【C++】类型转换和IO流
目录
C语言中的类型转换
C++ eplicit && volatitle
eplicit
volatile
C++强制类型转换
static_cast(相关类型)
reinterpret_cast(不相关类型)
const_cast(去掉const属性)
dynamic_cast
RTTI(了解)
IO流
C语言中的类型转换
- 隐式类型转换:编译器在编译阶段自动进行,能转就转,不能转就编译失败
- 显式类型转换:需要用户自己处理。
void Test ()
{int i = 1 ;// 隐式类型转换double d = i ;printf ( "%d, %.2f\n" , i , d );int* p = & i ;// 显示的强制类型转换int address = ( int ) p ;printf ( "%x, %d\n" , p , address );}
缺陷:转换的可视性比较差,所有的转换形式都是以一种相同形式书写,难以跟踪错误的转换。
C++ eplicit && volatitle
eplicit
自定义类型之间只要构造函数里面有联系也可以进行类型转换
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A(int a)
:_a(a)
{}
private:
int _a;
};class B
{
public:
B(const A& a)
{}
private:
//……
};int main()
{
A a1(1);
B b1 = a1;
return 0;
}
如果不想这个转换发生可以在B 的构造函数前面加 explicit 关键字
class B
{
public:
explicit B(const A& a)
{}
private:
//……
};
volatile
//这个n为常变量,不是常量,不能直接修改,但是可以通过类型转换间接修改
const int n = 10;
//去掉const 属性后,常变量就可以修改
int* p = (int*)&n;
(*p)++;//监视窗口中n已经变成11,但是打印为10
//原因是编译器的优化,去掉const 属性是有风险的,因此编译器所作的优化是在取n的值的
//时候没有从内存里取,而是从寄存器里取,有些编译器编译的时候会将const变量都替换成
//常量
cout << n << endl; //10
cout << *p << endl; //11//要解决上述情况,需要引入 volatile 关键字
//该关键字的作用是告诉编译器每次都去内存中取值
volatile const int n = 10;
C++强制类型转换
标准C++为了加强类型转换的可视性,引入了四种命名的强制类型转换操作符:
static_cast 、reinterpret_cast、const_cast、dynamic_case
static_cast(相关类型)
int main (){double d = 12.34 ;int a = static_cast < int > ( d );cout << a << endl ;return 0 ;}
reinterpret_cast(不相关类型)
int main (){double d = 12.34 ;int a = static_cast < int > ( d );cout << a << endl ;// 这里使用 static_cast 会报错,应该使用 reinterpret_cast//int *p = static_cast<int*>(a);int * p = reinterpret_cast < int* > ( a );return 0 ;}
const_cast(去掉const属性)
void Test (){volatile const int a = 2 ;int* p = const_cast < int* > ( & a );* p = 3 ;cout << a << endl ;}
dynamic_cast
- 向上转型:子类对象指针/引用->父类指针/引用(不需要转换,赋值兼容规则)
- 向下转型:父类对象指针/引用->子类指针/引用(用dynamic_cast转型是安全的)
- dynamic_cast只能用于父类含有虚函数的类
- dynamic_cast会先检查是否能转换成功,能成功则转换,不能则返回0
class A{public :virtual void f (){}};class B : public A{};void fun ( A * pa ){// dynamic_cast会先检查是否能转换成功,能成功则转换,不能则返回B * pb1 = static_cast < B *> ( pa );B * pb2 = dynamic_cast < B *> ( pa );cout << "pb1:" << pb1 << endl ;cout << "pb2:" << pb2 << endl ;}int main (){A a ;B b ;fun ( & a );fun ( & b );return 0 ;}
RTTI(了解)
- typeid运算符
- dynamic_cast运算符
- decltype
IO流
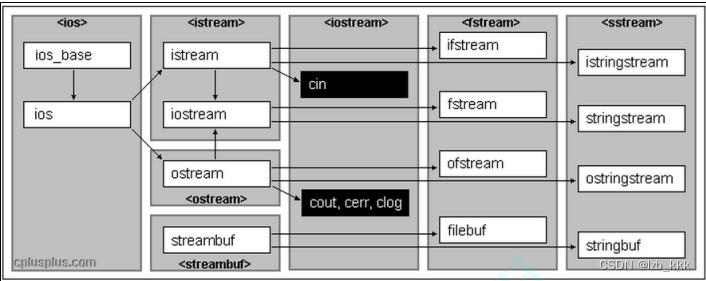
c++中自定义类型中重载流插入和流提取,方法如下示例:
class Date{friend ostream & operator << ( ostream & out , const Date & d );friend istream & operator >> ( istream & in , Date & d );public :Date ( int year = 1 , int month = 1 , int day = 1 ): _year ( year ), _month ( month ), _day ( day ){}operator bool (){// 这里是随意写的,假设输入 _year 为 0 ,则结束if ( _year == 0 )return false ;elsereturn true ;}private :int _year ;int _month ;int _day ;};istream & operator >> ( istream & in , Date & d ){in >> d . _year >> d . _month >> d . _day ;return in ;}ostream & operator << ( ostream & out , const Date & d ){out << d . _year << " " << d . _month << " " << d . _day ;return out ;}// C++ IO 流,使用面向对象 + 运算符重载的方式// 能更好的兼容自定义类型,流插入和流提取int main (){// 自动识别类型的本质 -- 函数重载// 内置类型可以直接使用 -- 因为库里面 ostream 类型已经实现了int i = 1 ;double j = 2.2 ;cout << i << endl ;cout << j << endl ;// 自定义类型则需要我们自己重载 << 和 >>Date d ( 2022 , 4 , 10 );cout << d ;while ( d ){cin >> d ;cout << d ;}return 0 ;}
C++文件IO流
struct ServerInfo{char _address [ 32 ];int _port ;Date _date ;};struct ConfigManager{public :ConfigManager ( const char* filename ): _filename ( filename ){}void WriteBin ( const ServerInfo & info ){ofstream ofs ( _filename , ios_base::out | ios_base::binary );ofs . write (( const char* ) & info , sizeof ( info ));}void ReadBin ( ServerInfo & info ){ifstream ifs ( _filename , ios_base::in | ios_base::binary );ifs . read (( char* ) & info , sizeof ( info ));}// C++ 文件流的优势就是可以对内置类型和自定义类型,都使用// 一样的方式,去流插入和流提取数据// 当然这里自定义类型 Date 需要重载 >> 和 <<// istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)// ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)void WriteText ( const ServerInfo & info ){ofstream ofs ( _filename );ofs << info . _address << " " << info . _port << " " << info . _date ;}void ReadText ( ServerInfo & info ){ifstream ifs ( _filename );ifs >> info . _address >> info . _port >> info . _date ;}private :string _filename ; // 配置文件};int main (){ServerInfo winfo = { "192.0.0.1" , 80 , { 2022 , 4 , 10 } };// 二进制读写ConfigManager cf_bin ( "test.bin" );cf_bin . WriteBin ( winfo );ServerInfo rbinfo ;cf_bin . ReadBin ( rbinfo );cout << rbinfo . _address << " " << rbinfo . _port << " " << rbinfo . _date << endl ;// 文本读写ConfigManager cf_text ( "test.text" );cf_text . WriteText ( winfo );ServerInfo rtinfo ;cf_text . ReadText ( rtinfo );cout << rtinfo . _address << " " << rtinfo . _port << " " <<rtinfo . _date << endl ;return 0 ;}
下面我们cin常用来读取数据直到输入结束,本质就是重载类型
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num;// while(cin>>a>>b) cin.operator>>(a).operator>>(b).operator bool()
while (cin >> num) //operator >>(cin,str). operator bool()
{
//……
}
return 0;
}
自定义类型 和 内置类型相互转换
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A(int a)
:_a(a)
{}//内置类型 <- 自定义类型
operator int ()
{
return _a;
}
private:
int _a;
};int main()
{//自定义类型 <- 内置类型
A a = 1;//内置类型 <- 自定义类型,需要重载类型
int num = a;
return 0;
}
