BufferQueue研究
我们在工作的过程中,肯定听过分析卡顿或者冻屏问题的时候,定位到APP卡在dequeueBuffer方法里面,或者也听身边的同事老说3Buffer等信息。所以3Buffer是什么鬼?
什么是BufferQueue?
搞Android,你一定知道Graphic Buffer和 Buffer Queue, 你的笔记中肯定也有下面这张Graphic Buffer的状态迁移图。

系统中有两类Buffer Queue,如下图所示:

Layer背后的Buffer Queue
第一类,也是最为大家所熟知的,就是Layer背后的BufferQueue,用来连接App与SurfaceFlinger。App为Producer端,而 SurfaceFlinger 为 Consumer 端。
App 绘制时,先从 Buffer Queue 中 dequeue(调用 Producer 的 dequeueBuffer()函数)出来一块图形缓冲,绘制完成后,再把绘制好的图形缓冲 queue(调用 Producer 的 queueBuffer()函数)到 Buffer Queue 中,并通知 SurfaceFlinger来消费。SurfaceFlinger 收到通知后,从 Buffer Queue 中 acquire 一块绘制过的 Buffer,然后进行合成处理:要么进行 GPU合成,要么交给 HWC 去合成。
合成完成之后,这个块 Buffer 就恢复自由身,会被返回到 Buffer Queue 中(调用 Consumer 的 releaseBuffer()函数),以备下一次使用。
但是在Android S代码上面,谷歌对SurfaceFlinger的代码进行了重构,从个人理解是为了减少SF的负责,Android S开始强制App端创建BufferQueue,也就是强制Client端分配Buffer。
在Android S的代码中引入了一个BLASTBufferQueue.java(后面简称BBQ)这个类,ViewRootImpl.java在调用relayoutWindow函数的时候,会创建BBQ这个对象。
Surface getOrCreateBLASTSurface() {if (!mSurfaceControl.isValid()) {return null;}Surface ret = null;if (mBlastBufferQueue == null) {mBlastBufferQueue = new BLASTBufferQueue(mTag, mSurfaceControl,mSurfaceSize.x, mSurfaceSize.y,mWindowAttributes.format);// We only return the Surface the first time, as otherwise// it hasn't changed and there is no need to update.ret = mBlastBufferQueue.createSurface();} else {mBlastBufferQueue.update(mSurfaceControl,mSurfaceSize.x, mSurfaceSize.y,mWindowAttributes.format);}return ret;
}
在BBQ对象初初始化的时候,会调用nativeCreate方法,BBQ对象会在构造方法中传入SurfaceControl对象,而这样就会和SurfaceFlinger创建了一个连接通道。SurfaceControl.java封装了很多Client调用的binder接口,而服务端是SurfaceFlinger。
通过nativeCreate本地方法,通过JNI(android_graphics_BLASTBufferQueue.cpp)的nativeCreate方法,创建了native层的BBQ。
static jlong nativeCreate(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jstring jName, jlong surfaceControl,jlong width, jlong height, jint format) {String8 str8;if (jName) {const jchar* str16 = env->GetStringCritical(jName, nullptr);if (str16) {str8 = String8(reinterpret_cast<const char16_t*>(str16), env->GetStringLength(jName));env->ReleaseStringCritical(jName, str16);str16 = nullptr;}}std::string name = str8.string();sp<BLASTBufferQueue> queue =new BLASTBufferQueue(name, reinterpret_cast<SurfaceControl*>(surfaceControl), width,height, format);queue->incStrong((void*)nativeCreate);return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(queue.get());
}
BLASTBufferQueue::BLASTBufferQueue(const std::string& name, const sp<SurfaceControl>& surface,int width, int height, int32_t format): mSurfaceControl(surface),mSize(width, height),mRequestedSize(mSize),mFormat(format),mNextTransaction(nullptr) {createBufferQueue(&mProducer, &mConsumer);// since the adapter is in the client process, set dequeue timeout// explicitly so that dequeueBuffer will blockmProducer->setDequeueTimeout(std::numeric_limits<int64_t>::max());// safe default, most producers are expected to override thismProducer->setMaxDequeuedBufferCount(2);mBufferItemConsumer = new BLASTBufferItemConsumer(mConsumer,GraphicBuffer::USAGE_HW_COMPOSER |GraphicBuffer::USAGE_HW_TEXTURE,1, false);static int32_t id = 0;mName = name + "#" + std::to_string(id);auto consumerName = mName + "(BLAST Consumer)" + std::to_string(id);mQueuedBufferTrace = "QueuedBuffer - " + mName + "BLAST#" + std::to_string(id);id++;mBufferItemConsumer->setName(String8(consumerName.c_str()));mBufferItemConsumer->setFrameAvailableListener(this);mBufferItemConsumer->setBufferFreedListener(this);mBufferItemConsumer->setDefaultBufferSize(mSize.width, mSize.height);mBufferItemConsumer->setDefaultBufferFormat(convertBufferFormat(format));mBufferItemConsumer->setBlastBufferQueue(this);ComposerService::getComposerService()->getMaxAcquiredBufferCount(&mMaxAcquiredBuffers);mBufferItemConsumer->setMaxAcquiredBufferCount(mMaxAcquiredBuffers);mTransformHint = mSurfaceControl->getTransformHint();mBufferItemConsumer->setTransformHint(mTransformHint);SurfaceComposerClient::Transaction().setFlags(surface, layer_state_t::eEnableBackpressure,layer_state_t::eEnableBackpressure).setApplyToken(mApplyToken).apply();mNumAcquired = 0;mNumFrameAvailable = 0;BQA_LOGV("BLASTBufferQueue created width=%d height=%d format=%d mTransformHint=%d", width,height, format, mTransformHint);
}
从上面的代码中,createBufferQueue创建了BufferQueue,同时也创建了Graphic Buffer的生产者和消费者。其中有个代码mProducer -> setMaxDequeuedBufferCount(2),这个就和3Buffer有关系了,我们先整理下Buffer的运转过程,如图所示:
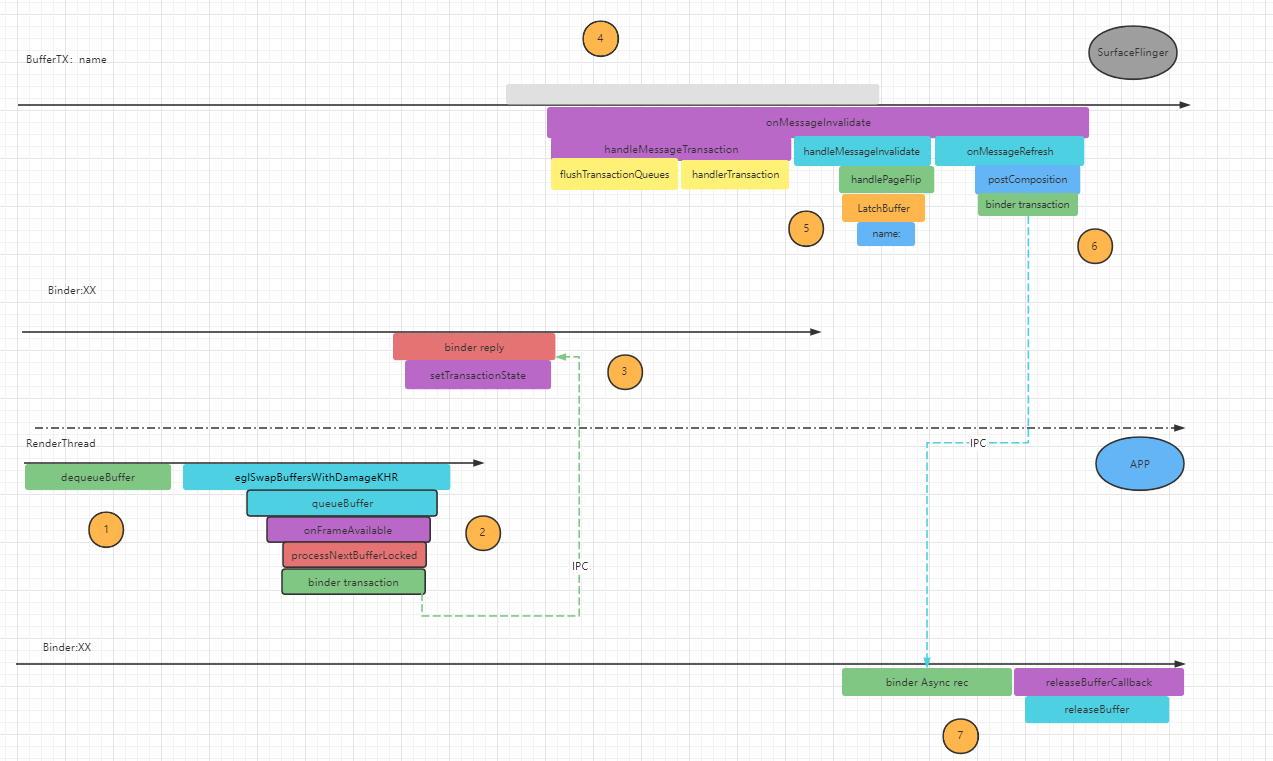
App的RenderThread 调用 Producer.dequeueBuffer()在BufferQueue中拿到一个空闲的Buffer。
App的RenderThread调用Producer.queueBuffer将绘制好的 Buffer 入列。注意,此时入列的 Buffer 可能还未绘制完成,即 GPU 可能还在进行绘制工作。
最终调用到 Procuder 的 Bn 端,即 SurfaceFliner 进程里的某个 Binder 线程里。在 Bn 端,会通过调用SurfaceFlinger的SetTransactionState方法,把当前的带有Buffer信息的State保存到一个TransactionQueue队列中。
当带有Buffer信息的Layer信息保存到队列中, 这个动作称作“上帧”。所以我么可以在 systrace 上看到该Layer待消费的 Buffer 数目+1。
而 Buffer Queue 的消费者就是 SurfaceFlinger,所以在下一个 Vsync信号到来后,在 SurfaceFlinger 的 handleMessageInvalidate()函数中,调用 acquireBuffer()去取 Buffer,取走之后,BufferQueue 中待消费的 Buffer 便减少一个。
因为有上帧,所以要重新进行合成,SurfaceFlinger 调用onMessageRefresh()函数去做合成,一般是 HWC 合成,直接把 Buffer 交给 HWC。合成完成后,在 postComposition()里,会调用binder接口进行通讯。
App端的binder收到消息后调用releaseBuffer()释放 Buffer,如 systrace 所示,这里释放的是上一帧的 Buffer。
上面图中7个步骤就是一个buffer详细的转运过程。
DisplayDevice 背后的Buffer Queue
第二类Buffer Queue是GPU合成特有的,一般在游戏APP渲染过程中会遇到,这个Buffer Queue隐藏在DisplayDevice之后,是在SurfaceFlinger为每个接入系统的显示屏创建DisplayDevice实例时创建的。
执行在SurfaceFlinger::processDisplayAdded函数中。
void SurfaceFlinger::processDisplayAdded(const wp<IBinder>& displayToken,const DisplayDeviceState& state) {......sp<compositionengine::DisplaySurface> displaySurface;sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> producer;sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> bqProducer;sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer> bqConsumer;getFactory().createBufferQueue(&bqProducer, &bqConsumer, /*consumerIsSurfaceFlinger =*/false);......
}这个函数是为DisplaySurface创建BufferQueue, createBufferQueue函数是指向BufferQueue::createBufferQueue,传入的第三个参数 consumerIsSurfaceFlinger 为false,表示BufferQueue的消费者不是SurfaceFlinger。
void SurfaceFlinger::processDisplayAdded(const wp<IBinder>& displayToken,const DisplayDeviceState& state) {......if (state.isVirtual()) {const auto displayId = VirtualDisplayId::tryCast(compositionDisplay->getId());LOG_FATAL_IF(!displayId);auto surface = sp<VirtualDisplaySurface>::make(getHwComposer(), *displayId, state.surface,bqProducer, bqConsumer, state.displayName);displaySurface = surface;producer = std::move(surface);} else {ALOGE_IF(state.surface != nullptr,"adding a supported display, but rendering ""surface is provided (%p), ignoring it",state.surface.get());const auto displayId = PhysicalDisplayId::tryCast(compositionDisplay->getId());LOG_FATAL_IF(!displayId);displaySurface =sp<FramebufferSurface>::make(getHwComposer(), *displayId, bqConsumer,state.physical->activeMode->getSize(),ui::Size(maxGraphicsWidth, maxGraphicsHeight));producer = bqProducer;}......
}除了虚拟盘,主屏或者外屏采用FrameBufferSurface,继承自ConsumerBase,把BufferQueueConsumer封装到FrameBufferSurface里面。
Buffer共享
Buffer分配
Buffer同步:fence
后面三个点的内容还在整理中,等整理完毕,再同步到这章内容中。
