Spring-AOP入门案例
文章目录
- Spring-AOP入门案例
- 简单需求:在接口执行前输出当前系统时间
- Demo原始未添加aop前
- 1 项目包结构
- 2 创建相关文件
- 2.1 pom.xml
- 2.2 创建BookDao类
- 2.3 创建BookDaoImpl实现类
- 2.4 创建MySpringConfig配置类
- 2.5 创建DemoAop主启动类
- 打印结果
- Demo案例添加aop
- 1 pom.xml引入相关的配置包
- 2 把共性的方法抽取出来,定义一个新的类(通知类,切入位置绑定相关的业务方法)
- 3 配置类添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- 4 启动主启动类,未修改update原有方法,已切入共性方法
- 项目中异常问题
- @Repository注解报红,需要引入Spring依赖,或者直接引入springboot依赖
- 方案解决一:
- 方案解决二:
- AOP注解综合概念使用
- Run方法获取class类,反射class类
- 1 使用注解
- 2 读取配置文件:
Spring-AOP入门案例
概念:
AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,又被称为面向切面编程, 对接口进行动态代理,需要引入切面框架Aspect,用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率;
不去动原来的代码,而是基于原来代码产生代理对象,通过代理的方法去包装原来的方法,就完成了对以前方法的增强。换句话说,AOP的底层原理就是动态代理的实现。应用场景:一般应用在需要多个业务流程中都需要相同或类似的业务处理,且与核心业务无关,则特别适合用AOP技术来解决; 包括权限,日志和持久化等等。
通知(Advice)
前置增强、后置增强、环绕增强、异常抛出增强、引介增强等类型。
(1)前置增强:org.springframework.aop.BeforeAdvice代表前置增强,spring只支持方法级的增强,目前可用MethodBeforeAdvice。
(2)后置增强:org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice代表后置增强,在目标方法执行后实施增强。
(3)环绕增强:org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor代表环绕增强,在目标方法执行前后实施增强。
(4)异常抛出增强:org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice,在目标方法执行抛出异常后实施增强。方法名必须为afterThrowing,
如参前三个可选,最后一个是Throwable或其子类。
(5)引介增强:org.springframework.aop.IntroductionInterceptor,表示目标类添加一些新的方法和属性,连接点是类级别,而不是方法级别。
如:
在方法执行之前验证用户是否有效。 在方法执行之后,打印方法的执行耗时。 在方法抛出异常后,记录异常信息发送到mq。
切入点(Pointcut )
用来指定需要将通知使用到哪些方法上; 比如需要用在哪些类的哪些方法上,切入点就是做这个配置的。
也可以把这个表达式理解为一个查询条件,系统会根据这个查询条件查询到我们要进行增强的代码位置。
切面(Aspect)
通知(Advice)和切入点(Pointcut)的组合。切面来定义在哪些地方(Pointcut)执行什么操作(Advice)。
简单地说,就是将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑或责任封装起来,
便于减少系统的重复代码,降低模块间的耦合度,并有利于未来的可操作性和可维护性。
AOP代表的是一个横向的关系,如果说“对象”是一个空心的圆柱体,其中封装的是对象的属性和行为;
那么面向方面编程的方法,就仿佛一把利刃,将这些空心圆柱体剖开,以获得其内部的消息。
而剖开的切面,也就是所谓的“方面”了。然后它又以巧夺天功的妙手将这些剖开的切面复原,不留痕迹。
目标对象(target)
目标对象指将要被增强的对象,即包含主业务逻辑的类对象;我们也称之为委托类。
代理对象(Proxy)
AOP中会通过代理的方式,对目标对象生成一个代理对象,代理对象中会加入需要增强功能,通过代理对象来间接的方式目标对象,起到增强目标对象的效果。
顾问(Advisor)
Advisor 其实它就是 Pointcut 与 Advice 的组合,Advice 是要增强的逻辑,而增强的逻辑要在什么地方执行是通过Pointcut来指定的,所以 Advice 必需与 Pointcut 组合在一起,这就诞生了 Advisor 这个类,spring Aop中提供了一个Advisor接口将Pointcut 与 Advice 的组合起来。Advisor有好几个称呼:顾问、通知器。其中这4个:连接点(JoinPoint)、通知(advise)、切入点(pointcut)、顾问(advisor),在spring中都定义了接口和类来表示这些对象。
连接点(JoinPoint)
就是SpringAOP通过告诉它的切入点的位置找的的具体的要增强的代码的位置,这个代码位置就是连接点。连接点由两个信息确定: 方法(表示程序执行点,即在哪个目标方法) 相对点(表示方位,即目标方法的什么位置,比如调用前,后等)简单来说,连接点就是被拦截到的程序执行点,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点就是被拦截到的方法。
简单需求:在接口执行前输出当前系统时间
开发模式:可以XML 或者 注解进行实现
思路分析:
- 1 导入坐标(pom.xml)
- 2 制作连接方法(Dao与实现类)
- 3 制作共性功能(通知类与通知)
- 4 定义切入点
- 5 绑定切入点与通知关系(切面)

Demo原始未添加aop前
1 项目包结构
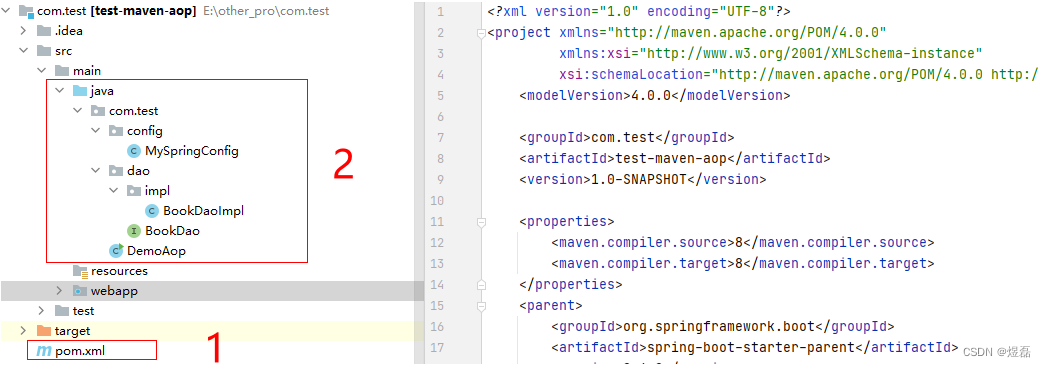
2 创建相关文件
2.1 pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.test</groupId><artifactId>test-maven-aop</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target></properties><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.6.2</version></parent><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency></dependencies></project>
2.2 创建BookDao类
package com.test.dao;public interface BookDao {public void save();public void update();
}
2.3 创建BookDaoImpl实现类
package com.test.dao.impl;import com.test.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao{public void save() {System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("book dao save ...");}public void update() {System.out.println("book dao update ...");}
}
2.4 创建MySpringConfig配置类
package com.test.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.test")
public class MySpringConfig {}
2.5 创建DemoAop主启动类
package com.test;import com.test.config.MySpringConfig;
import com.test.dao.BookDao;
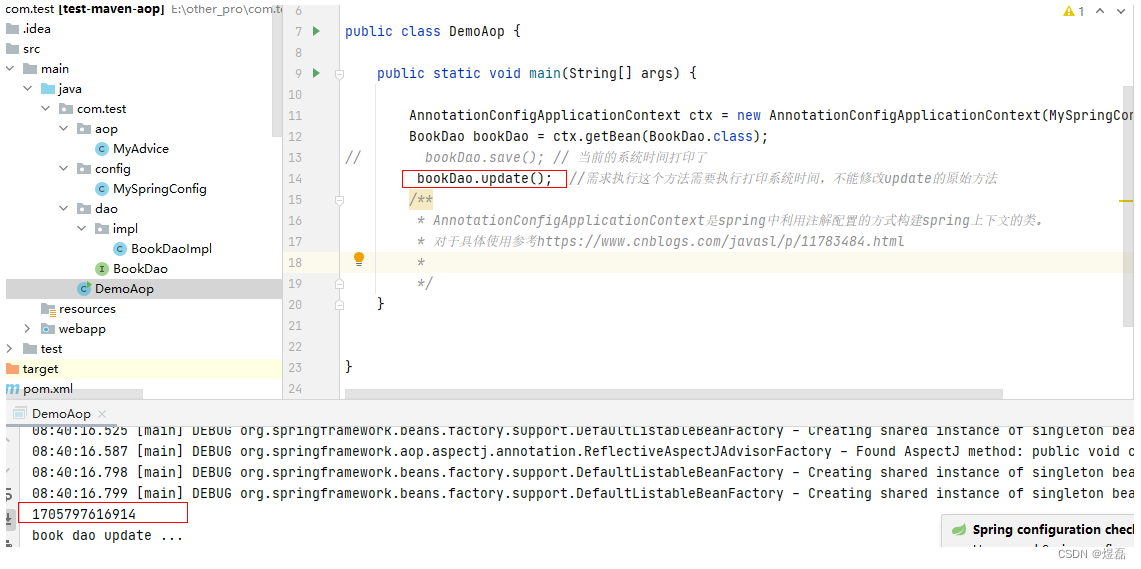
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;public class DemoAop {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MySpringConfig.class);BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);bookDao.save(); // 当前的系统时间打印了// bookDao.update(); 需求执行这个方法需要执行打印系统时间,不能修改update的原始方法/*** AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是spring中利用注解配置的方式构建spring上下文的类。* 对于具体使用参考https://www.cnblogs.com/javasl/p/11783484.html**/}}
打印结果

Demo案例添加aop
1 pom.xml引入相关的配置包
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.9.4</version></dependency></dependencies>
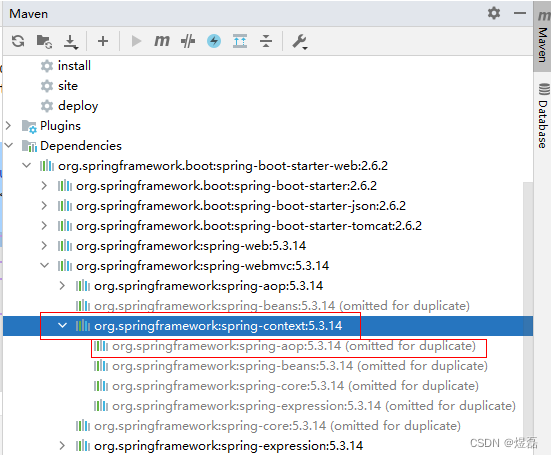
查看包依赖可以看到context包导入后,aop就会导入了
2 把共性的方法抽取出来,定义一个新的类(通知类,切入位置绑定相关的业务方法)
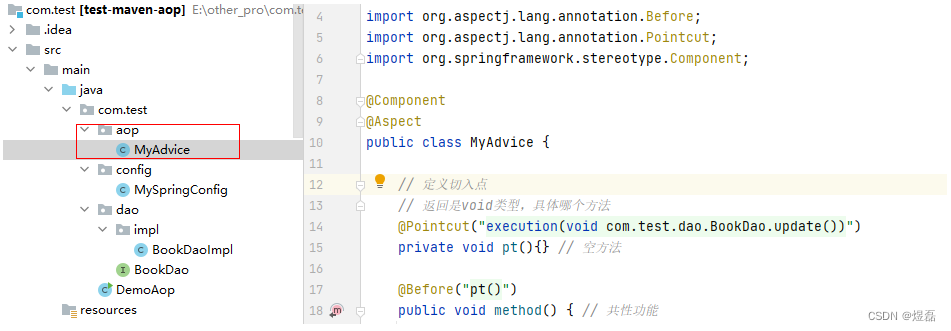
package com.test.aop;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {// 定义切入点// 返回是void类型,具体哪个方法@Pointcut("execution(void com.test.dao.BookDao.update())")private void pt(){} // 空方法@Before("pt()")public void method() { // 共性功能System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());}/*第1定义共性方法,切入的方法method(),还没有@Before注解,第3步加入的第2步 定义切入点Pointcut,当执行到pt(),执行切入点方法"execution(void com.test.dao.BookDao.update())"第3步 绑入切入点的之间关系 --在com.test.dao.BookDao.update()方法什么时候执行method()方法,使用@Before(“”)第4步 需要受到spring的管理,@component。定义bean,加@Aspect告诉spring,当aop处理,生效第5步 配置类中package com.test.config。MySpringConfig 通知这个类,我是注解开发的@EnableAspectJAutoProxy,这个启动了@Aspect,识别相关的Pointcut等注解*/
}
3 配置类添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
package com.test.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.test")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class MySpringConfig {}
4 启动主启动类,未修改update原有方法,已切入共性方法
项目中异常问题
@Repository是属于Spring的注解。它用来标注访问层的类(Dao层),它表示一个仓库,主要用于封装对于数据库的访问。其实现方式与@Component注解相同,只是为了明确类的作用而设立。
即@Repository是@Component注解的一个派生品,与@Service和@Controller都可以理解为@Component注解的扩展。他们的作用都是在类上实例化bean,并把当前类对象的实现类交给spring容器进行管理。
Repository注解修饰哪个类表明这个类具有对数据库CRUD的功能,用在持久层的接口上。
@Repository注解报红,需要引入Spring依赖,或者直接引入springboot依赖
方案解决一:
<properties><maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target><spring.version>5.3.15</spring.version>
</properties>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
方案解决二:
添加Web场景依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency>
</dependencies>
AOP注解综合概念使用
/** * 日志切面类 */
@Aspect //定义切面类
public class LogAnnotationAspect { @SuppressWarnings("unused") //定义切入点,提供一个方法,这个方法的名字就是改切入点的id @Pointcut("execution(* com.abc.service.*.*(..))") private void allMethod(){} //针对指定的切入点表达式选择的切入点应用前置通知 @Before("execution(* com.abc.service.*.*(..))") public void before(JoinPoint call) { String className = call.getTarget().getClass().getName(); String methodName = call.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("【注解-前置通知】:" + className + "类的" + methodName + "方法开始了"); } //访问命名切入点来应用后置通知 @AfterReturning("allMethod()") public void afterReturn() { System.out.println("【注解-后置通知】:方法正常结束了"); } //应用最终通知 @After("allMethod()") public void after(){ System.out.println("【注解-最终通知】:不管方法有没有正常执行完成," + "一定会返回的"); } //应用异常抛出后通知 @AfterThrowing("allMethod()") public void afterThrowing() { System.out.println("【注解-异常抛出后通知】:方法执行时出异常了"); } //应用周围通知 //@Around("allMethod()") public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint call) throws Throwable{ Object result = null; //相当于前置通知 this.before(call);try { result = call.proceed();//相当于后置通知 this.afterReturn(); } catch (Throwable e) { //相当于异常抛出后通知 this.afterThrowing(); throw e; }finally{ //相当于最终通知 this.after(); } return result; }
}
Run方法获取class类,反射class类
1 使用注解
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是spring中利用注解配置的方式构建spring上下文的类。
第一种方式:构造函数传入一个或者多个类。可以是注解类,也可以是普通类,传入的类都会纳入到spring容器中。如下:
第二种方式:构造函数传入一个包名,该包下的类都会创建bean,并且纳入spring容器中
App.java,User.class没有加注解,不会创建bean
第三种方式:构造函数传入一个加了@ComponentScan注解的类,该注解指明了扫描的包和排除掉的类参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/javasl/p/11783484.html
2 读取配置文件:
使用XML创建bean参考文章:`https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/572380275`
