一文梭哈动态代理
大家好,这里是教授.F
引入:
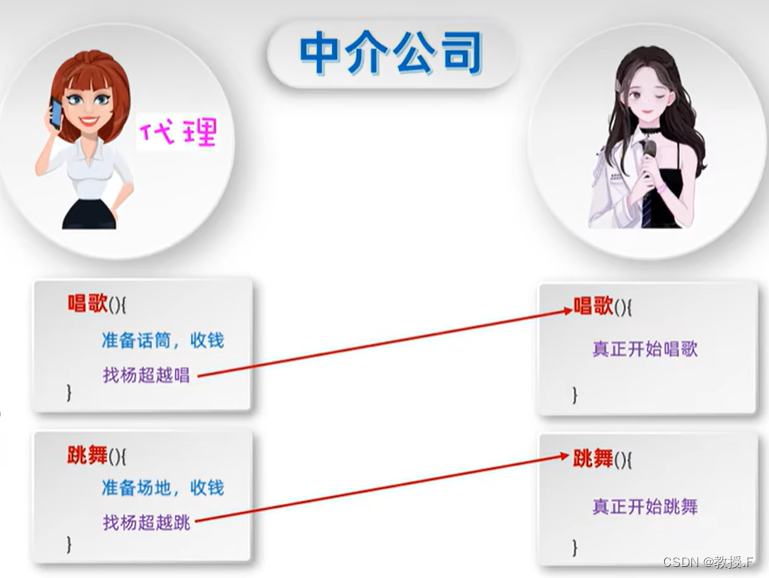
先看一个生活化的例子,如果一个明星他会唱歌,会跳舞。但是自己太忙了,没时间去宣传自己和去找工作,所以他需要有人帮他代理。然后呢这个代理者也需要知道他会什么,什么时间有空。
其实为什么要有动态代理,本质上是我们为了统一管理,让我们在一个方法执行前和执行后能进行一下业务操作。类似明星跟经纪人的关系。所以动态代理就是进行抽离出一些相同的业务。(其实就是切面编程)
如果我们没有使用代理,就会造成在唱歌前,自己这个方法去准备场地。跳舞前自己去安排老师去教。这样也会导致不够灵活:我们很难对唱歌这个方法进行控制。复用性也差:如果其他的类也有跟唱歌前一样的操作(比如:准备场地),那这样就不能使用到这个业务操作了。
看来上面的例子,折射到我们代码中的动态代理就是这样:
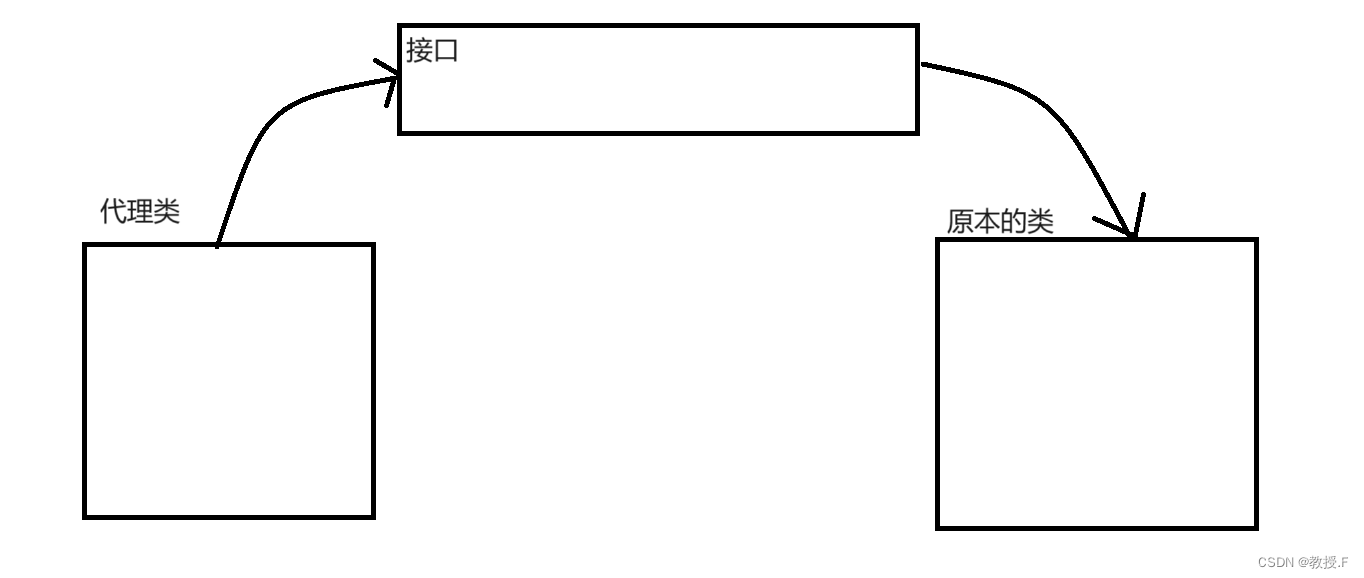
代理的这个类,怎么知道这个明星会什么呢?就需要一个接口,存着这位明星会的技能。
更详细一点的说明:
在实际代码的编写中,我们需要有一个类能返回一个代理对象。
核心代码:
public (接口) getProxy(){//得到类加载器......//得到要代理的对象/被执行对象的接口信息,底层是通过接口来完成......//创建InvocationHandler 对象....../*** public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,* Class<?>[] interfaces,* InvocationHandler h)* Proxy.newProxyInstance()可以返回一个代理对象* ClassLoader loader类的加载器* Class<?>[] interfaces 将来要代理的对象的接口信息* InvocationHandler h 调用处理器/对象 有一个方法非常重要 invoke***/接口 proxy = (接口)Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,interfaces,invocationHandler);
}实际代码示例:
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;/*** 该类可以返回一个代理对象*/
public class VehicleProxyProvider {//定义一个属性//target_vehicle 表示真正要执行的对象//该对象实现Vehicle接口private Vehicle target_vehicle;//构造器public VehicleProxyProvider(Vehicle target_vehicle) {this.target_vehicle = target_vehicle;}//编写一个方法,可以返回一个代理对象public Vehicle getProxy(){//得到类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = target_vehicle.getClass().getClassLoader();//得到要代理的对象/被执行对象的接口信息,底层是通过接口来完成Class<?>[] interfaces = target_vehicle.getClass().getInterfaces();//创建InvocationHandler 对象/*** public interface InvocationHandler {//接口不能实例化,那怎么得到该对象呢?使用匿名内部类的方式来创建。* public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)* throws Throwable;* }*/InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler(){/*** invoke 方法是将来执行我们的target_Vehicle的方法时,会调用到* @param proxy the proxy instance that the method was invoked on 表示代理对象** @param method the {@code Method} instance corresponding to 就是通过代理对象调用方法时的那个方法,代理对象.run()* the interface method invoked on the proxy instance. The declaring* class of the {@code Method} object will be the interface that* the method was declared in, which may be a superinterface of the* proxy interface that the proxy class inherits the method through.** @param args an array of objects containing the values of the 表示调用 代理对象.run(xx) 传入的参数* arguments passed in the method invocation on the proxy instance,* or {@code null} if interface method takes no arguments.* Arguments of primitive types are wrapped in instances of the* appropriate primitive wrapper class, such as* {@code java.lang.Integer} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}.** @return 表示代理对象.run(xx)执行后的结果* @throws Throwable*/@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {System.out.println("交通工具开始运行");//method是?:public abstract void com.hspedu.spring.proxy2.Vehicle.run()//target_vehicle?:ship对象,//args?:null【因为没有传值】Object result = method.invoke(target_vehicle,args);System.out.println("交通工具停止运行");return result;}};/*** public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,* Class<?>[] interfaces,* InvocationHandler h)* Proxy.newProxyInstance()可以返回一个代理对象* ClassLoader loader类的加载器* Class<?>[] interfaces 将来要代理的对象的接口信息* InvocationHandler h 调用处理器/对象 有一个方法非常重要 invoke***/Vehicle proxy = (Vehicle)Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,interfaces,invocationHandler);return proxy;}
}