C++算法之双指针、BFS和图论
一、双指针
1.AcWing 1238.日志统计
分析思路

前一区间和后一区间有大部分是存在重复的
我们要做的就是利用这部分 来缩短我们查询的时间
并且在使用双指针时要注意对所有的博客记录按时间从小到大先排好顺序
因为在有序的区间内才能使用双指针记录两个区间相差
相当于把一个有序的时间序列进行每次递增1的划分
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
PII logs[N];
bool st[N];
int cnt[N];
int main()
{int n,d,k;cin>>n>>d>>k;for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>logs[i].x>>logs[i].y;sort(logs,logs+n);for(int i=0,j=0;i<n;i++){int t=logs[i].y;cnt[t]++;while(logs[i].x-logs[j].x>=d){cnt[logs[j].y]--;j++;}if(cnt[t]>=k) st[t]=true;}for(int i=0;i<100000;i++){if(st[i]) cout<<i<<endl;}return 0;
}2.AcWing 1240.完全二叉树的权值
分析思路
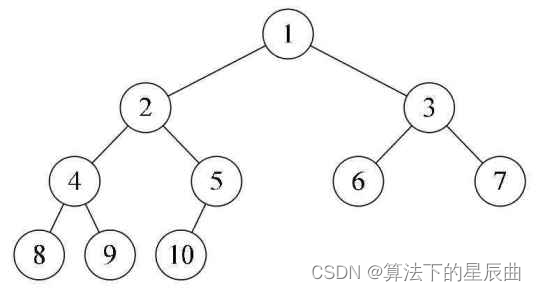

双指针:
从第一层根节点i=1,开始每一层开头都是2i,而每一层的长度就为pow(2,d-1)(d为层数)
前缀和:
因为是完全二叉树,所以算到最后要考虑是否越界。
代码实现
双指针
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=100010;
int q[N];
LL sum[N];
int n,t;int main()
{scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&q[i]);LL m=-1e18;for(int i=1,d=1;i<=n;i*=2,d++){LL s=0;for(int j=i;j<i+pow(2,d-1)&&j<=n;j++) s+=q[j];if(s>m){m=s;t=d;}}cout<<t<<endl;return 0;
}
前缀和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=100010;
int q[N];
LL sum[N];
int n,t;int main()
{scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&q[i]);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) sum[i]=sum[i-1]+q[i];LL m=-1e18;for(int i=1,d=1;i<=n;i*=2,d++){LL s=0;LL r=i+pow(2,d-1)-1;if(r<=n) s=sum[r]-sum[i-1];else s=sum[n]-sum[i-1];if(s>m){m=s;t=d;}}cout<<t<<endl;return 0;
}
二、BFS
1.AcWing 1101.献给阿尔吉侬的花束
分析思路
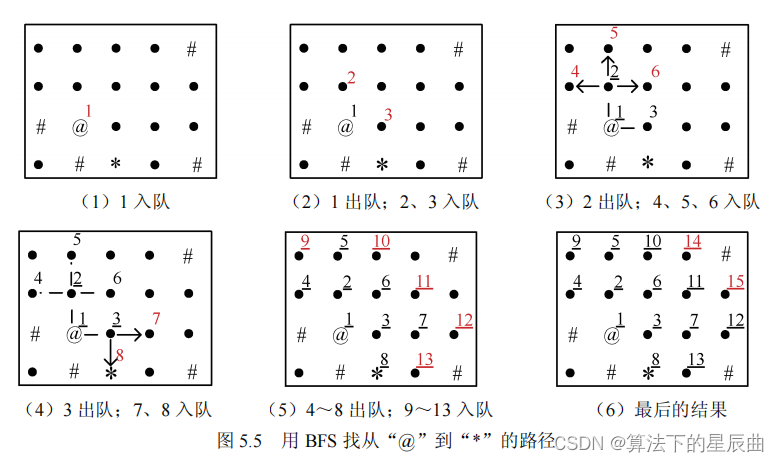
BFS广度优先遍历,就是队首出队,然后与队首相关的入队。上图为模拟过程!
代码实现
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>#define x first
#define y secondusing namespace std;typedef pair<int,int> PII;const int N=210;int n,m;
char g[N][N];
int dist[N][N];int bfs(PII start,PII end)
{//队列queue<PII>q;memset(dist,-1,sizeof dist);//初始化距离为-1;dist[start.x][start.y]=0;q.push(start);int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};while(q.size())//队列不为空{auto t=q.front();//队首q.pop();//枚举四种方向上的情况for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ){int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m) continue; // 出界if (g[x][y] == '#') continue; // 障碍物if (dist[x][y] != -1) continue; // 之前已经遍历过dist[x][y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;if (end == make_pair(x, y)) return dist[x][y];q.push({x, y});}}return -1;
}int main()
{int t;cin>>t;while(t--){cin>>n>>m;for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",g[i]);//读入的是字符串,不需要加&PII start,end;//起点与终点for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(g[i][j]=='S') start={i,j};else if(g[i][j]=='E') end={i,j};}}int distance = bfs(start, end);if (distance == -1) puts("oop!");else printf("%d\n", distance);}return 0;
}
2.AcWing 1096.地牢大师
分析思路
二维上多加了一维,就有六个方向,读入用二维读入。
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>using namespace std;struct Point
{int x,y,z;
};const int N=100;
char g[N][N][N];
int dist[N][N][N];
int l,r,c;
Point q[N * N * N];
int dx[6] = {1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0};
int dy[6] = {0, 0, 1, -1, 0, 0};
int dz[6] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1};int bfs(Point start,Point end)
{int hh=0,tt=0;q[0]=start;memset(dist,-1,sizeof dist);dist[start.x][start.y][start.z]=0;while(hh<=tt){auto t=q[hh++];for(int i=0;i<6;i++){int x=t.x+dx[i],y=t.y+dy[i],z=t.z+dz[i];if(x<0||y<0||z<0||x>=l||y>=r||z>=c) continue;if(g[x][y][z]=='#'||dist[x][y][z]!=-1) continue;dist[x][y][z]=dist[t.x][t.y][t.z]+1;if(g[x][y][z]=='E') return dist[x][y][z];q[++tt]={x,y,z};}}return -1;}int main()
{while(cin>>l>>r>>c,l||r||c){Point start,end;for(int i=0;i<l;i++){for(int j=0;j<r;j++){scanf("%s",g[i][j]);//三维用两维来存for(int k=0;k<c;k++){if(g[i][j][k]=='S') start={i,j,k};else if(g[i][j][k]=='E') end={i,j,k};}}}int distance=bfs(start,end);if(distance==-1) puts("Trapped!");else printf("Escaped in %d minute(s).\n",distance);}return 0;
}用队列的方式:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>using namespace std;struct Point
{int x,y,z;
};const int N=100;
char g[N][N][N];
int dist[N][N][N];
int l,r,c;int dx[6] = {1, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0};
int dy[6] = {0, 0, 1, -1, 0, 0};
int dz[6] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1};int bfs(Point start,Point end)
{queue<Point> q;int hh=0;q.push(start);memset(dist,-1,sizeof dist);dist[start.x][start.y][start.z]=0;while(q.size()){auto t=q.front();for(int i=0;i<6;i++){int x=t.x+dx[i],y=t.y+dy[i],z=t.z+dz[i];if(x<0||y<0||z<0||x>=l||y>=r||z>=c) continue;if(g[x][y][z]=='#'||dist[x][y][z]!=-1) continue;dist[x][y][z]=dist[t.x][t.y][t.z]+1;if(g[x][y][z]=='E') return dist[x][y][z];q.push({x,y,z});}q.pop();}return -1;}int main()
{while(cin>>l>>r>>c,l||r||c){Point start,end;for(int i=0;i<l;i++){for(int j=0;j<r;j++){scanf("%s",g[i][j]);//三维用两维来存for(int k=0;k<c;k++){if(g[i][j][k]=='S') start={i,j,k};else if(g[i][j][k]=='E') end={i,j,k};}}}int distance=bfs(start,end);if(distance==-1) puts("Trapped!");else printf("Escaped in %d minute(s).\n",distance);}return 0;
}