Java中的7大设计原则
在面向对象的设计过程中,首先需要考虑的是如何同时提高一个软件系统的可维护性和可复用性。这时,遵从面向对象的设计原则,可以在进行设计方案时减少错误设计的产生,从不同的角度提升一个软件结构的设计水平。
1、单一职责
一个类尽可能只干一件事情。普通会员、vip会员、黄金会员三个类,各干自己的事。
优点:低耦合、高内聚。
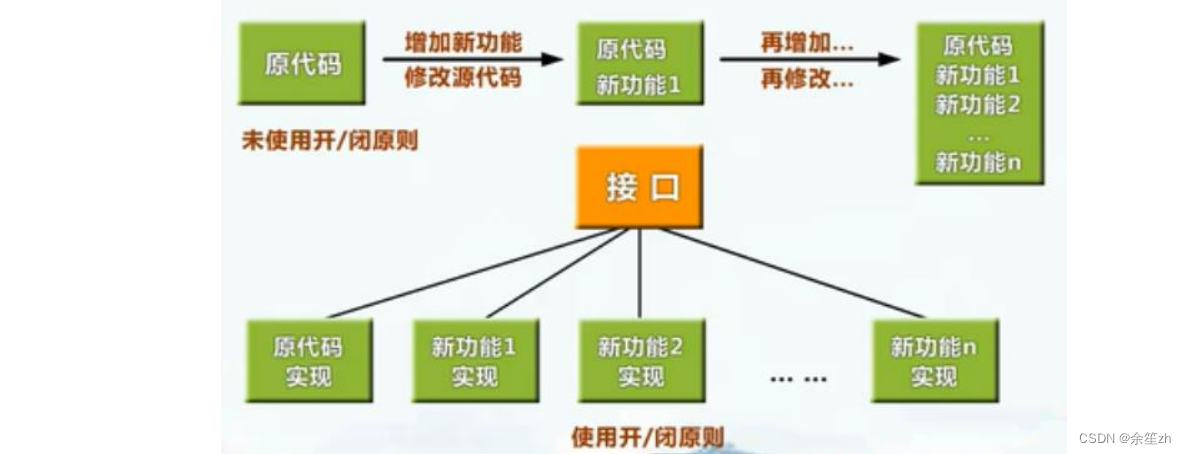
2、开闭原则
对扩展开放,对修改关闭。(继承或多态)
不建议对原来的代码进行修改,可以扩展一个新的类,来实现功能。
对程序进行抽象化设计,设计出抽象类/接口,根据不同的功能来扩展子类。
class CarDemo{public static void main(String[] args) {new CarFactory().carfactory(new Aodi());new CarFactory().carfactory(new DaZhong());}
}class CarFactory{void carfactory(Car car){car.createCar();}
}abstract class Car{public abstract void createCar();
}class Aodi extends Car{@Overridepublic void createCar() {System.out.println("造奥迪汽车");}
}class DaZhong extends Car{@Overridepublic void createCar() {System.out.println("造大众汽车");}
}3、里氏替换原则
使用父类的地方,都可以替换成子类,程序不会产生任何错误和异常。
子类继承父类后,子类对父类方法进行重写时,需要注意:本来是要用父类中的方法,但是 子类重新修改了功能,可能会导致结果不正确。尽量不要重写父类的方法,可以新增扩展其他的功能。
package com.ffyc.javapro.ooptenet.tenet3;
public class CalculatorDemo{public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(new SuperCalculator().sum(5,5,5));}
}
//计算器
class Calculator {//加法public int add(int a,int b){return a+b;}//减法public int sub(int a,int b){return a-b;}
}
//超级计算器子类
class SuperCalculator extends Calculator{//重写了父类加法@Overridepublic int add(int a, int b) {return a+b+5;}//求和方法 子类新增的功能public int sum(int a,int b,int c){//调用add(),但是子类重写了父类方法,此处调用的子类方法发生了变化int result = this.add(a,b);return result+c;}
}4、依赖倒置
如果有多个同类型时,需要抽取抽象层(抽象类、接口)。上层定义为抽象或接口,底层实现抽象或接口,进行扩展功能。

//反例
public class WorkerDemo{public static void main(String[] args) {new Worker().getMessage(new DingDing());new Worker().getMessage(new WeChat());}
}class Worker {public void getMessage(DingDing ding){System.out.println(ding.sendMessage());}public void getMessage(WeChat weChat){System.out.println(weChat.sendMessage());}
}class DingDing{public String sendMessage(){return "钉钉消息";}
}class WeChat{public String sendMessage(){return "微信消息";}
}//正例
public class WorkerDemo{public static void main(String[] args) {new Worker().getMessage(new WeChat());}
}class Worker {public void getMessage(Message message){System.out.println(message.sendMessage());}
}interface Message{public String sendMessage();
}class WeChat implements Message{@Overridepublic String sendMessage() {return "微信消息";}
}
class DingDing implements Message{@Overridepublic String sendMessage() {return "钉钉消息";}
}5、接口隔离
接口功能设计时,尽量减少一个接口中有过多的功能(方法),可以细分为多个接口。不要把所有的功能定义到同一个接口中,不然要实现接口中的所有方法。
6、迪米特原则
也叫最少了解原则,在一个类中,尽量不要直接使用与此类无关的类;只与最好的朋友交谈,不与默认人说话。
反例:
public class Demeter {public static void main(String[] args) {new SchoolManger().printAllEmployee(new CollegeManger());}
}
//学校员工类
class SchoolEmployee{private String id;public void setId(String id){this.id = id;}public String getId(){return id;}
}
//学院员工类
class CollegeEmployee{private String id;public void setId(String id){this.id = id;}public String getId(){return id;}
}//学院员工管理管理类
class CollegeManger{//生成学员所有的员工public List<CollegeEmployee> getCollegeEmployee(){ArrayList<CollegeEmployee> collegeEmployeeArrayList = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {CollegeEmployee collegeEmployee = new CollegeEmployee();collegeEmployee.setId("学院员工的id="+i); //添加学院员工collegeEmployeeArrayList.add(collegeEmployee);}return collegeEmployeeArrayList;}}
//学校员工管理类
class SchoolManger {//生成学校的员工public List<SchoolEmployee> getSchoolEmployee() {ArrayList<SchoolEmployee> employeeArrayList = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {SchoolEmployee employee = new SchoolEmployee();employee.setId("学校的员工id=" + i);employeeArrayList.add(employee);}return employeeArrayList;}//输出学校员工和学院员工信息public void printAllEmployee(CollegeManger collegeManger) {//获取到学校员工List<SchoolEmployee> employeeArrayList = this.getSchoolEmployee();System.out.println("--------学校员工--------");for (SchoolEmployee employee1 : employeeArrayList) {System.out.println(employee1.getId());}System.out.println("--------学院员工--------");List<CollegeEmployee> collegeEmployees = collegeManger.getCollegeEmployee();//SchoolManger中出现CollegeEmployee,此类与SchoolManger并非直接朋友,不合理for (CollegeEmployee collegeEmployee : collegeEmployees) {System.out.println(collegeEmployee.getId());}}
}正例:
public class Demeter {public static void main(String[] args) {new SchoolManger().printAllEmployee(new CollegeManger());}
}
//学校员工类
class SchoolEmployee{private String id;public void setId(String id){this.id = id;}public String getId(){return id;}
}
//学院员工类
class CollegeEmployee{private String id;public void setId(String id){this.id = id;}public String getId(){return id;}
}//学院员工管理管理类
class CollegeManger{//生成学院所有的员工public List<CollegeEmployee> getCollegeEmployee(){ArrayList<CollegeEmployee> collegeEmployeeArrayList = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {CollegeEmployee collegeEmployee = new CollegeEmployee();collegeEmployee.setId("学院员工的id="+i); //添加学院员工collegeEmployeeArrayList.add(collegeEmployee);}return collegeEmployeeArrayList;}public void printCollegeEmployee(){List<CollegeEmployee> collegeEmployee = getCollegeEmployee();for (CollegeEmployee employee : collegeEmployee) {System.out.println("学员员工id="+employee.getId());}}
}
//学校员工管理类
class SchoolManger {//生成学校的员工public List<SchoolEmployee> getSchoolEmployee() {ArrayList<SchoolEmployee> employeeArrayList = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {SchoolEmployee employee = new SchoolEmployee();employee.setId("学校的员工id=" + i);employeeArrayList.add(employee);}return employeeArrayList;}//输出学校员工和学院员工信息public void printAllEmployee(CollegeManger collegeManger) {//获取到学校员工List<SchoolEmployee> employeeArrayList = this.getSchoolEmployee();System.out.println("--------学校员工--------");for (SchoolEmployee employee1 : employeeArrayList) {System.out.println(employee1.getId());}//CollegeManger与SchoolManger是直接朋友,相互之间访问System.out.println("--------学院员工-----------");collegeManger.printCollegeEmployee();}
}7、组合/聚合复用原则
如果想在一个类中达到复用别的类中的方法,优先使用关联/依赖,其次才考虑继承。
案例:现在假设有一个A类,里面有两个方法,B类想要复用这两个方法,请问有几种方案?
public class A {public void method01(){}public void method02(){}
}class B{A a;//关联关系。A作为B类的成员变量,尽量避免使用继承public void setA(A a){this.a = a;}public void use(){a.method01();a.method02();}
}class Test{public static void main(String[] args) {A a = new A();B b = new B();b.setA(a);b.use();}
}public class A {public void method01(){}public void method02(){}
}class B{public void use(A a){//将A作为参数使用,依赖关系a.method01();a.method02();}
}class Test{public static void main(String[] args) {A a = new A();B b = new B();b.use(a);}
}