make sure the parent is startedval handle = parent.attachChild(this)
parentHandle = handle// now check our state _after_ registering (see tryFinalizeSimpleState order of actions)if (isCompleted) {
handle.dispose()
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandle // release it just in case, to aid GC}}这里会执行parent.attachChild(this)。字面上理解即将launch创建出来的新Job作为Child加入到顶层的Job中去。
关联父子Job
看下具体实现:
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.kt
public final override fun attachChild(child: ChildJob): ChildHandle {val node = ChildHandleNode(child).also { it.job = this }val added = tryPutNodeIntoList(node) { _, list ->// First, try to add a child along the cancellation handlersval addedBeforeCancellation = list.addLast(
node,
LIST_ON_COMPLETION_PERMISSION or LIST_CHILD_PERMISSION or LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)...
node.invoke(rootCause)if (addedBeforeCompletion) {/** The root cause can't be null: since the earlier addition to the list failed, this means that
* the job was already cancelled or completed. */
assert { rootCause != null }true} else {/** No sense in retrying: we know it won't succeed, and we already invoked the handler. */return NonDisposableHandle}}}if (added) return node/** We can only end up here if [tryPutNodeIntoList] detected a final state. */
node.invoke((state as? CompletedExceptionally)?.cause)return NonDisposableHandle}首先构造一个ChildHandleNode
private class ChildHandleNode(@JvmField val childJob: ChildJob
) : JobNode(), ChildHandle {override val parent: Job get() = joboverride val onCancelling: Boolean get() = trueoverride fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) = childJob.parentCancelled(job)override fun childCancelled(cause: Throwable): Boolean = job.childCancelled(cause)
}这里parent传入的是顶层Job,childJob是launch新建的Job
tryPutNodeIntoList
private inline fun tryPutNodeIntoList(
node: JobNode,
tryAdd: (Incomplete, NodeList) -> Boolean): Boolean {
loopOnState { state ->when (state) {is Empty -> { // EMPTY_X state -- no completion handlersif (state.isActive) {// try to move to the SINGLE stateif (_state.compareAndSet(state, node)) return true} elsepromoteEmptyToNodeList(state) // that way we can add listener for non-active coroutine}is Incomplete -> when (val list = state.list) {null -> promoteSingleToNodeList(state as JobNode)else -> if (tryAdd(state, list)) return true}else -> return false}}}private val _state = atomic<Any?>(if (active) EMPTY_ACTIVE else EMPTY_NEW)private inline fun loopOnState(block: (Any?) -> Unit): Nothing {while (true) {block(state)}}state是什么?
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.ktprivate val EMPTY_NEW = Empty(false)
private val EMPTY_ACTIVE = Empty(true)在JobSupport中,维护了一个状态机,管理Job的不同状态阶段。这里EMPTY_NEW和 EMPTY_ACTIVE是其具体状态。
private class Empty(override val isActive: Boolean) : Incomplete {override val list: NodeList? get() = nulloverride fun toString(): String = "Empty{${if (isActive) "Active" else "New" }}"
}其内维护了一个list
简言之,就是tryAdd(state, list)会将自己的state内的list传递给调用它的tryPutNodeIntoList,在回头看tryPutNodeIntoList,
val addedBeforeCompletion = list.addLast(
node,
LIST_CHILD_PERMISSION or LIST_ON_COMPLETION_PERMISSION)会将子Job加到list中。
由此一来,CoroutineScope边构建了它的Job树。
Job的执行
回到CoroutineScope.launch
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) elseStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)return coroutine
}在构建完coroutine后,执行coroutine.start
public fun <R> start(start: CoroutineStart, receiver: R, block: suspend R.() -> T) {start(block, receiver, this)}public enum class CoroutineStart {
...
public operator fun <R, T> invoke(block: suspend R.() -> T, receiver: R, completion: Continuation<T>): Unit =when (this) {
DEFAULT -> block.startCoroutineCancellable(receiver, completion)
ATOMIC -> block.startCoroutine(receiver, completion)
UNDISPATCHED -> block.startCoroutineUndispatched(receiver, completion)
LAZY -> Unit // will start lazily}在这里开始执行协程。
Structured Concurrency的典型作用:协程的cancel
当执行scope的cancel时:
public fun CoroutineScope.cancel(cause: CancellationException? = null) {val job = coroutineContext[Job] ?: error("Scope cannot be cancelled because it does not have a job: $this")
job.cancel(cause)
}是通过coroutineContext[Job]获取了顶层Job,然后执行其cancel
kotlinx.coroutines-master\kotlinx-coroutines-core\common\src\JobSupport.kt
public override fun cancel(cause: CancellationException?) {cancelInternal(cause ?: defaultCancellationException())}public open fun cancelInternal(cause: Throwable) {cancelImpl(cause)}internal fun cancelImpl(cause: Any?): Boolean {var finalState: Any? = COMPLETING_ALREADYif (onCancelComplete) {// make sure it is completing, if cancelMakeCompleting returns state it means it had make it// completing and had recorded exception
finalState = cancelMakeCompleting(cause)if (finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN) return true}if (finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY) {
finalState = makeCancelling(cause)}return when {
finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY -> true
finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN -> true
finalState === TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL -> falseelse -> {afterCompletion(finalState)true}}}以makeCancelling为例
private fun makeCancelling(cause: Any?): Any? {var causeExceptionCache: Throwable? = null // lazily init result of createCauseException(cause)
loopOnState { state ->when (state) {is Finishing -> { // already finishing -- collect exceptionsval notifyRootCause = synchronized(state) {if (state.isSealed) return TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL // already sealed -- cannot add exception nor mark cancelled// add exception, do nothing is parent is cancelling child that is already being cancelledval wasCancelling = state.isCancelling // will notify if was not cancelling// Materialize missing exception if it is the first exception (otherwise -- don't)if (cause != null || !wasCancelling) {val causeException = causeExceptionCache ?: createCauseException(cause).also { causeExceptionCache = it }
state.addExceptionLocked(causeException)}// take cause for notification if was not in cancelling state before
state.rootCause.takeIf { !wasCancelling }}
notifyRootCause?.let { notifyCancelling(state.list, it) }return COMPLETING_ALREADY}is Incomplete -> {// Not yet finishing -- try to make it cancellingval causeException = causeExceptionCache ?: createCauseException(cause).also { causeExceptionCache = it }if (state.isActive) {// active state becomes cancellingif (tryMakeCancelling(state, causeException)) return COMPLETING_ALREADY} else {// non active state starts completingval finalState = tryMakeCompleting(state, CompletedExceptionally(causeException))when {
finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY -> error("Cannot happen in $state")
finalState === COMPLETING_RETRY -> return@loopOnStateelse -> return finalState}}}else -> return TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL // already complete}}}假如协程在运行中,则执行tryMakeCancelling
private fun tryMakeCancelling(state: Incomplete, rootCause: Throwable): Boolean {
assert { state !is Finishing } // only for non-finishing states
assert { state.isActive } // only for active states// get state's list or else promote to list to correctly operate on child listsval list = getOrPromoteCancellingList(state) ?: return false// Create cancelling state (with rootCause!)val cancelling = Finishing(list, false, rootCause)if (!_state.compareAndSet(state, cancelling)) return false// Notify listenersnotifyCancelling(list, rootCause)return true}state.compareAndSet进行状态机切换,随后执行notifyCancelling
private fun notifyCancelling(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable) {// first cancel our own childrenonCancelling(cause)
list.close(LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)notifyHandlers(list, cause) { it.onCancelling }// then cancel parentcancelParent(cause) // tentative cancellation -- does not matter if there is no parent}private fun notifyCancelling(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable) {// first cancel our own childrenonCancelling(cause)
list.close(LIST_CANCELLATION_PERMISSION)notifyHandlers(list, cause) { it.onCancelling }// then cancel parentcancelParent(cause) // tentative cancellation -- does not matter if there is no parent}private inline fun notifyHandlers(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable?, predicate: (JobNode) -> Boolean) {var exception: Throwable? = null
list.forEach { node ->if (node is JobNode && predicate(node)) {try {
node.invoke(cause)} catch (ex: Throwable) {
exception?.apply { addSuppressed(ex) } ?: run {
exception = CompletionHandlerException("Exception in completion handler $node for $this", ex)}}}}
exception?.let { handleOnCompletionException(it) }node.invoke(cause)的实现
private class InvokeOnCancelling(private val handler: CompletionHandler
) : JobNode() {// delegate handler shall be invoked at most once, so here is an additional flagprivate val _invoked = atomic(false)override val onCancelling get() = trueoverride fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) {if (_invoked.compareAndSet(expect = false, update = true)) handler.invoke(cause)}
}private fun cancelParent(cause: Throwable): Boolean {// Is scoped coroutine -- don't propagate, will be rethrownif (isScopedCoroutine) return true/* CancellationException is considered "normal" and parent usually is not cancelled when child produces it.
* This allow parent to cancel its children (normally) without being cancelled itself, unless
* child crashes and produce some other exception during its completion.
*/val isCancellation = cause is CancellationExceptionval parent = parentHandle// No parent -- ignore CE, report other exceptions.if (parent === null || parent === NonDisposableHandle) {return isCancellation}// Notify parent but don't forget to check cancellationreturn parent.childCancelled(cause) || isCancellation}即先将自己的状态切换到取消中,随后notifyHandlers通过遍历list通知自己的children执行cancel。最后再通过cancelParent告知父Job自己的分支cancel完毕。
总结:
- 所有协程都运行在CoroutineScope中,这种限定是通过launch、async、runBlock等构建协程的函数都是作为CoroutineScope扩展函数来实现的。
- CoroutineScope创建过程中,必定会构建一个顶层Job(后者外部传入),通过coroutineContext与其关联。
- 每个launch都响应构建了一个Job,并将此Job加入到父Job的list中,由此维护了一个Job树。
- Structure Concurrency 的 具体实现 是 通过 维护 Job 树 的生命周期 完成 的 。
