Linux——基础IO

文章目录
- 一、C语言IO
- 1、写文件
- 2、读文件
- 3、stdin & stdout & stderr
- 二、系统文件I/O
- 1、写文件
- 2、读文件
- 三、接口介绍
- 四、文件描述符fd
- 五、文件描述符的分配规则
- 六、重定向
一、C语言IO
1、写文件
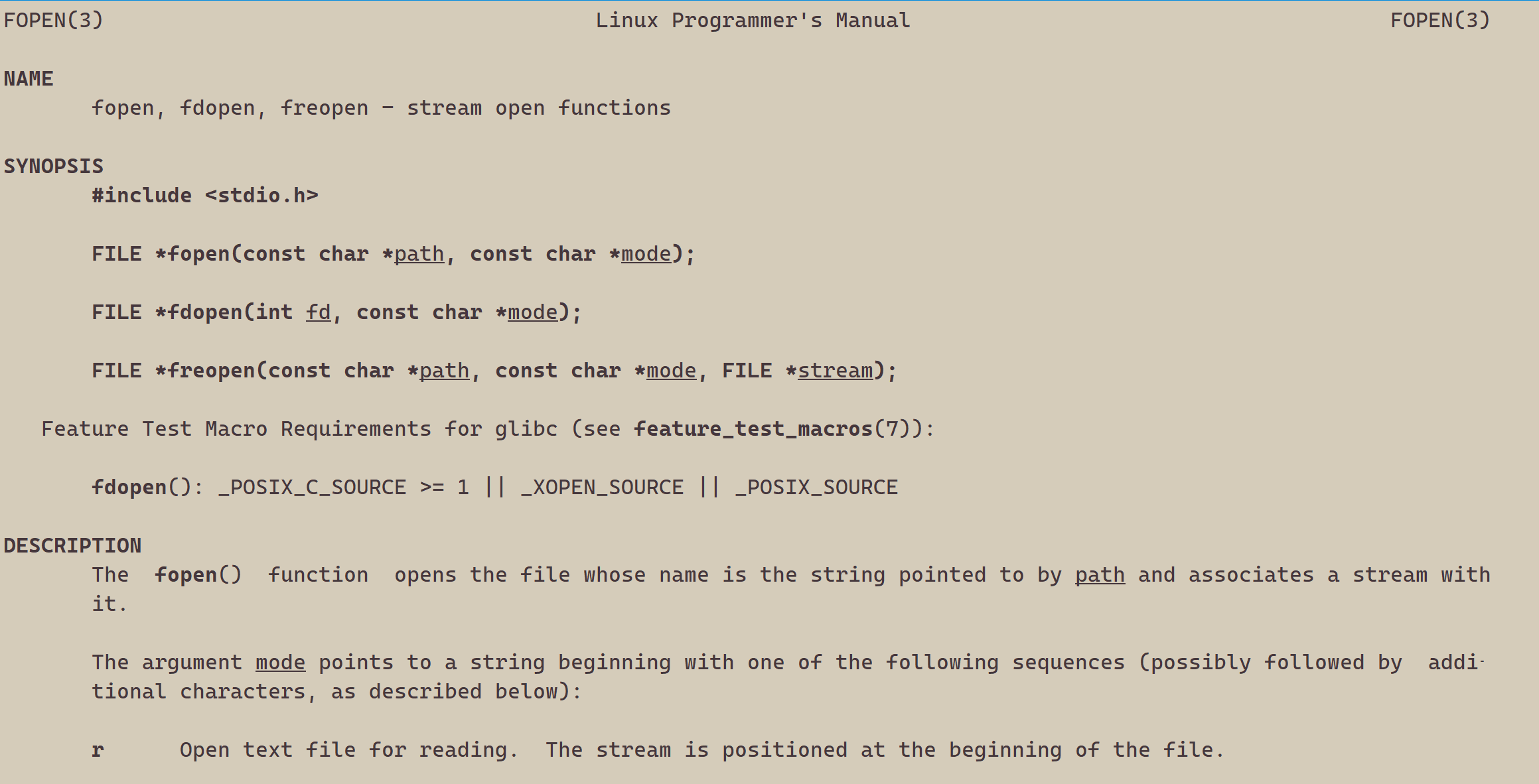
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{FILE *fp = fopen("myfile", "w");if(!fp){printf("fopen error!\n");}const char *msg = "hello bit!\n";int count = 5;while(count--){fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, fp);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
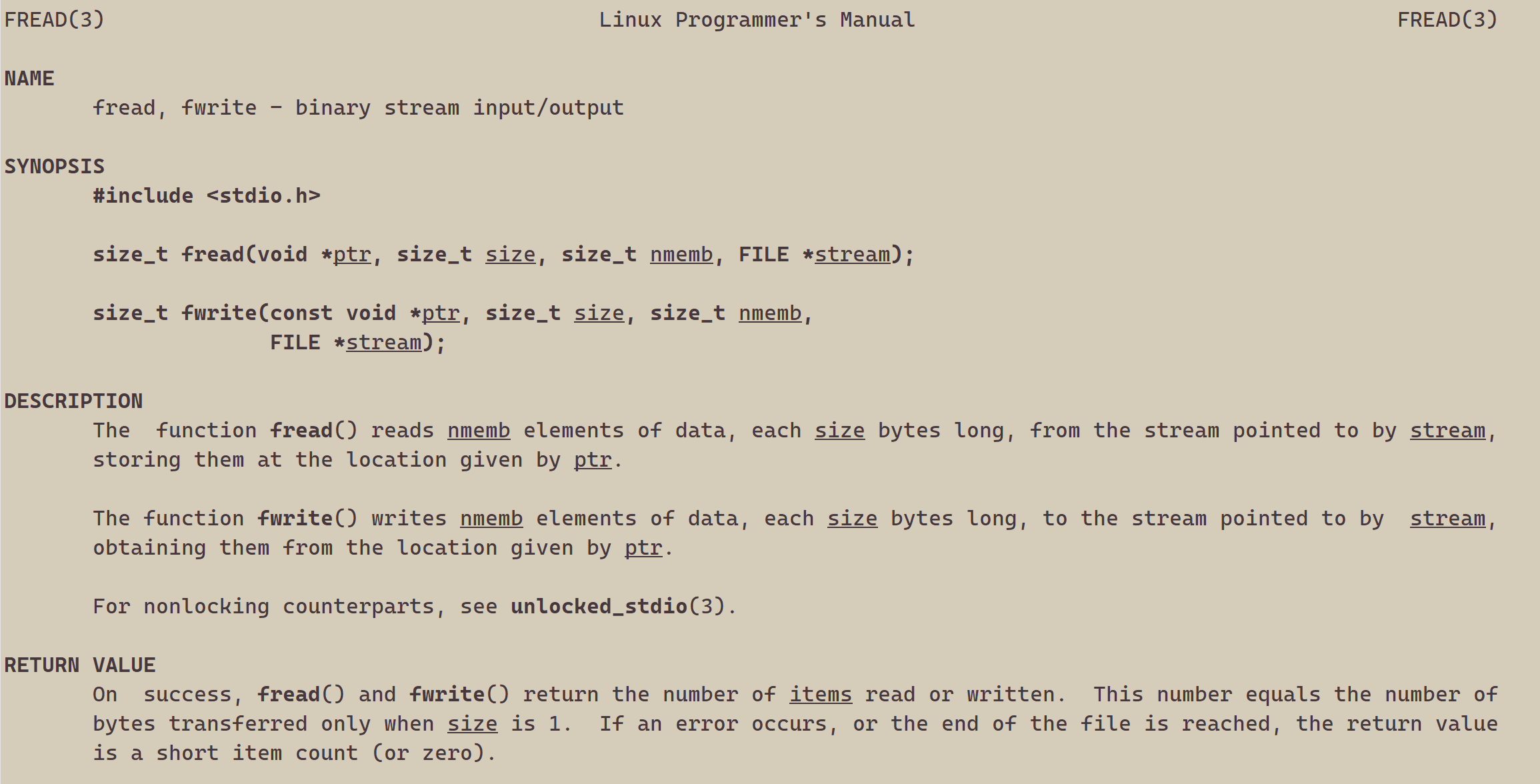
2、读文件
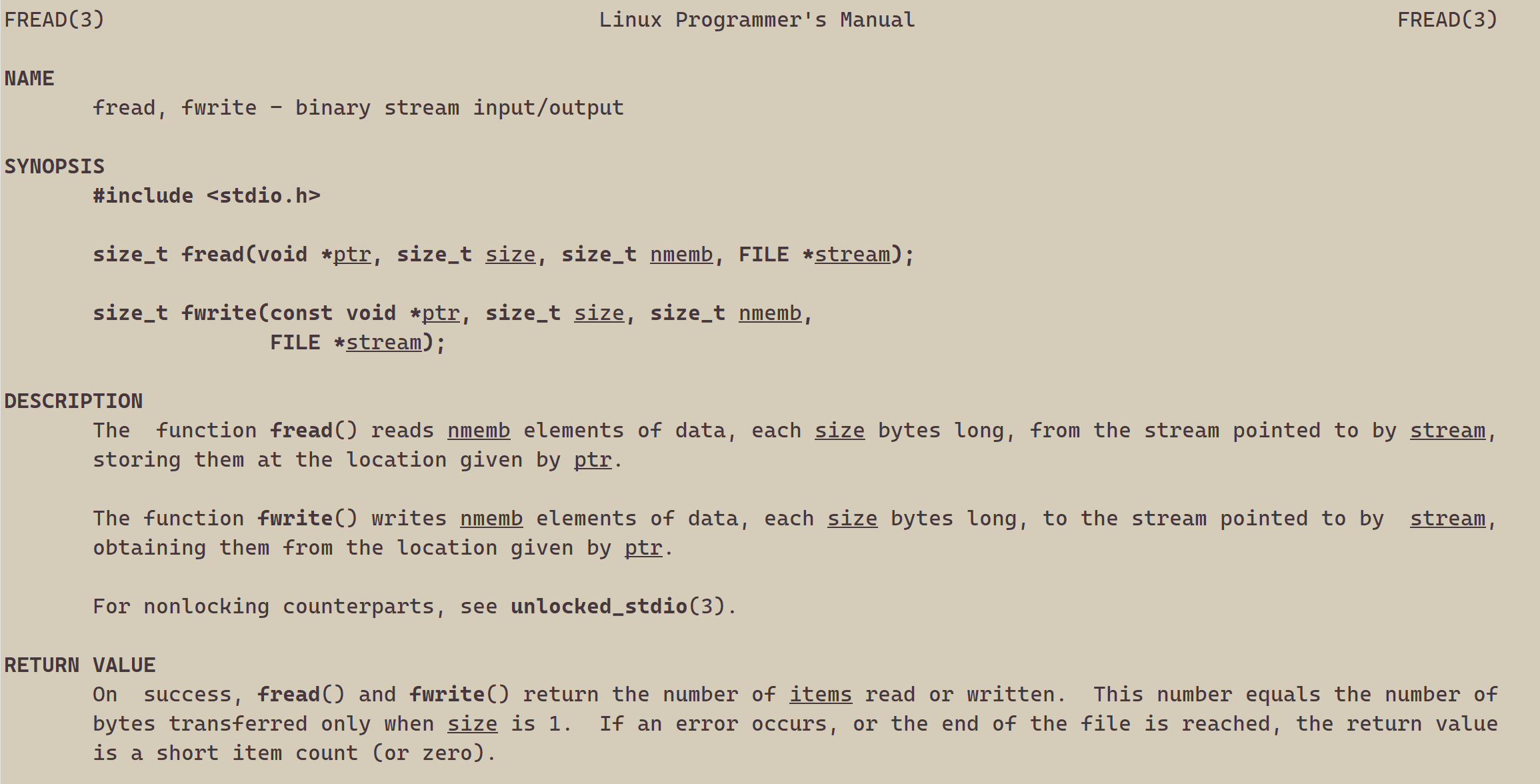
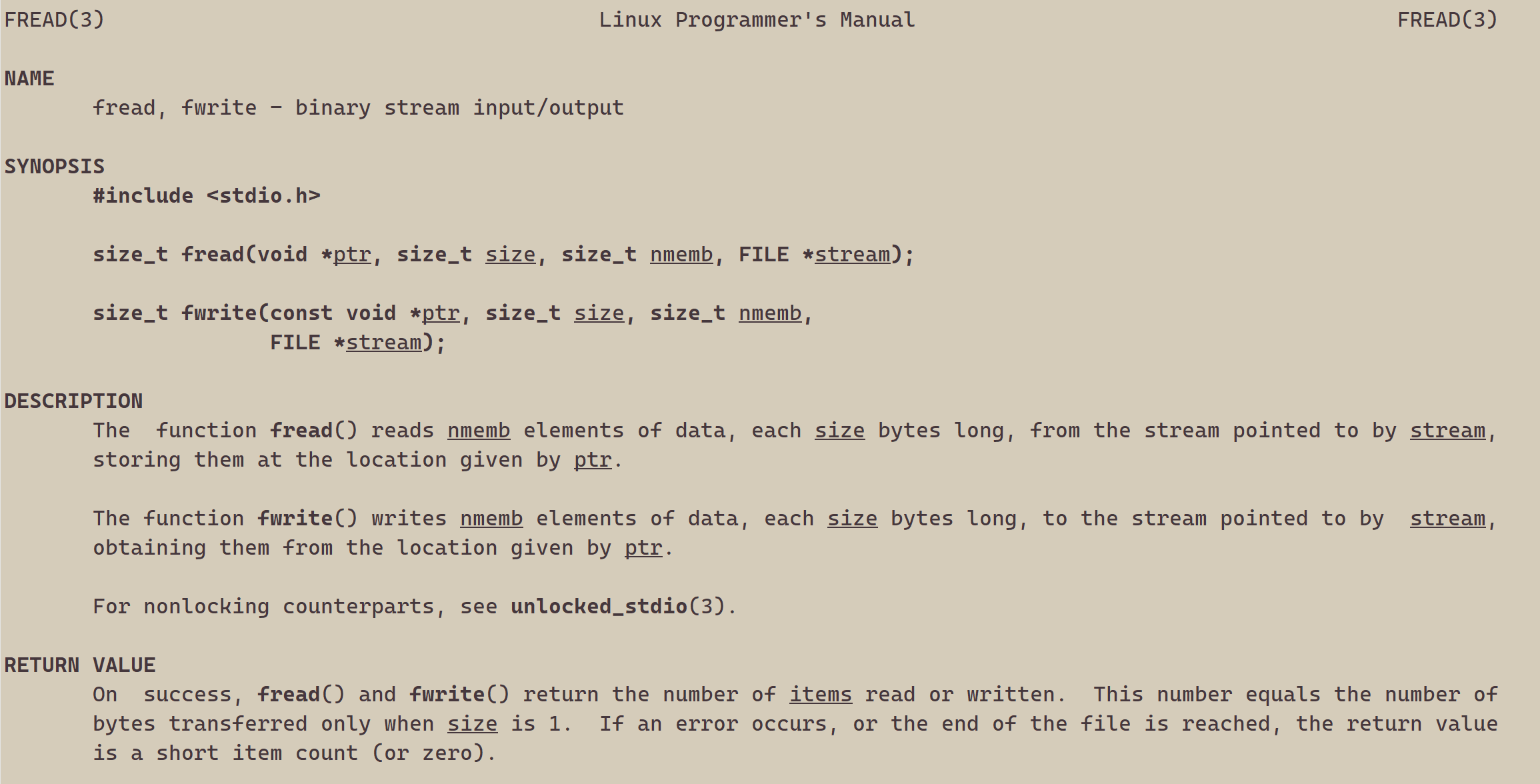
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{FILE *fp = fopen("myfile", "r");if(!fp){printf("fopen error!\n");}char buf[1024];const char *msg = "hello bit!\n";while(1){//注意返回值和参数,此处有坑,仔细查看man手册关于该函数的说明ssize_t s = fread(buf, 1, strlen(msg), fp);if(s > 0){buf[s] = 0;printf("%s", buf);}if(feof(fp)){break;}}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
3、stdin & stdout & stderr
C默认会打开三个输入输出流,分别是stdin, stdout, stderr
仔细观察发现,这三个流的类型都是FILE*, fopen返回值类型,文件指针
二、系统文件I/O
1、写文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
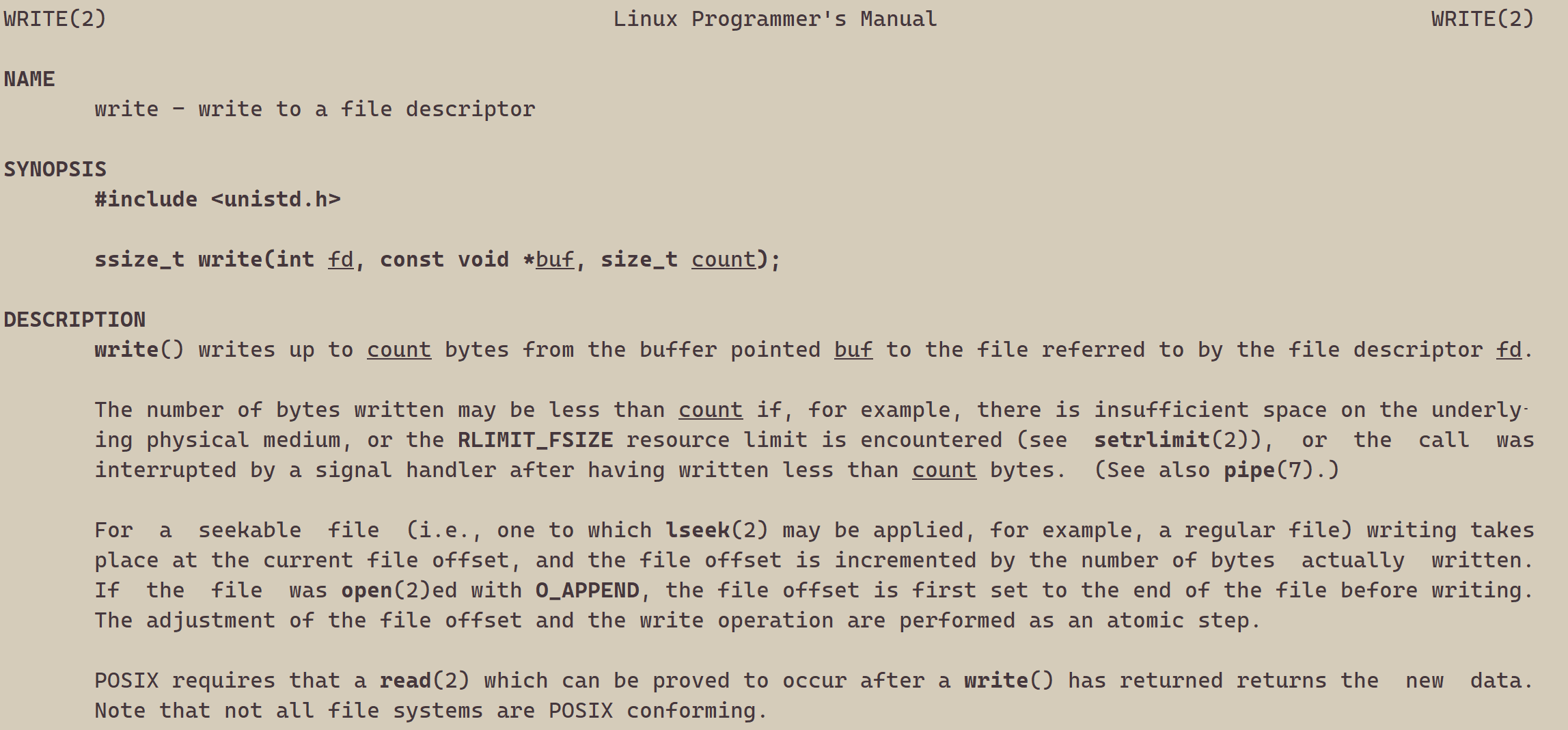
{umask(0);int fd = open("myfile", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0644);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return 1;}int count = 5;const char *msg = "hello bit!\n";int len = strlen(msg);while(count--){write(fd, msg, len);//fd: 后面讲, msg:缓冲区首地址, len: 本次读取,期望写入多少个字节的数 据。 返回值:实际写了多少字节数据}close(fd);return 0;
}
2、读文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
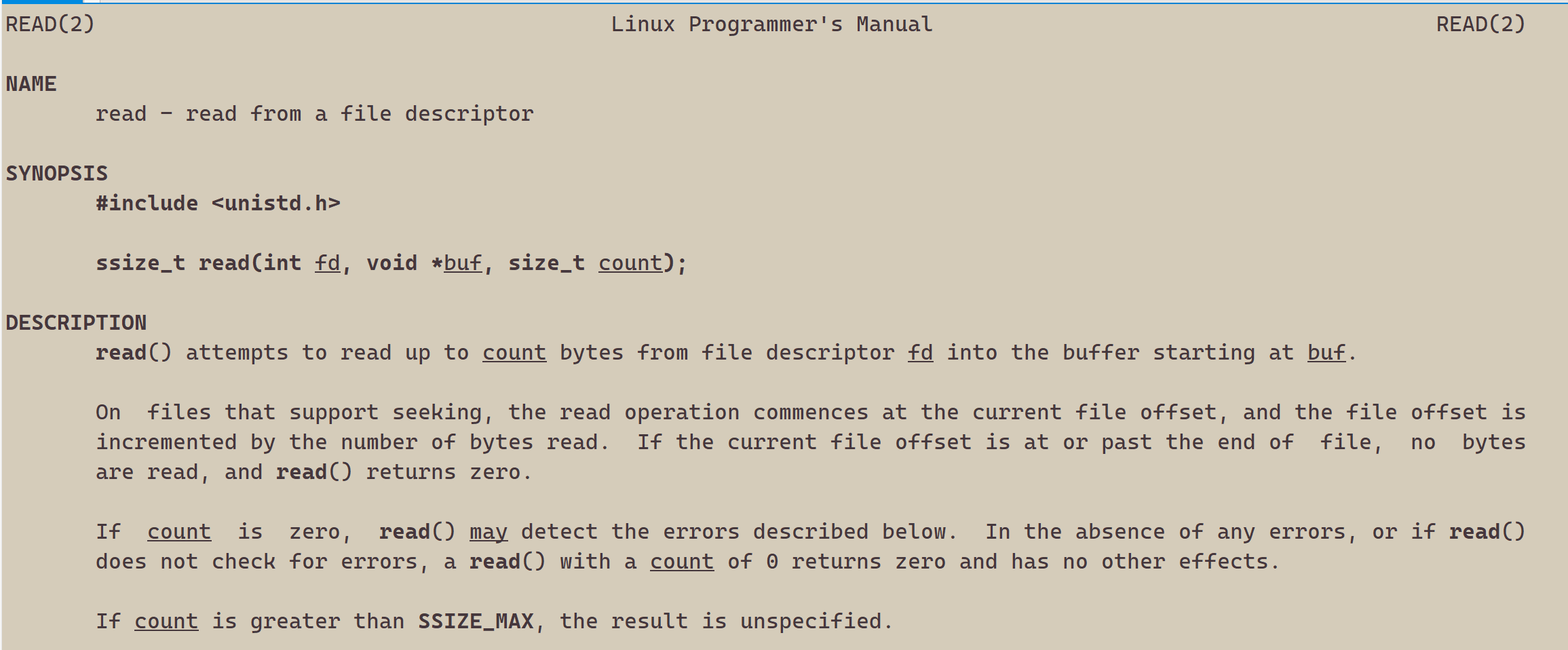
{int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return 1;}const char *msg = "hello bit!\n";char buf[1024];while(1){ssize_t s = read(fd, buf, strlen(msg));//类比writeif(s > 0){printf("%s", buf);}else{break;}}close(fd);return 0;
}
三、接口介绍
使用man2号手册
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
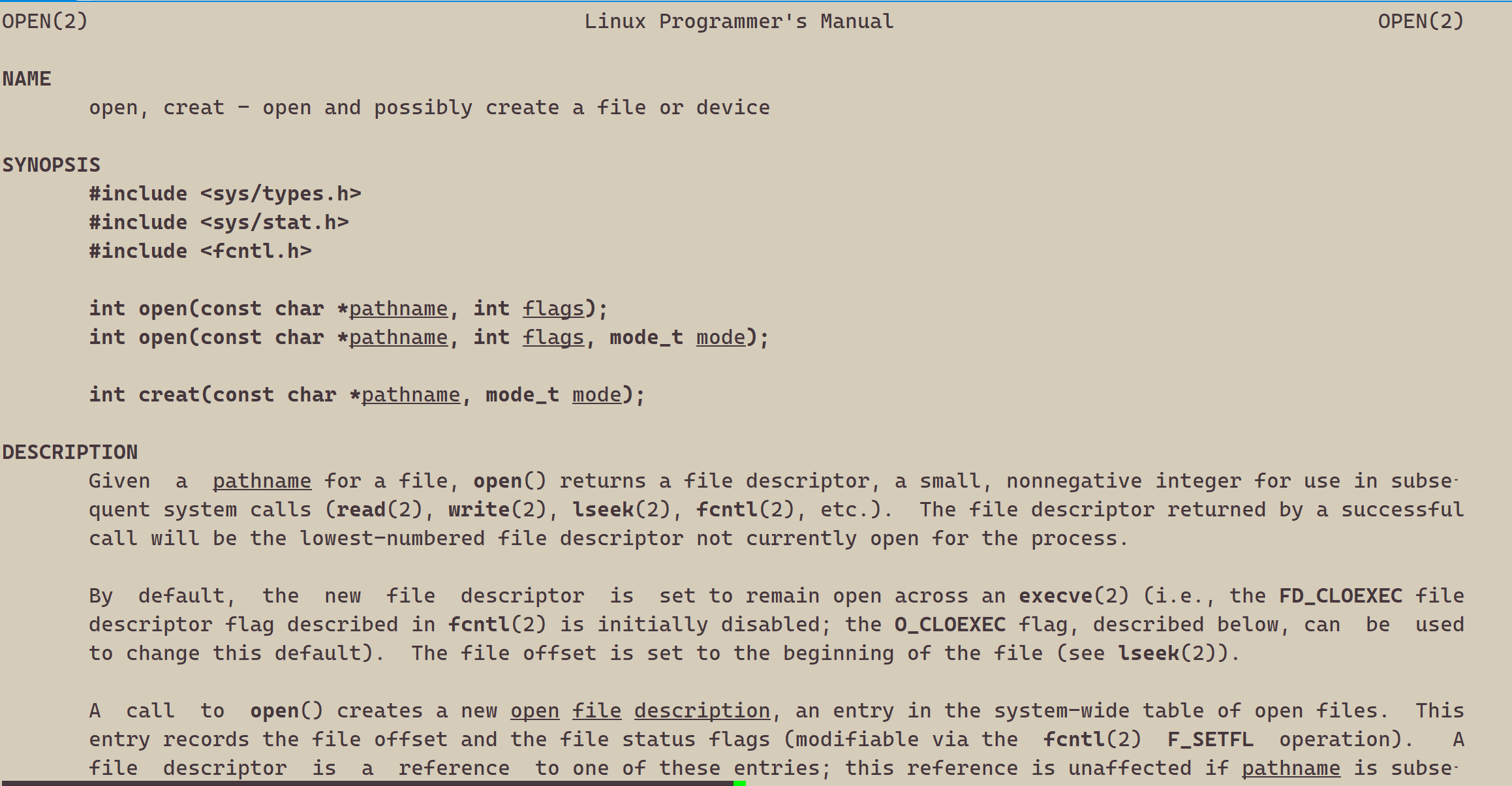
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
pathname: 要打开或创建的目标文件
flags: 打开文件时,可以传入多个参数选项,用下面的一个或者多个常量进行“或”运算,构成flags。
参数:O_RDONLY: 只读打开O_WRONLY: 只写打开O_RDWR : 读,写打开这三个常量,必须指定一个且只能指定一个O_CREAT : 若文件不存在,则创建它。需要使用mode选项,来指明新文件的访问权限O_APPEND: 追加写返回值:成功:新打开的文件描述符失败:-1
四、文件描述符fd
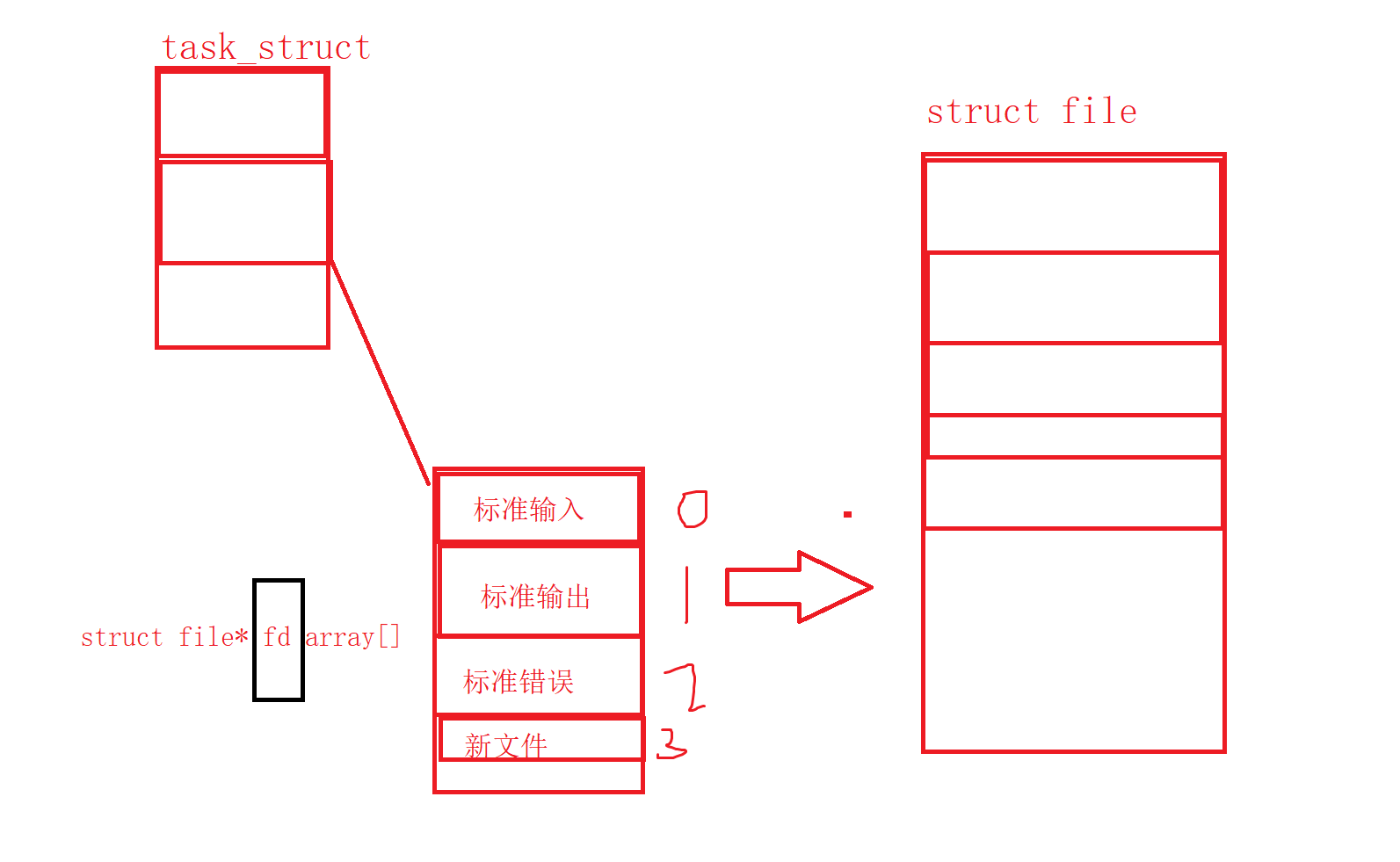
Linux进程默认情况下会有3个缺省打开的文件描述符,分别是标准输入0, 标准输出1, 标准错误2.
0,1,2对应的物理设备一般是:键盘,显示器,显示器
而现在知道,文件描述符就是从0开始的小整数。当我们打开文件时,操作系统在内存中要创建相应的数据结构来描述目标文件。于是就有了file结构体。表示一个已经打开的文件对象。而进程执行open系统调用,所以必须让进程和文件关联起来。每个进程都有一个指针*files, 指向一张表files_struct,该表最重的部分就是包涵一个指针数组,每个元素都是一个指向打开文件的指针!所以,本质上,文件描述符就是该数组标。所以,只要拿着文件描述符,就可以找到对应的文件
五、文件描述符的分配规则
直接看代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return 1;}printf("fd: %d\n", fd);close(fd);return 0;
}
发现输入3
关闭0或者2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{close(0);//close(2);int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return 1;}printf("fd: %d\n", fd);close(fd);return 0;
}
发现是结果是: fd: 0 或者 fd 2 可见,文件描述符的分配规则:在files_struct数组当中,找到当前没有被使用的最小的一个下标,作为新的文件描述符。
六、重定向
那如果关闭1呢?看代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{close(1);int fd = open("myfile", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 00644);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return 1;}printf("fd: %d\n", fd);fflush(stdout);close(fd);exit(0);
}
此时,我们发现,本来应该输出到显示器上的内容,输出到了文件 myfile 当中,其中,fd=1。这种现象叫做输出重定向。常见的重定向有:>, >>, <
那重定向的本质是什么呢?
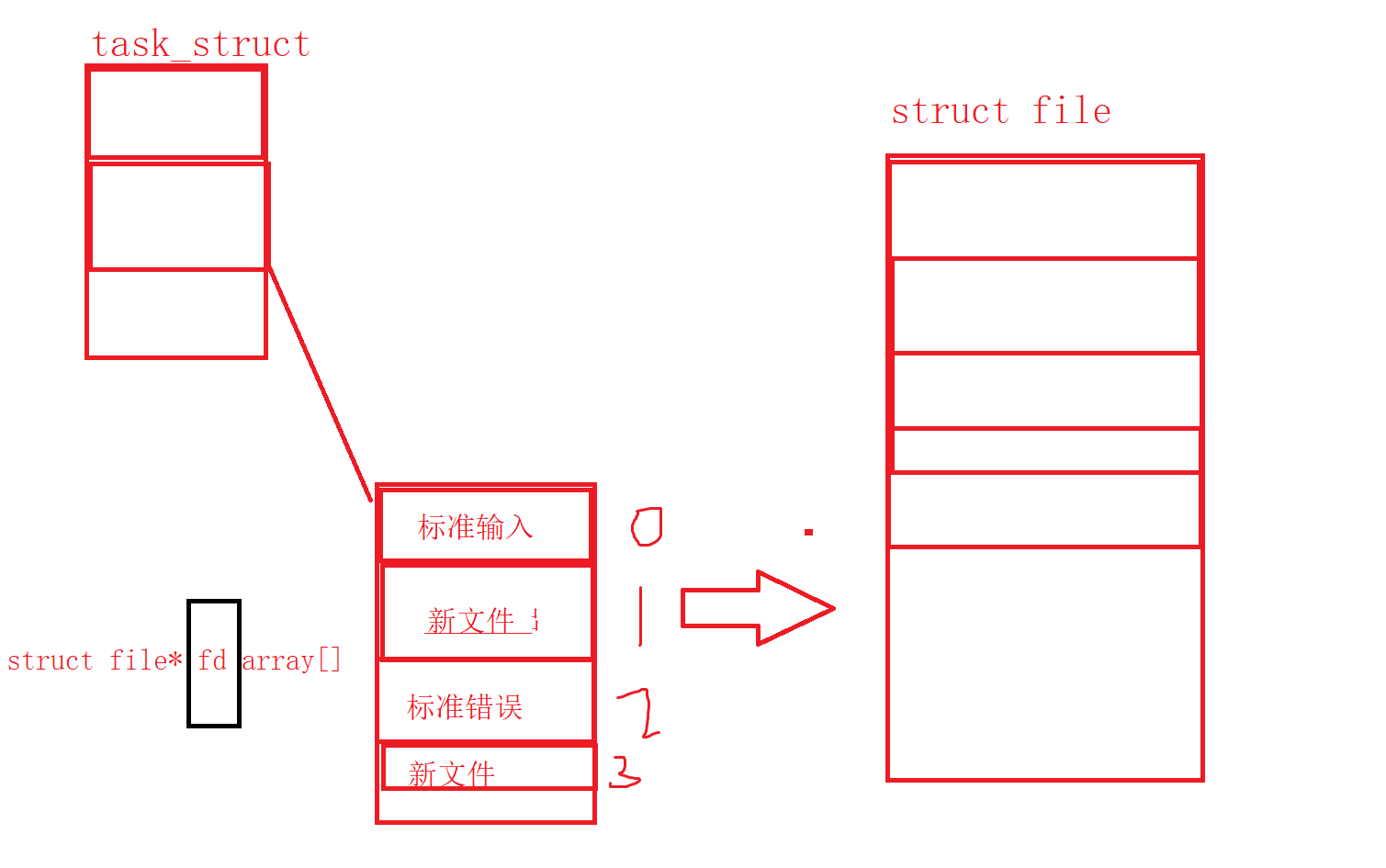
使用 dup2 系统调用
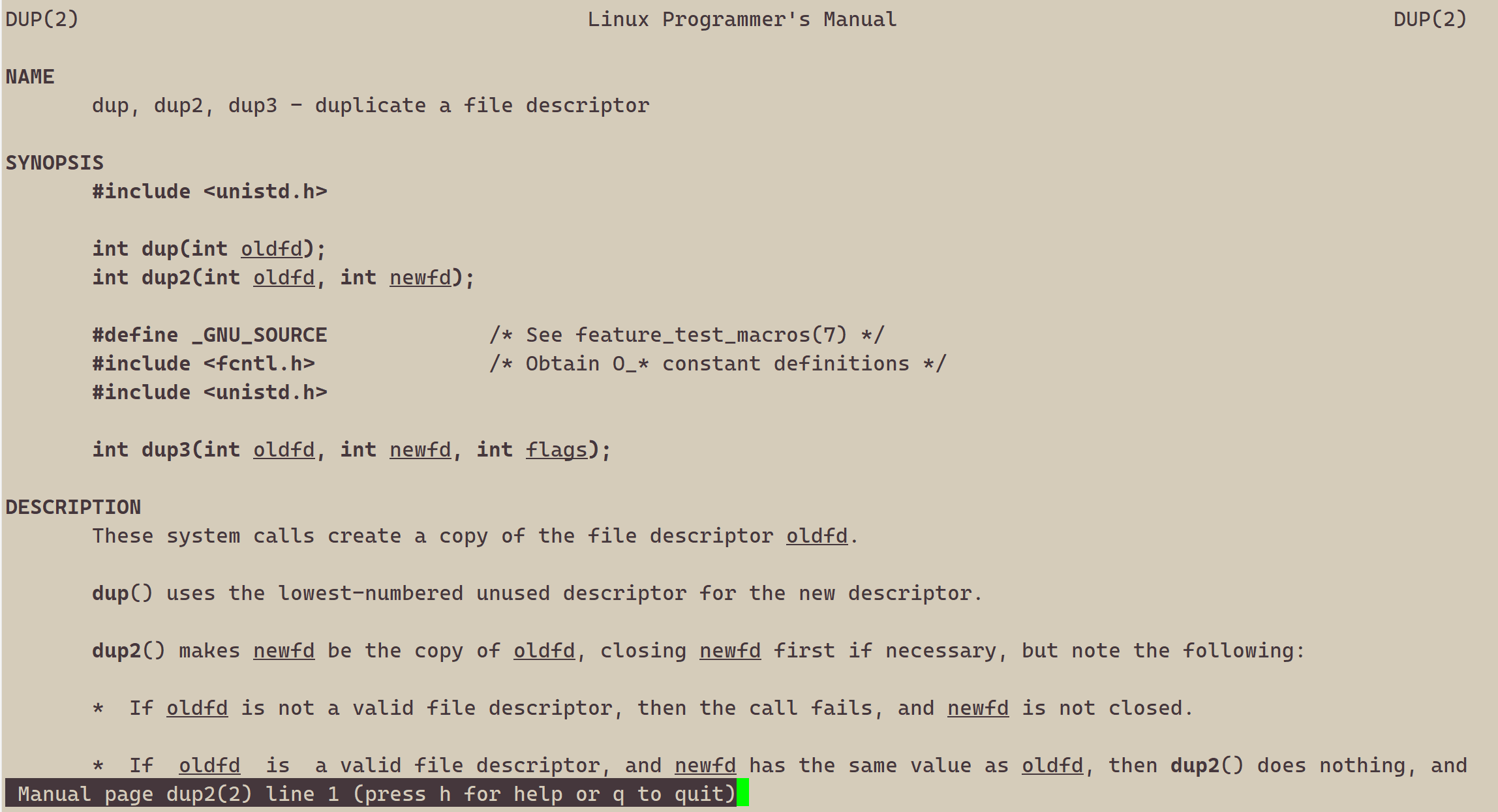
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {int fd = open("./log", O_CREAT | O_RDWR);if (fd < 0) {perror("open");return 1;}close(1);dup2(fd, 1);for (;;) {char buf[1024] = {0};ssize_t read_size = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1);if (read_size < 0) {perror("read");break;}printf("%s", buf);fflush(stdout);}return 0;
}
