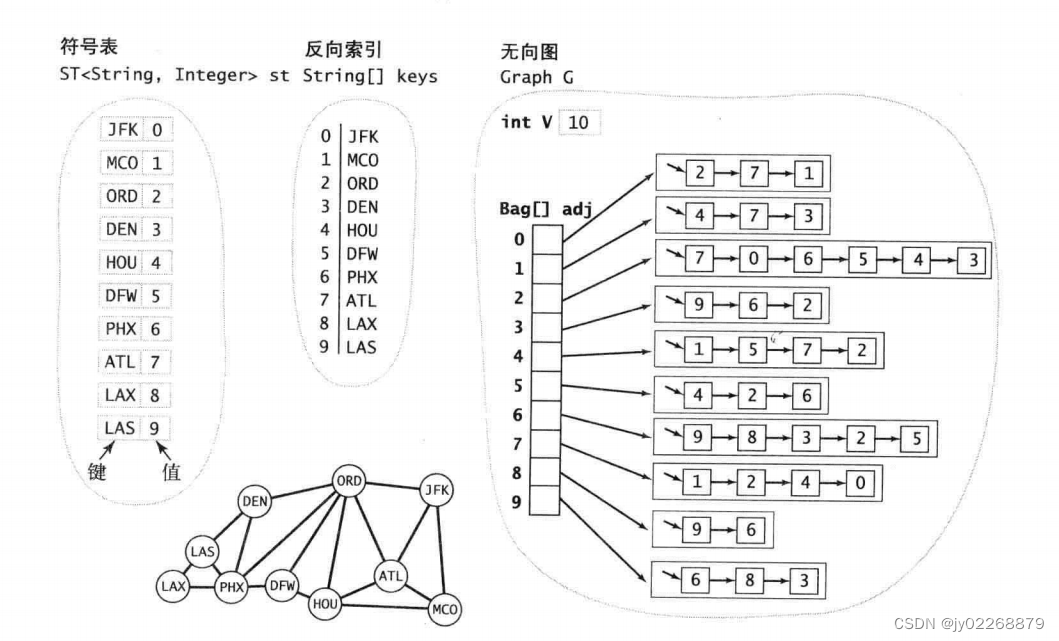
图----无向图
1.定义
图的定义:图是由一组顶点和一组能够将两个顶点相连的边组成
边:edge
顶点:vertex
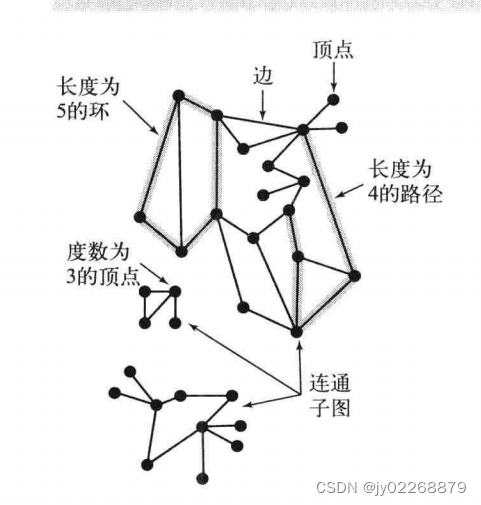
连通图:如果从任意一个顶点都存在一条路径到达另外一个任意顶点,我们称这幅图是连通图。
非连通图:由若干连通的部分组成,他们都是其极大连通子图。
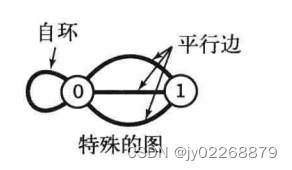
自环:即一条连接一个顶点和其自身的边
平行边:连接同一顶点的两条边称为平行边
图的密度:是指已经连接的顶点对占所有可能被连接的顶点对的比例。在稀疏图中,被连接的顶点对很少;而在稠密图中,只有少部分顶点对之间没有边连接。

二分图:是一种能够将所有结点分为两部分的图,其中图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不同的部分。
2.图的不同表示方法
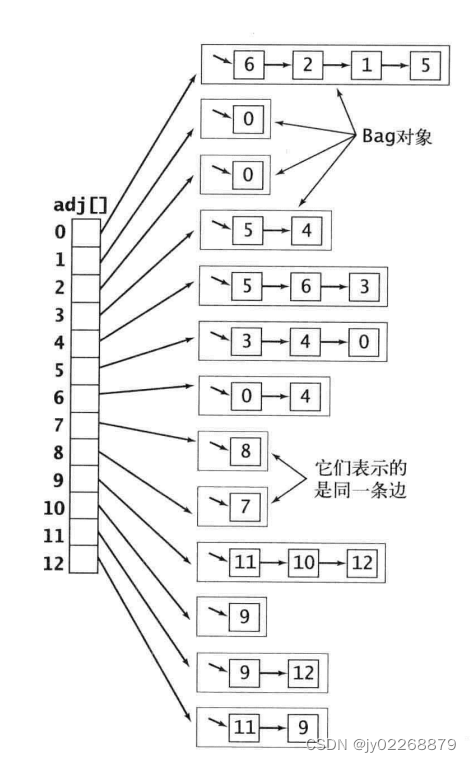
2.1邻接表数组表示
用一个以顶点为索引的列表数组,其中的每个元素都是和该顶点相邻的定点列表
2.2邻接矩阵 表示
用一个V乘以V的布尔矩阵。当顶点V和顶点W之间有相连的边时,定义V行W列的元素值为true,否则为false。如果含有上百万个顶点,V的平方个布尔值所需要的空间会非常大。
3.相关API及代码


package com.sid.graph;public class Vertex {String value;//顶点的值Edge firstEdge;//第一条边int index;//在外层数组的下标public Vertex(String value, Edge firstEdge,int index) {super();this.value = value;this.firstEdge = firstEdge;this.index = index;}
}
package com.sid.graph;public class Edge {Vertex vertex;//该边对应的顶点int weight;//权重,无向图,有向图权重为0Edge next;//下一个边/*** 构建一条边 weight未0表示无向图或者有向图 不为0表示网* @param vertex* @param weight* @param next*/public Edge(Vertex vertex, int weight, Edge next) {super();this.vertex = vertex;this.weight = weight;this.next = next;}
}
package com.sid.graph;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;public class Graph {/*** 顶点数*/private final int V;/*** 边数*/private int E;/*** 邻接表*/private List<Vertex> adj;public Graph(int V) {this.V = V;this.E = 0;adj = new ArrayList<Vertex>(V); /** 创建邻接表 */}public int V() {return V;}public int E() {return E;}/*** 插入顶点*/public Vertex addVertex(String value) {int size = adj.size();Vertex vertex = new Vertex(value, null,size);adj.add(vertex);return vertex;}/*** 获取顶点*/public Vertex getVertexByValue(String value) {for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {if (adj.get(i).value.equals(value)) {return adj.get(i);}}return null;}/*** 获取顶点*/public Vertex getVertexByIndex(int index) {return adj.get(index);}/*** 添加无向图的边* @param vertex1 第一个顶点* @param vertex2 第二个顶点*/public void addUndigraphEdge(Vertex vertex1,Vertex vertex2) {//因为是无向图,所以就直接加入addEdgeByVertex(vertex1,vertex2,0);addEdgeByVertex(vertex2,vertex1,0);}/*** 添加有向图的边* @param start 开始节点* @param end 结束节点*/public void addDigraphEdge(Vertex start,Vertex end) {//因为是有向图,所以只有一条边addEdgeByVertex(start,end,0);}/*** 添加一条由start-->end的边** @param start* @param end* @param weight 权重未0表示无向图或者有向图,部位0表示网*/private void addEdgeByVertex(Vertex start, Vertex end, int weight) {//1、找到第一个顶点Vertex v1 = this.getVertexByValue(start.value);if(v1 == null){v1 = addVertex(start.value);}//2、检查这条边是否已经存在,已经存在就直接报错for (Vertex w : adj(v1)) {if (end.value.equals(w.value)) {System.out.println("边" + start.value + "-->" + end.value + "已经加入,不可以再加入");return;}}//3.添加Edge firstEdge = v1.firstEdge;if (firstEdge == null) {firstEdge = new Edge(end, weight, null);v1.firstEdge = firstEdge;} else {//当前节点变为第一个节点Edge nowEdge = new Edge(end, weight, null);v1.firstEdge = nowEdge;nowEdge.next = firstEdge;}E++;}/*** 计算V节点的度数*/public static int degree(Graph g, int v) {int degree = 0;Edge firstEdge = g.getVertexByIndex(v).firstEdge;while (firstEdge != null) {degree++;firstEdge = firstEdge.next;}return degree;}/*** 计算所有顶点的最大度数*/public static int maxDegree(Graph G) {int max = 0;for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {if (degree(G, v) > max) {max = degree(G, v);}}return max;}/*** 计算所有顶点的平均度数*/public static int avgDegree(Graph G) {return 2 * G.E() / G.V();}/*** 计算自环的的个数*/public static int numberOfSelfLoops(Graph g) {int count = 0;for (int v = 0; v < g.V(); v++) {for(int w : g.adj(v)){if(v == w){count++;}}}return count / 2; //每条边都被记过两次}/*** 得到跟V节点相邻的所有节点*/public static List<Vertex> adj(Vertex vertex) {List result = new LinkedList();Edge firstEdge = vertex.firstEdge;while (firstEdge != null) {result.add(firstEdge.vertex);firstEdge = firstEdge.next;}return result;}/*** 得到跟V节点相邻的所有节点下标 入参是节点的数组下标*/public List<Integer> adj(int index) {List result = new ArrayList();Edge firstEdge = this.getVertexByIndex(index).firstEdge;while (firstEdge != null) {result.add(firstEdge.vertex.index);firstEdge = firstEdge.next;}return result;}/*** 图的邻接表的字符串表示*/public String toString() {String s = V + " vertices, " + E + " edges\n";for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {Vertex vertex = this.getVertexByIndex(v);s += vertex.value + ": ";for (Vertex w : adj(vertex)) {s += w.value + "";}s += "\n";}return s;}
}
4.深度优先搜索
4.1 找到以起点s连通的所有顶点,和个数
实现:
用一个递归方法来遍历所有顶点,在访问一个顶点时:
将它标记为已访问
递归地访问它的所有没有被标记过的邻居顶点

package com.sid.graph;public class DepthFirstSearch {private boolean[] marked;private int count;public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G,int s){marked = new boolean[G.V()];dfs(G,s);}private void dfs(Graph G, int index) {marked[index] = true;count++;for(int w : G.adj(index)){if(!marked[w]){dfs(G,w);}}}public boolean marked(int w ){return marked[w];}public int count(){return count;}
}
4.2深度优先搜索查找图中路径

注意这不一定是最短路径,比如说下面这个例子,查出来的0到1的路径,不是0----1,而是0----2----1

package com.sid.graph;import java.util.Stack;public class DepthFirstPaths {private boolean[] marked; //这个顶点上调用过dfs()了吗private int[] edgeTo; //从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点 比如S---A---C 则 edgeTo[C]=A edgeTo[C]其实表示的是谁直接指向C点private final int s; //起点public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {marked = new boolean[G.V()];edgeTo = new int[G.V()];this.s = s;dfs(G, s);}private void dfs(Graph G, int index) {marked[index] = true;for (int w : G.adj(index)) {if (!marked[w]) {edgeTo[w] = index;dfs(G, w);}}}public boolean hasPathTo(int v){ //起点S是否有路径到Vreturn marked[v];}public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){if(!hasPathTo(v)){return null;}Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();for(int x = v ; x != s ; x = edgeTo[x]){path.push(x);}path.push(s);return path;}
}
5.广度优先搜索
深度优先搜索得到的路径不仅取决于图的结构,还取决于图的表示和递归调用的性质。
“从S到给定目标的顶点V是否存在一条路径?如果有,找出其中最短的那条”,则需要用广度优先搜索。
实现:
1.使用一个队列来保存所有已经被标记过,但其邻接表还未被检查过的顶点
2.先将起点加入队列,然后重复以下步骤直到队列为空
取队列中的下一个顶点v并标记它
将与v相邻的所有未被标记过的顶点加入队列

package com.sid.graph;import java.util.*;public class BreadthFirstPaths {private boolean[] marked; //这个顶点上调用过dfs()了吗private int[] edgeTo; //从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点 比如S---A---C 则 edgeTo[C]=A edgeTo[C]其实表示的是谁直接指向C点private final int s; //起点public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {marked = new boolean[G.V()];edgeTo = new int[G.V()];this.s = s;bfs(G, s);}private void bfs(Graph G, int s) {Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();marked[s] = true;queue.add(s);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int v = queue.poll();for(int w : G.adj(v)){if(!marked[w]){edgeTo[w] = v;marked[w] = true;queue.add(w);}}}}public boolean hasPathTo(int v){return marked[v];}public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){if(!hasPathTo(v)){return null;}Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>();for(int x = v ; x != s ; x = edgeTo[x]){path.push(x);}path.push(s);return path;}
}
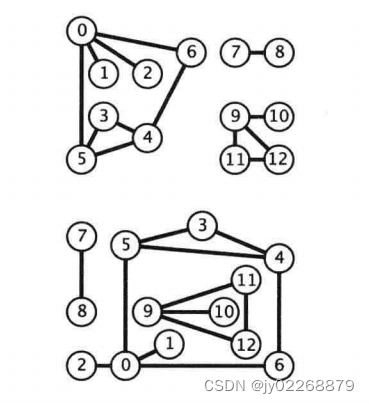
6.连通分量
无向图G的极大连通子图称为G的连通分量( Connected Component)。
任何连通图的连通分量只有一个,即是其自身,非连通的无向图有多个连通分量。

实现
使用marked[]数组来寻找一个顶点作为每个连通分量中深度优先搜索的起点。
递归的深度优先搜索第一次调用的参数是顶点0,它会标记所有与0连通的顶点。
然后构造函数中for循环会查找每个没有被标记的顶点,并且递归调用dfs()来标记和它相邻的所有顶点。
使用一个以顶点作为索引的数组id[],将同一个连通分量的顶点和连通分量的标识符关联起来(int 值)。这个数组是的connected()方法的实现变得十分简单。
标识符0会被赋予第一个连通分量中的所有顶点,1会被赋予第二个连通分量中的所有顶点,以此类推。这样所有的标识符都会如API中指定的那样在0到count()-1之间。这个约定使得以子图作为索引的数组成为可能。
例子

最后
id[0]= 0
id[1]= 0
id[2]= 0
id[3]= 0
id[4]= 0
id[5]= 0
id[6]= 0
id[7]= 1
id[8]= 1
id[9]= 2
id[10]= 2
id[11]= 2
id[12]= 2
也就是说count[]的值相同的是一个连通分量,count[]的值不同的节点之间是走不通的。
代码
package com.sid.graph;public class CC {private boolean[] marked;private int[] id;private int count;public CC(Graph G){marked = new boolean[G.V()];id = new int[G.V()];for(int s = 0 ; s < G.V(); s++){if(!marked[s]){dfs(G,s);count++;}}}private void dfs(Graph G,int v){marked[v] = true;id[v] = count;for(int w : G.adj(v)){if(!marked[w]){dfs(G,w);}}}public boolean connected(int v, int w){return id[v] == id[w];}public int id(int v){return id[v];}public int count(){return count;}
}
7.G是无环图吗
使用深度优先处理
如果不存在自环和平行边,就是无环图
package com.sid.graph;public class Cycle {private boolean[] marked;private boolean hasCycle;public Cycle(Graph G){marked = new boolean[G.V()];for(int s = 0 ; s < G.V(); s++){if(!marked[s]){dfs(G,s,s);}}}private void dfs(Graph G, int v , int u){marked[v] = true;for(int w : G.adj(v)){if(!marked[w]){dfs(G,w,v);}else if(w != u){ //A---B 与B相邻的节点肯定有A,我理解的是无向图中他们属于同一条边,不是环。hasCycle = true;}}}public boolean hasCycle(){return hasCycle;}
}
8.G是二分图吗(双色问题)
package com.sid.graph;public class TwoColor {private boolean[] marked;private boolean[] color;private boolean isTowColorable = true;public TwoColor(Graph G){marked = new boolean[G.V()];color = new boolean[G.V()];for(int s = 0 ; s < G.V(); s++){if(!marked[s]){dfs(G,s);}}}private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {marked[v] = true;for (int w : G.adj(v)){if(!marked[w]){color[w] = !color[v];}else if(color[w] == color[v]){isTowColorable = false;return;}}}public boolean isBipartite(){return isTowColorable;}
}
9.符号图
节点里面装的不是数字,而是其他的,比如字符串