微服务实战系列之API加密
前言
随着一阵阵凛冽寒风的呼啸,新的年轮不知不觉滚滚而来。故事随着2023的远去,尘封于案底;希望迎着新年,绽放于枝头。在2024新岁启航,扬帆破浪之时,让烦恼抛洒于九霄,让生机蓬勃于朝朝暮暮。
2024,博主祝福各位盆友,书写新的人生,获得新的希望!

新年开篇第一博,希望带给各位盆友新的收获。“踏破铁鞋无觅处,博主文章可驻足”,此刻的我,不禁沾沾自喜…
废话少叙,言归正传。今日,我们开始新的旅程,微服务实战系列继续乘势而上,博主该谈谈API安全的“那些事儿”了。
一、API
什么是API?请先了解来自百度百科的定义:
应用程序编程接口(Application Programming Interface,简称:API),是一些预先定义的函数,目的是提供应用程序与开发人员基于某软件或硬件得以访问一组例程的能力,而又无需访问源码,或理解内部工作机制的细节。——百度百科
通俗讲,就是一个面向开发者使用的接口或程序。既然是API,那么一定是具备某些能力,所谓“麻雀虽小五脏俱全”。
但凡是API,必定涉及数据安全问题。因为API本质是完成“以数易数”的过程。这个过程中一般会遇到诸如以下安全问题:
1、数据泄密
我们说数据有多“敏感”,责任有多严重,这力不再赘述。
2、数据劫持
API请求过程中,被黑客劫持数据报文后,后果不堪设想。
3、恶意调用
恶意调用其实是饱和攻击的一种,直至系统服务瘫痪,会造成严重的经济损失。
二、API安全
针对以上API安全风险,我们显然已具备针对性的防范措施和能力。
具体有:
- 采用HTTPS协议传输
- 数据加密
- 数据签名
- 限流降级
…
以上措施,均可有效提高API的风险壁垒,“防火于未燃”。而今天博主重点讲一讲其中的第2点,即数据加密是如何完成的。其他内容可回看博主历史文章,均有涉猎。
三、API数据加密
首先,API数据加密,是针对传输过程中的请求报文和返回报文而言的。API的请求过程,其实是一次两端(C/S)通信的过程,所以涉及数据的传输安全。
如何保障传输安全,加密是一个不错的选择。实现的核心逻辑,可参考下图:
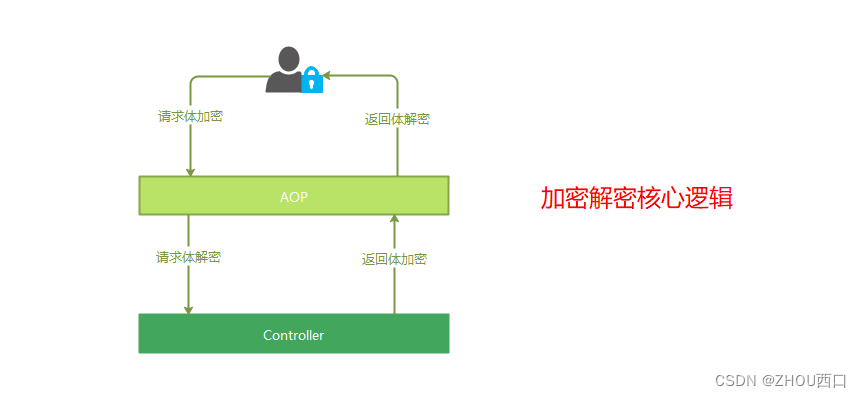
基于SpringBoot的开发框架,我们通常选择AOP,以注解的方式,完成以上逻辑实现。接下来,博主提供相关实现代码,以供参考。
1、引入依赖
本文加密机制,使用了jasypt-spring-boot-starter,务必添加以下依赖:
<dependency><groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId><artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、定义注解
首先需要准备2个注解,分别如下:
| 注解名称 | 注解简介 |
|---|---|
| Encrypt | 用于请求体的加密注解 |
| Decrypt | 用于返回体的解密注解 |
2.1 Encrypt 代码参考:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;//加密
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Encrypt {
}
2.2 Decrypt 代码参考:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;//解密
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER})
public @interface Decrypt {
}
3、定义AOP
3.1 返回体加密Advice(EncryptResponse)
一句话总结:通过将返回体(response)转换为String,实现数据加密。
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;/*** @description:加密* @date 2024/01/06 14:02*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class EncryptResponse implements ResponseBodyAdvice<Object> {public EncryptResponse() {}public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {return returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(Encrypt.class);}@Overridepublic Object beforeBodyWrite(Object res, MethodParameter returnType,MediaType selectedContentType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> selectedConverterType,ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {try {String content = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(JSONUtil.parseObj(res, false));//加密算法,自选,可以是AES,可以是RSA...String encryptResBody = AesEncryptUtils.encrypt(content, Constants.AESKEY);return encryptResBody;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return res; }
}3.2 请求体解密Advice(DecryptRequest)
一句话总结:通过将请求体(request)转换为字节流,实现数据解密。
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestBodyAdviceAdapter;/*** @description:解密* @date 2024/01/06 14:35*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class DecryptRequest extends RequestBodyAdviceAdapter {public DecryptRequest() {}public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {return methodParameter.hasMethodAnnotation(Decrypt.class) || methodParameter.hasParameterAnnotation(Decrypt.class);}public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(final HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException {byte[] body = new byte[inputMessage.getBody().available()];inputMessage.getBody().read(body);try {//解密算法,自选,可以是AES,可以是RSA...byte[] decrypt = AesEncryptUtils.decrypt(new String(body,Constants.UTF8),Constants.AESKEY).getBytes();final ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(decrypt);return new HttpInputMessage() {public InputStream getBody() throws IOException {return bais;}public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {return inputMessage.getHeaders();}};} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return super.beforeBodyRead(inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);}}
}4、使用注解
完成以上注解实现, 即可满足API的加密需求了。
如何使用?那不就简单了…直接在Controller的接口中使用注解即可,可参考:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;/*** @description: API加密* @date 2024/01/06 15:58*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class TestController
{@Encrypt@Decrypt@PostMapping("/getData")public Object getData(@RequestBody String input){// TODO}
}四、AES算法
本文使用的加密算法是基于AES完成,博主分享大家(已解决已知问题,比如长度不足128,支持分段),供参考:
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;/*** AES加解密*/
public class AesEncryptUtils {private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AesEncryptUtils.class);private static final String ALGORITHMSTR = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding";private static final String KEY = "1234567890abcdef";//可支持128位长度private static final String AES = "AES";/*** 解密算法*/public static String decrypt(String decryptStr, String decryptKey) {try {KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(AES);SecureRandom secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");secureRandom.setSeed(decryptKey.getBytes());kgen.init(128, secureRandom);SecretKey secretKey = kgen.generateKey();Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHMSTR);cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), AES));//采用base64算法进行转码,避免出现中文乱码byte[] encryptBytes = Base64.decodeBase64(decryptStr);byte[] decryptBytes = cipher.doFinal(encryptBytes);return new String(decryptBytes);}catch (Exception e){log.error("decryptNew({} , {})解密异常", decryptStr, decryptKey, e);}return null;}/*** 加密算法*/public static String encrypt(String encryptStr, String encryptKey) {try {KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(AES);SecureRandom secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");secureRandom.setSeed(encryptKey.getBytes());kgen.init(128,secureRandom);SecretKey secretKey = kgen.generateKey();Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHMSTR);cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), AES));byte[] b = cipher.doFinal(encryptStr.getBytes("utf-8"));//采用base64算法进行转码,避免出现中文乱码return Base64.encodeBase64String(b);}catch (Exception e){log.error("encryptNew({} , {})加密异常", encryptStr, encryptKey, e);}return null;}public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{String content = "今天是2024年1月6日";String encrypt1 = encrypt(content, KEY);System.out.println("加密后:" + encrypt1);String decrypt1 = decrypt(encrypt1, KEY);System.out.println("解密后:" + decrypt1);}
}结语
本文通过对API安全问题进行粗浅探讨,并从常用的数据加密措施入手,提供相关操作规范和指导,希望各位盆友有所收获。如需进一步了解,可留言,欢迎大家订阅与指正!
2024首篇博文,正式发布喽!!!
历史回顾
- 微服务实战系列之Dubbo(下)
- 微服务实战系列之Dubbo(上)
- 微服务实战系列之ZooKeeper(实践篇)
- 微服务实战系列之ZooKeeper(下)
- 微服务实战系列之ZooKeeper(中)
- 微服务实战系列之ZooKeeper(上)
- 微服务实战系列之MQ
- 微服务实战系列之通信
- 微服务实战系列之J2Cache
- 微服务实战系列之Cache(技巧篇)
- 微服务实战系列之MemCache
- 微服务实战系列之EhCache
- 微服务实战系列之Redis
- 微服务实战系列之Cache
- 微服务实战系列之Nginx(技巧篇)
- 微服务实战系列之Nginx
- 微服务实战系列之Feign
- 微服务实战系列之Sentinel
- 微服务实战系列之Token
- 微服务实战系列之Nacos
- 微服务实战系列之Gateway
- 微服务实战系列之加密RSA
- 微服务实战系列之签名Sign

