Sequence(矩阵连乘+数论)
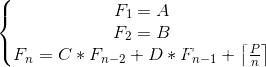
求Fn mod 1e9+7
Input
第一行是一个t代表有t组数据 接下来有t行每行有6个整数A,B,C,D,P,n 1<=t<=10 0<=A,B,C,D<=1e9 1<=p,n<=1e9
Output
输出一个答案Fn对1e9+7取余
Sample Input
2 1 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 1 10 4
Sample Output
9 10
思路:
p/n上取整,一直会随着n的变化而变化,所以我们可以分一段一段的计算;
p/n上取整=(p+n-1)/n=(p-1)/n+1;
有个数学小知识:求∑(1,n)⌊k/i⌋∗i-CSDN博客
当我们知道一段区间的下界i,我们可以利用k/(k/i),求出其上界;
当我们知道一段区间的下界时,可以计算出它的上界,快速幂连乘即可。
代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define per(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define ber(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
const int N = 1e5;
const long long mod = 1e9+7;
const double eps = 1e-2;
typedef struct data
{
LL m[3][3];
}J;
J Q,E;
LL a, b, c, d, p, n;
J now, e,ans;
LL f[3],tmp[3];
void into()
{
Q= { d,c,1,
1,0,0,
0,0,1 };
E = { 1,0,0,
0,1,0,
0,0,1 };
}
J quickfu(J a, J b)
{
J c;
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= 2; j++)
{
c.m[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; k++)
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j] + a.m[i][k] * b.m[k][j] % mod) % mod;
c.m[i][j] = (c.m[i][j] % mod + mod)%mod;
}
return c;
}
J quick(J a, LL b)
{
J ans = e;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
ans = quickfu(ans , a);
b >>= 1;
a = quickfu(a, a);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> p >> n;
into();
now = Q;
e = E;
if (n == 1)
{
cout << a % mod << endl;
continue;
}
if (n == 2)
{
cout << b % mod << endl;
continue;
}
p -= 1;
f[0] = b, f[1] = a;
for (LL i = 3, j = 1; i <= n; i = j + 1)
{
f[2] = p / i + 1;
LL x =p / i;
if (x == 0)
j = n;
else
j = min(n, p / x);
ans = quick(Q, j - i+1);
for (int l = 0; l <= 2; l++)
{
tmp[l] = 0;
for (int w = 0; w <= 2; w++)
tmp[l] = (tmp[l] + ans.m[l][w] * f[w]) % mod;
}
for (int l = 0; l <= 2; l++)
f[l] = tmp[l];
}
cout <<f[0]<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
