C++学习路线(二十四)
静态成员函数
类的静态方法:
1.可以直接通过类来访问【更常用】,也可以通过对象(实例)来访问。
2.在类的静态方法中,不能访问普通数据成员和普通成员函数(对象的数据成员和成员函数)
1)静态数据成员
可以直接访问“静态数据成员”对象的成员函数(没有static的成员函数)内部,类的静态成员函数(有static的成员函数)内部,可以直接访问“静态数据成员”即:所有的成员函数,都可以访问静态数据成员。类不能直接访问普通的静态数据成员(Human::humanCount非法)
2)静态成员函数
对象可以直接访问静态成员函数
类可以直接访问静态成员函数(Human::getHumanCount())在类的静态成员函数(类的静态方法)内部,不能直接访问this指针和对象的数据成员!在类的静态成员函数(类的静态方法)内部,只能访问类的数据成员。
const数据成员
定义为const数据类型(常量数据成员)const数据成员的初始化方式
1.使用类内值(C++11支持)


我们猜一猜 类内初始值=2 然后再类外进行初始值定义 以哪个为准?
答案是报错,多次初始化

2.使用构造函数的初始化列表(如果同时使用这两种方式,以初始化列表中的值为最终初始化结果)
注意:不能在构造函数或其他成员函数内,对const成员赋值!


const static int count 可以类内赋值 ,但是去掉了const 就不可以了,得在类外赋值
组合和聚合
说明:组合和聚合,不是C++的语法要求,是应用中的常用手段
组合
构建一个计算机类,一台计算机,由CPU芯片,硬盘,内存等组成。
CPU 芯片也使用类来表示。
CPU.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
class CPU {
public:CPU(const char* brand = "intel", const char* version = "i5-7500");~CPU();
private:std::string brand;std::string version;
};CPU.cpp
#include "CPU.h"
#include <iostream>CPU::CPU(const char* brand, const char* version) {this->brand = brand;this->version = version;std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}CPU::~CPU() {std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}
Computer.h
#pragma once
#include "CPU.h"class Computer {
public:Computer(const char* cpuBrand , const char* cpuVersion , int harDisk , int memory);~Computer();
private:CPU cpu;int hardDisk;int memory;
};Computer.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Computer.h"Computer::Computer(const char* cpuBrand, const char* cpuVersion, int hardDisk, int memory) : cpu(cpuBrand, cpuVersion) {this->hardDisk = hardDisk;this->memory = memory;std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}Computer::~Computer() {std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Computer.h"int main() {Computer computer1("intel" , "i9" , 1000 , 8);}
聚合
给计算机配备一台音响
Computer.h
#pragma once
#include "CPU.h"class VoiceBox {
public:VoiceBox() {}~VoiceBox() {}void VioceBoxOn() {std::cout << "Voice box is on." << std::endl;}
};class Computer {
public:Computer(const char* cpuBrand , const char* cpuVersion , int harDisk , int memory);~Computer();void addVoiceBox(VoiceBox* vb);
private:CPU cpu;int hardDisk;int memory;VoiceBox *voiceBox;
};Computer.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Computer.h"Computer::Computer(const char* cpuBrand, const char* cpuVersion, int hardDisk, int memory) : cpu(cpuBrand, cpuVersion) {this->hardDisk = hardDisk;this->memory = memory;std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}Computer::~Computer() {std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}void Computer::addVoiceBox(VoiceBox* voiceBox) {this->voiceBox = voiceBox;std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << " called" << std::endl;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Computer.h"int main() {VoiceBox voicebox1;{Computer computer1("intel", "i9", 1000, 8);computer1.addVoiceBox(&voicebox1);}voicebox1.VioceBoxOn();
}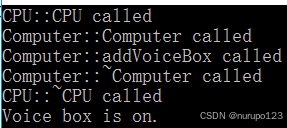
可以看到Computer这个类不能左右VoiceBox的构造和析构。
聚合不是组成关系,被包含的对象,也可能被其他对象包含拥有者,不需要对被拥有的对象的生命周期负责。
项目-相亲系统
Girl.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>class Boy;class Girl {
public:Girl();Girl(std::string name, int age, int beauty);~Girl();int getAge() const;std::string getName() const;int getBeauty() const;std::string Description() const;bool satisfy(const Boy& boy) const;static void inputsGirls(std::vector<Girl>& girls);private:std::string name;int age;int beauty;
};Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class Girl;class Boy {Boy();Boy(std::string name, int age, int beauty);~Boy();int getAge() const;int getBeauty() const;std::string Description() const;bool satisfy(const Boy& other);static void inputsBoys(std::vector<Boy>& boys);
private:std::string name;int age;int beauty;
};Girl.cpp
#include "girl.h"
#include "boy.h"
#include <string>
#include <sstream>#define YANZHI_FACTOR 1.1Girl::Girl(){}
Girl::Girl(std::string name, int age, int beauty) {this->name = name;this->age = age;this->beauty = beauty;
}
Girl::~Girl(){}
int Girl::getAge() const {return age;
}
std::string Girl::getName() const {return name;
}
int Girl::getBeauty() const {return beauty;
}
std::string Girl::Description() const {std::stringstream ss;ss << name << "颜值" << beauty << " 年龄" << age;return ss.str();
}bool Girl::satisfy(const Boy& boy) const {if(boy.getSalary() >= beauty * YANZHI_FACTOR) return true;return false;
}void Girl::inputsGirls(std::vector<Girl>& girls) {int age;std::string name;int beauty;int n = 1;while (1) {std::cout << "请输入第" << n << "位女孩的信息(输入0结束输入):" << std::endl;std::cout << "年龄:" << std::endl;std::cin >> age;if (age == 0) break;std::cout << "姓名:" << std::endl;std::cin >> name;std::cout << "颜值:" << std::endl;std::cin >> beauty;n++;girls.push_back(Girl(name, age, beauty));}
}Boy.cpp
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include "boy.h"
#include "girl.h"#define SALARY_FACTOR 0.005Boy::Boy(){}
Boy::Boy(std::string name, int age, int salary) {this->name = name;this->age = age;this->salary = salary;
}
Boy::~Boy(){}
std::string Boy::getName() const {return name;
}
int Boy::getAge() const {return age;
}
int Boy::getSalary() const {return salary;
}
std::string Boy::Description() const {std::stringstream ss;ss << "Name: " << name << ", Age: " << age << ", Salary: " << salary;return ss.str();
}
void Boy::inputsBoys(std::vector<Boy>& boys) {int n = 1;std::string name;int age;int salary;while (1) {std::cout << "请输入第" << n << "位男孩的信息(输入0结束输入):" << std::endl;std::cout << "年龄:" << std::endl;std::cin >> age;if (age == 0) break;std::cout << "姓名:" << std::endl;std::cin >> name;std::cout << "工资:" << std::endl;std::cin >> salary;boys.push_back(Boy(name, age, salary));n++;}
}bool Boy::satisfy(const Girl& girl) {if (girl.getBeauty() >= salary * SALARY_FACTOR) {return true;}else return false;
}
main.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include "boy.h"
#include "girl.h"
using namespace std;void autoPair(vector<Boy>& boys, vector<Girl>& girls) {for (Boy& b : boys) {for (Girl& g : girls) {if (b.satisfy(g) && g.satisfy(b)) {cout << b.Description() << " and " << g.Description() << endl;}}}
}int main() {vector<Boy> boys;vector<Girl> girls;Boy::inputsBoys(boys);Girl::inputsGirls(girls);cout << "pairs\n" << endl;autoPair(boys, girls);
}