YOLOv8改进 - 注意力篇 - 引入iRMB注意力机制
#YOLO# #目标检测# #计算机视觉#
一、本文介绍
作为入门性篇章,这里介绍了iRMB注意力在YOLOv8中的使用。包含iRMB原理分析,iRMB的代码、iRMB的使用方法、以及添加以后的yaml文件及运行记录。
二、iRMB原理分析
iRMB官方论文地址:文章
iRMB官方代码地址:代码
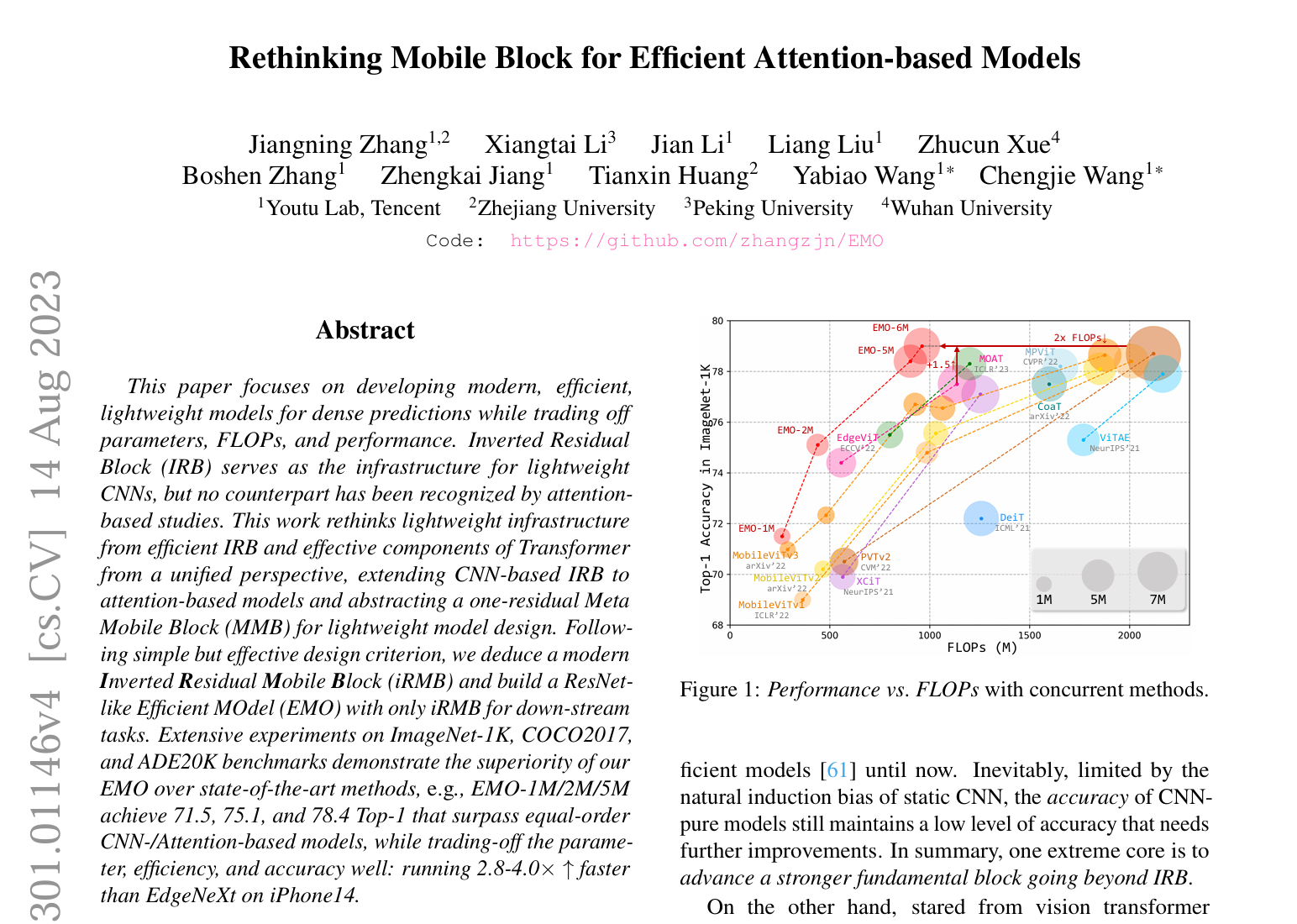
iRMB注意力机制:iRMB是一种混合网络模块,结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)的轻量级特性和 Transformer 模型的动态处理能力。


三、相关代码:
iRMB注意力的代码,如下:
from timm.models._efficientnet_blocks import SqueezeExcite
from functools import partial
inplace = Trueclass LayerNorm2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self, normalized_shape, eps=1e-6, elementwise_affine=True):super().__init__()self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape, eps, elementwise_affine)def forward(self, x):x = rearrange(x, 'b c h w -> b h w c').contiguous()x = self.norm(x)x = rearrange(x, 'b h w c -> b c h w').contiguous()return xdef get_norm(norm_layer='in_1d'):eps = 1e-6norm_dict = {'none': nn.Identity,'in_1d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm1d, eps=eps),'in_2d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, eps=eps),'in_3d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm3d, eps=eps),'bn_1d': partial(nn.BatchNorm1d, eps=eps),'bn_2d': partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=eps),# 'bn_2d': partial(nn.SyncBatchNorm, eps=eps),'bn_3d': partial(nn.BatchNorm3d, eps=eps),'gn': partial(nn.GroupNorm, eps=eps),'ln_1d': partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=eps),'ln_2d': partial(LayerNorm2d, eps=eps),}return norm_dict[norm_layer]def get_act(act_layer='relu'):act_dict = {'none': nn.Identity,'relu': nn.ReLU,'relu6': nn.ReLU6,'silu': nn.SiLU}return act_dict[act_layer]class ConvNormAct(nn.Module):def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_out, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False,skip=False, norm_layer='bn_2d', act_layer='relu', inplace=True, drop_path_rate=0.):super(ConvNormAct, self).__init__()self.has_skip = skip and dim_in == dim_outpadding = math.ceil((kernel_size - stride) / 2)self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, groups, bias)self.norm = get_norm(norm_layer)(dim_out)self.act = get_act(act_layer)(inplace=inplace)self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_rate) if drop_path_rate else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):shortcut = xx = self.conv(x)x = self.norm(x)x = self.act(x)if self.has_skip:x = self.drop_path(x) + shortcutreturn xclass iRMB(nn.Module):def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_out, norm_in=True, has_skip=True, exp_ratio=1.0, norm_layer='bn_2d',act_layer='relu', v_proj=True, dw_ks=3, stride=1, dilation=1, se_ratio=0.0, dim_head=8, window_size=7,attn_s=True, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., drop=0., drop_path=0., v_group=False, attn_pre=False):super().__init__()self.norm = get_norm(norm_layer)(dim_in) if norm_in else nn.Identity()dim_mid = int(dim_in * exp_ratio)self.has_skip = (dim_in == dim_out and stride == 1) and has_skipself.attn_s = attn_sif self.attn_s:assert dim_in % dim_head == 0, 'dim should be divisible by num_heads'self.dim_head = dim_headself.window_size = window_sizeself.num_head = dim_in // dim_headself.scale = self.dim_head ** -0.5self.attn_pre = attn_preself.qk = ConvNormAct(dim_in, int(dim_in * 2), kernel_size=1, bias=qkv_bias, norm_layer='none',act_layer='none')self.v = ConvNormAct(dim_in, dim_mid, kernel_size=1, groups=self.num_head if v_group else 1, bias=qkv_bias,norm_layer='none', act_layer=act_layer, inplace=inplace)self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)else:if v_proj:self.v = ConvNormAct(dim_in, dim_mid, kernel_size=1, bias=qkv_bias, norm_layer='none',act_layer=act_layer, inplace=inplace)else:self.v = nn.Identity()self.conv_local = ConvNormAct(dim_mid, dim_mid, kernel_size=dw_ks, stride=stride, dilation=dilation,groups=dim_mid, norm_layer='bn_2d', act_layer='silu', inplace=inplace)self.se = SqueezeExcite(dim_mid, rd_ratio=se_ratio,act_layer=get_act(act_layer)) if se_ratio > 0.0 else nn.Identity()self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(drop)self.proj = ConvNormAct(dim_mid, dim_out, kernel_size=1, norm_layer='none', act_layer='none', inplace=inplace)self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):shortcut = xx = self.norm(x)B, C, H, W = x.shapeif self.attn_s:# paddingif self.window_size <= 0:window_size_W, window_size_H = W, Helse:window_size_W, window_size_H = self.window_size, self.window_sizepad_l, pad_t = 0, 0pad_r = (window_size_W - W % window_size_W) % window_size_Wpad_b = (window_size_H - H % window_size_H) % window_size_Hx = F.pad(x, (pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b, 0, 0,))n1, n2 = (H + pad_b) // window_size_H, (W + pad_r) // window_size_Wx = rearrange(x, 'b c (h1 n1) (w1 n2) -> (b n1 n2) c h1 w1', n1=n1, n2=n2).contiguous()# attentionb, c, h, w = x.shapeqk = self.qk(x)qk = rearrange(qk, 'b (qk heads dim_head) h w -> qk b heads (h w) dim_head', qk=2, heads=self.num_head,dim_head=self.dim_head).contiguous()q, k = qk[0], qk[1]attn_spa = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scaleattn_spa = attn_spa.softmax(dim=-1)attn_spa = self.attn_drop(attn_spa)if self.attn_pre:x = rearrange(x, 'b (heads dim_head) h w -> b heads (h w) dim_head', heads=self.num_head).contiguous()x_spa = attn_spa @ xx_spa = rearrange(x_spa, 'b heads (h w) dim_head -> b (heads dim_head) h w', heads=self.num_head, h=h,w=w).contiguous()x_spa = self.v(x_spa)else:v = self.v(x)v = rearrange(v, 'b (heads dim_head) h w -> b heads (h w) dim_head', heads=self.num_head).contiguous()x_spa = attn_spa @ vx_spa = rearrange(x_spa, 'b heads (h w) dim_head -> b (heads dim_head) h w', heads=self.num_head, h=h,w=w).contiguous()# unpaddingx = rearrange(x_spa, '(b n1 n2) c h1 w1 -> b c (h1 n1) (w1 n2)', n1=n1, n2=n2).contiguous()if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:x = x[:, :, :H, :W].contiguous()else:x = self.v(x)x = x + self.se(self.conv_local(x)) if self.has_skip else self.se(self.conv_local(x))x = self.proj_drop(x)x = self.proj(x)x = (shortcut + self.drop_path(x)) if self.has_skip else xreturn x四、YOLOv8中iRMB使用方法
1.YOLOv8中添加iRMB模块:
首先在ultralytics/nn/modules/conv.py最后添加模块的代码。
2.在conv.py的开头__all__ = 内添加iRMB模块的类别名:
3.在同级文件夹下的__init__.py内添加iRMB的相关内容:(分别是from .conv import iRMB ;以及在__all__内添加iRMB)
4.在ultralytics/nn/tasks.py进行iRMB注意力机制的注册,以及在YOLOv8的yaml配置文件中添加iRMB即可。
首先打开task.py文件,按住Ctrl+F,输入parse_model进行搜索。找到parse_model函数。找以下注册代码,将iRMB添加进去即可:
elif m in {iRMB}:args = [ch[f], ch[f]]然后,就是新建一个名为YOLOv8_iRMB.yaml的配置文件:(路径:ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/YOLOv8_iRMB.yaml)其中参数中nc,由自己的数据集决定。本文测试,采用的coco8数据集,有80个类别。
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call CPAM-yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'# [depth, width, max_channels]n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPss: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPsm: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPsl: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPsx: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:# [from, repeats, module, args]- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]- [-1, 1, iRMB, [1024,1024]]- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9# YOLOv8.0n head
head:- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
在根目录新建一个train.py文件,内容如下:
from ultralytics import YOLO# 加载一个模型
model = YOLO('ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/YOLOv8_iRMB.yaml') # 从YAML建立一个新模型
# 训练模型
results = model.train(data='ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco8.yaml', epochs=1,imgsz=640,optimizer="SGD")训练输出:


五、总结
以上就是iRMB的原理及使用方式,但具体iRMB注意力机制的具体位置放哪里,效果更好。需要根据不同的数据集做相应的实验验证。希望本文能够帮助你入门YOLO中注意力机制的使用。
