端杂七杂八系列篇四-Java8篇
后端杂七杂八系列篇四-Java8篇
- ① Lombok插件
- ① @RequiredArgsConstructor
- ② @SneakyThrows
- ③ @UtilityClass
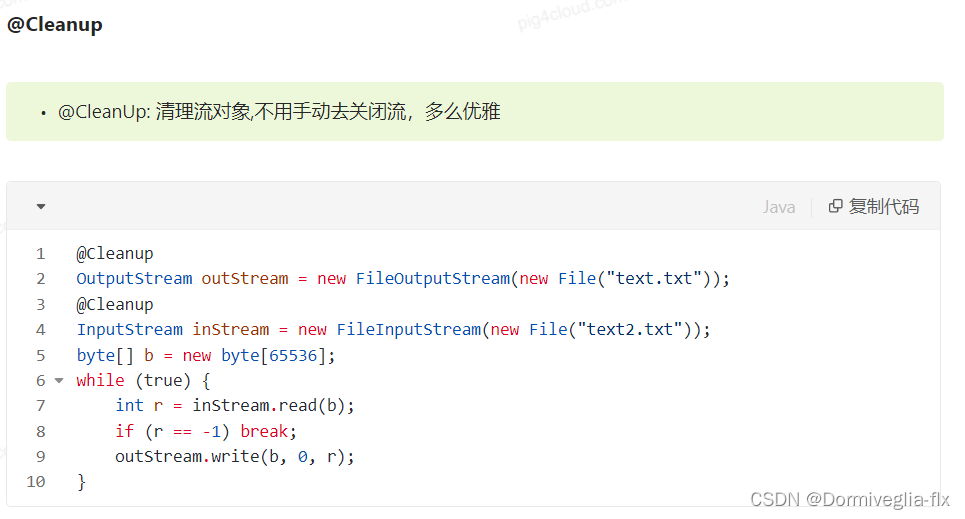
- ④ @Cleanup
- ② Lambda 4个常用的内置函数
- ① Function<T, R> - 接受一个输入参数并返回一个结果
- ② Consumer - 接受一个输入参数,并执行某种操作(无返回值)
- ③ Supplier - 不接受任何参数,但产生一个结果
- ④ Predicate - 接受一个输入参数并返回一个布尔值
- ③ Optional
- ④ 常用Stream流
- stream 中间操作
- stream 终端操作
- Java 8中的Future和CompletableFuture
- Future
- CompletableFuture
① Lombok插件
Lombok是一个可以通过简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 Java 代码的工具。
① @RequiredArgsConstructor

② @SneakyThrows
在 Java 中,异常被分为了
受查异常(checked exception)和非受查异常(unchecked exception)两种。
非受查异常又叫运行时异常,即 RuntimeException。
受查异常,即 Exception。
受查异常是Java给你检查的异常,需要你手动try catch
比如这个,写的时候会报错,IDE会提示我们需要加上try catch
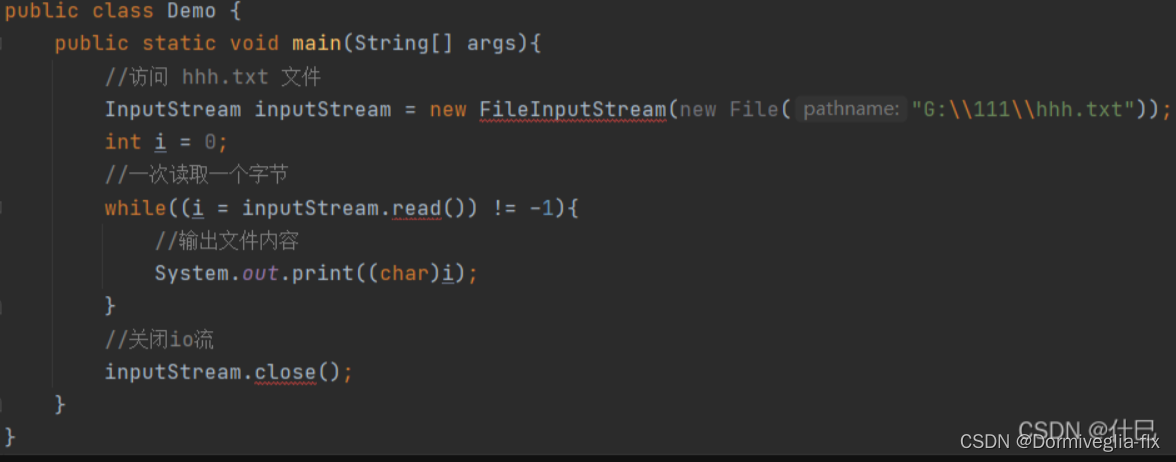
运行时异常是Java 运行时候报出来的异常,一般是我们程序员写错了。
我们的@SneakyThrows就是为了让我们少写try catch 代码, 即在有受查异常的时候,我们加上注解,就不用写try catch了。
代码举例
import lombok.SneakyThrows;public class SneakyThrowsDemo {// 使用注解@SneakyThrowspublic String readFile(String filePath) {File file = new File(filePath);BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {content.append(line).append("\n");}reader.close();return content.toString();}// 不使用注解public String readFileWithout(String filePath) {try{File file = new File(filePath);BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {content.append(line).append("\n");}reader.close();return content.toString();}catch(e){}}public static void main(String[] args) {SneakyThrowsDemo demo = new SneakyThrowsDemo();// 无需捕获FileNotFoundException和IOExceptionSystem.out.println(demo.readFile("example.txt"));}
}
③ @UtilityClass
用于定义工具类的时候,不用定义static的方法了。

举个例子
public class UtilClass {// 静态变量,全局存储public static int globalCount = 0;// 静态方法,可以直接通过类名调用,无需创建对象public static void incrementCount() {globalCount++;}// 其他静态工具方法public static String formatString(String input) {return "Formatted: " + input.toUpperCase();}// 使用示例:public static void main(String[] args) {// 不需要创建UtilClass对象,直接访问静态成员UtilClass.incrementCount();System.out.println(UtilClass.globalCount); // 输出:1String formattedString = UtilClass.formatString("hello world");System.out.println(formattedString); // 输出:Formatted: HELLO WORLD}
}
在Java中,静态工具类中的属性默认情况下是可以一直保留的,除非显式地进行修改或者JVM垃圾回收机制清除了该类的Class对象(这在正常应用中非常罕见)。

使用注解时候的demo
@UtilityClass
public class WxMpContextHolder {private final ThreadLocal<String> THREAD_LOCAL_APPID = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();/*** TTL 设置appId* @param appId*/public void setAppId(String appId) {THREAD_LOCAL_APPID.set(appId);}/*** 获取TTL中的appId* @return*/public String getAppId() {return THREAD_LOCAL_APPID.get();}public void clear() {THREAD_LOCAL_APPID.remove();}}④ @Cleanup
// Java 标准的写法public class CleanupExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);try {OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);try {byte[] b = new byte[10000];while (true) {int r = in.read(b);if (r == -1) break;out.write(b, 0, r);}} finally {if (out != null) {out.close();}}} finally {if (in != null) {in.close();}}}
}// 注解的写法
public class CleanupExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);@Cleanup OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);byte[] b = new byte[10000];while (true) {int r = in.read(b);if (r == -1) break;out.write(b, 0, r);}}
}
② Lambda 4个常用的内置函数
① Function<T, R> - 接受一个输入参数并返回一个结果
public class FunctionDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> names = Arrays.asList("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie");// 使用lambda表达式转换字符串为大写Function<String, String> toUpperCase = s -> s.toUpperCase();names.stream().map(toUpperCase).forEach(System.out::println);}
}
② Consumer - 接受一个输入参数,并执行某种操作(无返回值)
public class ConsumerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);// 使用lambda表达式打印数字Consumer<Integer> printNumber = n -> System.out.println("Number: " + n);numbers.forEach(printNumber);}
}
③ Supplier - 不接受任何参数,但产生一个结果
public class SupplierDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用lambda表达式生成随机数Supplier<Integer> randomIntSupplier = () -> (int) (Math.random() * 100);System.out.println("Random number: " + randomIntSupplier.get());}
}
④ Predicate - 接受一个输入参数并返回一个布尔值
public class PredicateDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> fruits = Arrays.asList("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry", "Durian");// 使用lambda表达式检查字符串长度是否大于5个字符Predicate<String> isLongFruit = fruit -> fruit.length() > 5;fruits.stream().filter(isLongFruit).forEach(System.out::println);}
}
③ Optional




用法例子一
public class Student {private String name;private int age;private Integer score;//省略 construct get set
}public List<Student> initData(){Student s1 = new Student("张三", 19, 80);Student s2 = new Student("李四", 19, 50);Student s3 = new Student("王五", 23, null);Student s4 = new Student("赵六", 16, 90);Student s5 = new Student("钱七", 18, 99);Student s6 = new Student("孙八", 20, 40);Student s7 = new Student("吴九", 21, 88);return Arrays.asList(s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7);
}@Test
public void beforeJava8() {List<Student> studentList = initData();for (Student student : studentList) {if (student != null) {if (student.getAge() >= 18) {Integer score = student.getScore();if (score != null && score > 80) {System.out.println("入选:" + student.getName());}}}}
}@Test
public void useJava8() {List<Student> studentList = initData();for (Student student : studentList) {Optional<Student> studentOptional = Optional.of(student);Integer score = studentOptional.filter(s -> s.getAge() >= 18).map(Student::getScore).orElse(0);if (score > 80) {System.out.println("入选:" + student.getName());}}
}
用法例子二
public String test0(AlarmAllParmeter alarmAllParmeter) {String errorResult = "";if (null != alarmAllParmeter) {Integer alarmId = alarmAllParmeter.getAlarmEventInputId();if (null != alarmId) {AlarmEventInput alarmEventInput = alarmEventInputService.get(alarmId);if (null != alarmEventInput) {String alarmName = alarmEventInput.getAlarmName();int alarmType = alarmEventInput.getAlarmType();return String.valueOf(alarmType) + "-" + alarmName;} else {return errorResult;}} else {return errorResult;}} else {return errorResult;}}// 改进方案一public String test1(AlarmAllParmeter alarmAllParmeter){String errorResult = "";Optional<AlarmAllParmeter> op = Optional.ofNullable(alarmAllParmeter);if(op.isPresent()){Integer alarmId = op.get().getAlarmEventInputId();Optional<Integer> op1 = Optional.ofNullable(alarmId);if(op1.isPresent()){AlarmEventInput alarmEventInput = alarmEventInputService.get(op1.get());Optional<AlarmEventInput> op2 = Optional.ofNullable(alarmEventInput);if (op2.isPresent()) {String alarmName = alarmEventInput.getAlarmName();int alarmType = alarmEventInput.getAlarmType();return String.valueOf(alarmType) + "-" + alarmName;} else {return errorResult;}}else {return errorResult;}}else {return errorResult;}}// 改进方案二
public String test2(AlarmAllParmeter alarmAllParmeter){return Optional.ofNullable(alarmAllParmeter).map(a -> a.getAlarmEventInputId()).map(a -> alarmEventInputService.get(a)).map(a -> String.valueOf(a.getAlarmType())+"-"+a.getAlarmName()).orElse("");}
④ 常用Stream流


stream 中间操作
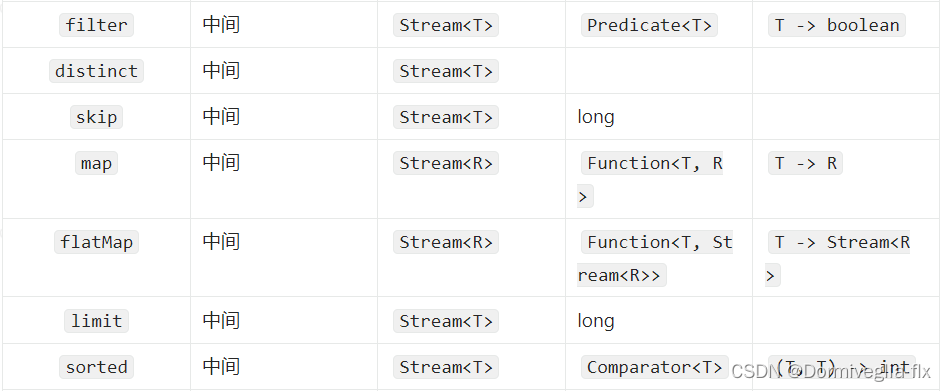
// filter
List<Person> result = list.stream().filter(Person::isStudent).collect(toList());// distinct
List<Person> result = list.stream().distinct().collect(toList());// limit
List<Person> result = list.stream().limit(3).collect(toList());// skip
List<Person> result = list.stream().skip(3).collect(toList());// map
List<String> result = list.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(toList());
stream 终端操作

// anyMatch
boolean result = list.stream().anyMatch(Person::isStudent);// allMatch
boolean result = list.stream().allMatch(Person::isStudent);// noneMatch
boolean result = list.stream().noneMatch(Person::isStudent);// findAny
Optional<Person> person = list.stream().findAny();// findFirst
Optional<Person> person = list.stream().findFirst();
Java 8中的Future和CompletableFuture
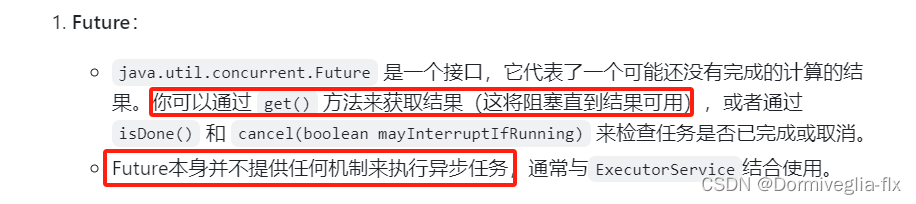

Future
用法demo
public class FutureExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 创建一个线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();// 提交一个Callable任务到线程池,返回一个Future对象Future<String> future = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟耗时操作return "Hello from Future!";}});// 主线程可以继续执行其他任务,不被阻塞System.out.println("Main thread is doing other tasks...");// 当需要获取结果时,调用Future的get方法,该方法会阻塞直到结果准备好String result = future.get();System.out.println(result);// 关闭线程池executor.shutdown();}
}
CompletableFuture
用法demo
public class CompletableFutureExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 创建一个CompletableFuture对象并提供一个异步计算的任务CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟耗时操作} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}return "Hello from CompletableFuture!";});// 使用thenApply方法进行链式处理,将上一步的结果转换为新的结果CompletableFuture<Integer> lengthFuture = future.thenApply(result -> result.length());// 使用thenAccept方法处理完成后的结果,不返回任何值lengthFuture.thenAccept(length -> System.out.println("Length: " + length));// 等待所有任务完成CompletableFuture.allOf(future, lengthFuture).join();// 或者直接获取结果(这会阻塞直到结果准备好)// int length = lengthFuture.get();// System.out.println("Length: " + length);}
}
