Java中的反射使用
1、获取Class对象的三种方式
1、对象调用Object类的getClass()方法(对象.getClass())
2、调用类的class属性(类名.class)
3、调用Class类的静态方法(Class.forName(“包名.类名”))常用
Student类
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {
}
测试类
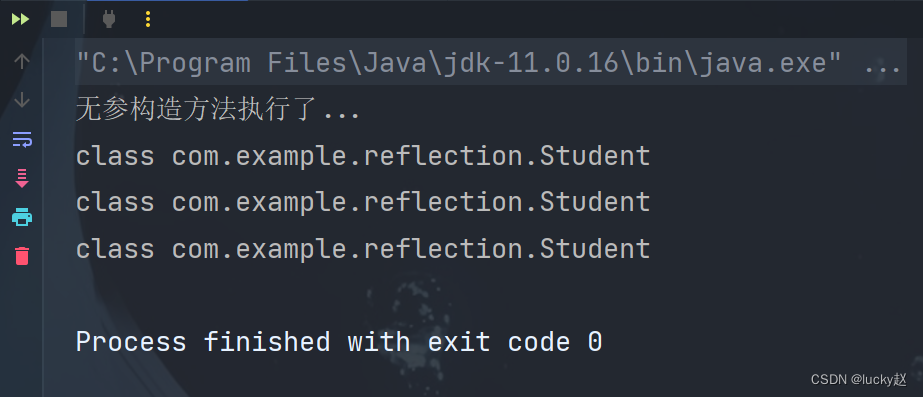
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {//对象调用父类Object的getClass()方法Student student = new Student();Class<? extends Student> clazz = student.getClass();System.out.println(clazz);//调用类的class属性Class<Student> stu = Student.class;System.out.println(stu);//调用Class类的静态方法forName()向方法中传一个字符串(包名.类名)try {Class<?> c = Class.forName("com.example.reflection.Student");System.out.println(c);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
运行结果:
2、获取构造方法
1、getConstructors() 获取被public修饰构造方法
2、getDeclaredConstructors() 获取所有构造方法(包括:private、protected、默认、public)
3、getConstructor(参数类型…) 获取单个被public修饰构造方法 (参数类型为可变参数,有几个参数就写几个,值为null时,表示获取无参构造)
4、getDeclaredConstructor(参数类型…) 根据参数类型获取单个构造方法(包括:private、protected、默认、public),参数类型同getConstructor一样
5、setAccessible(true) Constructor对象调用该方法 暴力访问该方法,忽略掉所有访问修饰符
Student类
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {/*** 默认构造方法** @param str 形参*/Student(String str) {System.out.println("默认构造方法执行了...");}/*** 无参构造方法*/public Student() {System.out.println("无参构造方法执行了...");}/*** 一个参数的构造方法** @param age 年龄*/public Student(int age) {System.out.println("年龄:" + age);}/*** 多参构造方法** @param name 姓名* @param age 年龄* @param password 密码*/public Student(String name, int age, String password) {System.out.println("姓名:" + name + "年龄:" + age + "密码:" + password);}protected Student(boolean n) {System.out.println("受保护的构造方法执行了..." + n);}/*** 私有构造方法** @param sex 性别*/private Student(char sex) {System.out.println("私有构造方法执行了..." + sex);}
}测试类
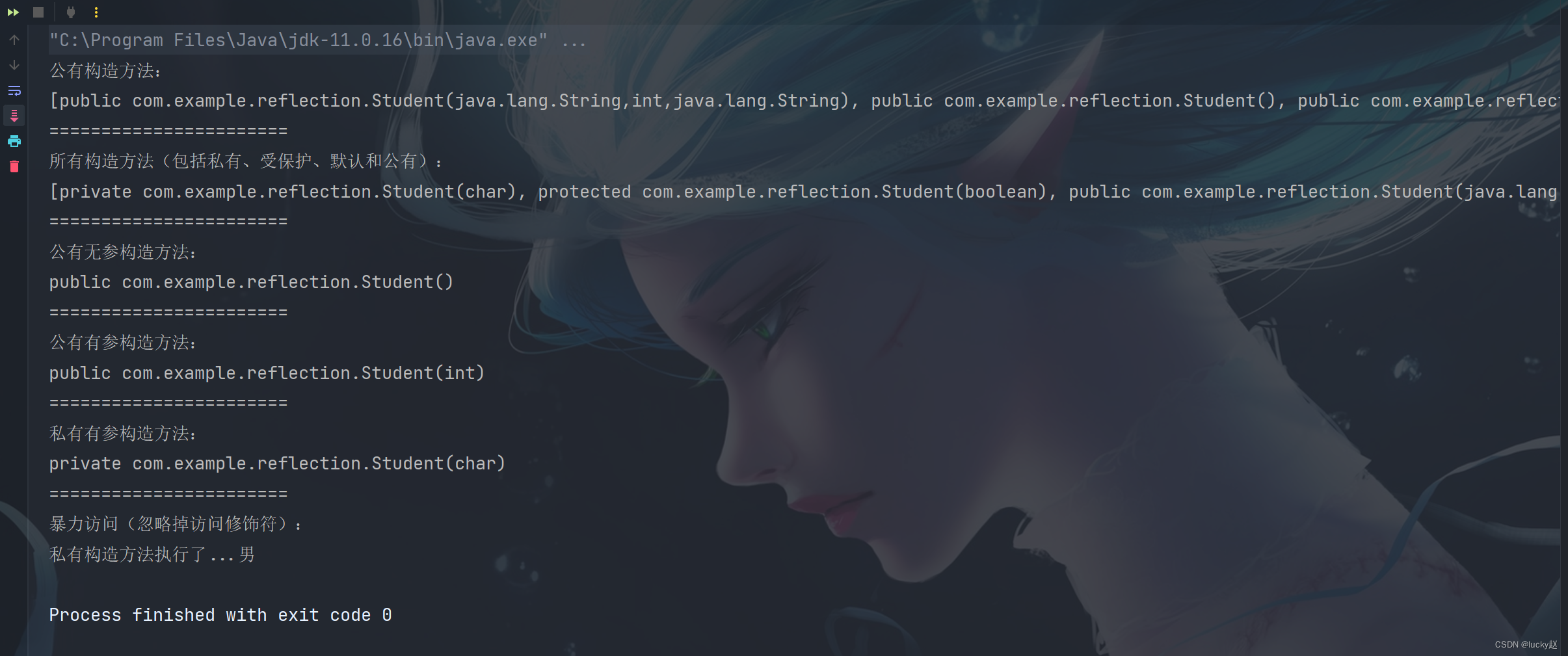
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//加载Class对象Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.reflection.Student");//获取所有公有构造方法Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();System.out.println("公有构造方法:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(constructors));System.out.println("=======================");constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();System.out.println("所有构造方法(包括私有、受保护、默认和公有):");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(constructors));System.out.println("=======================");System.out.println("公有无参构造方法:");Constructor<?> con = clazz.getConstructor(null);System.out.println(con);System.out.println("=======================");con = clazz.getConstructor(int.class);System.out.println("公有有参构造方法:");System.out.println(con);System.out.println("=======================");con = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(char.class);System.out.println("私有有参构造方法:");System.out.println(con);System.out.println("=======================");System.out.println("暴力访问(忽略掉访问修饰符):");Constructor<?> c = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(char.class);c.setAccessible(true);c.newInstance('男');} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
运行结果:
3、获取成员变量并调用
1、getFields() 获取所有被public修饰字段
2、getDeclaredFields() 获取所有字段(包括:private、protected、默认、public)
3、getField(字段名) 根据字段名获取被public修饰字段
4、getDeclaredField(字段名) 根据字段名获取字段(包括:private、protected、默认、public所修饰的字段)
Student
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {public int height;double weight;private String name;private int age;private char sex;private String password;/*** 无参构造方法*/public Student() {System.out.println("无参构造方法执行了...");}
}
测试类
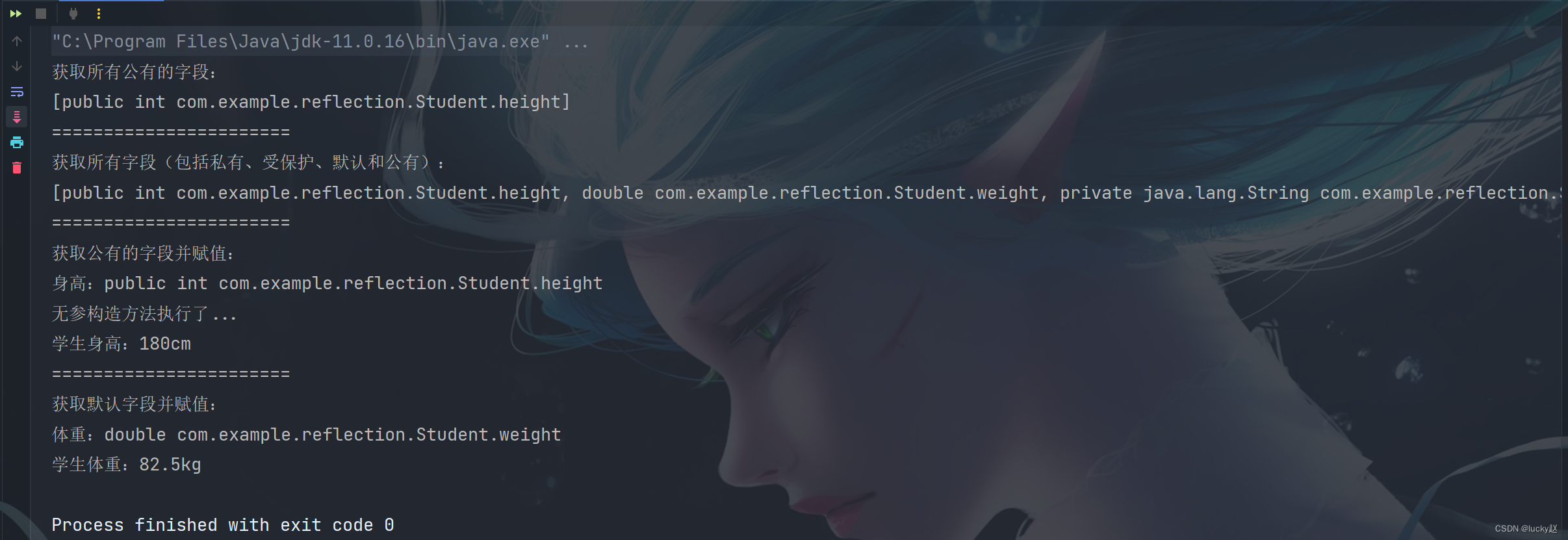
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.reflection.Student");Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();System.out.println("获取所有公有的字段:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fields));System.out.println("=======================");fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();System.out.println("获取所有字段(包括私有、受保护、默认和公有):");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fields));System.out.println("=======================");System.out.println("获取公有的字段并赋值:");Field height = clazz.getField("height");System.out.println("身高:" + height);Object obj = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();height.set(obj, 180);Student stu = (Student) obj;System.out.println("学生身高:" + stu.height + "cm");System.out.println("=======================");System.out.println("获取默认字段并赋值:");Field weight = clazz.getDeclaredField("weight");System.out.println("体重:" + weight);weight.set(obj, 82.5);System.out.println("学生体重:" + stu.weight + "kg");} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
运行结果:
4、获取成员方法并调用
1、getMethods() 获取所有被public所修饰的成员方法
2、getDeclared() 获取所有成员方法(包括:private、protected、默认、public)
3、getMethod(方法名称,方法参数…) 根据方法名称、参数获取被public修饰的方法
4、getDeclaredMethod(方法名称,方法参数…) 根据方法名称、参数获取默认、被protected修饰的方法
5、Method中的invoke(对象,参数值…)可以执行方法,若要执行被private修饰的方法,需要设置Method对象.setAccessible(true)解除私有限定
Student
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {/*** 无参构造方法*/public Student() {System.out.println("无参构造方法执行了...");}public void test1(String str) {System.out.println("调用了公有的、String参数的方法" + str + "...");}protected void test2() {System.out.println("调用了受保护的、无参的方法test2...");}void test3() {System.out.println("调用了默认的、无参的方法test3...");}private static String test4(int age) {System.out.println("调用了私有的、有参、有返回值的方法test4..." + age);return "test4的返回值";}
}
测试类
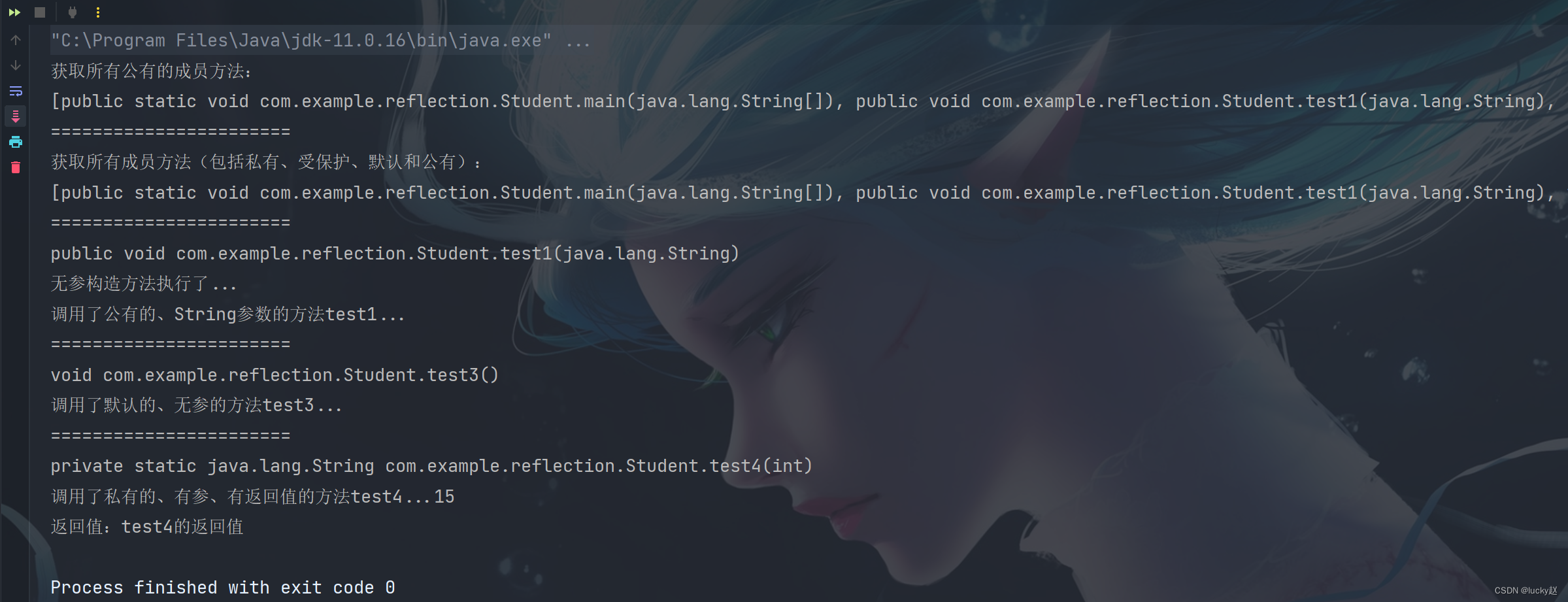
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.reflection.Student");Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();System.out.println("获取所有公有的成员方法:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(methods));System.out.println("=======================");methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();System.out.println("获取所有成员方法(包括私有、受保护、默认和公有):");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(methods));System.out.println("=======================");Method test1 = clazz.getMethod("test1", String.class);System.out.println(test1);Object obj = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();test1.invoke(obj, "test1");System.out.println("=======================");Method test3 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test3");System.out.println(test3);test3.invoke(obj);System.out.println("=======================");Method test4 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test4", int.class);System.out.println(test4);test4.setAccessible(true); //解除私有限定Object result = test4.invoke(obj, 15);System.out.println("返回值:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
5、获取main方法并执行
Student
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("Student中的main方法执行了...");}
}
测试类
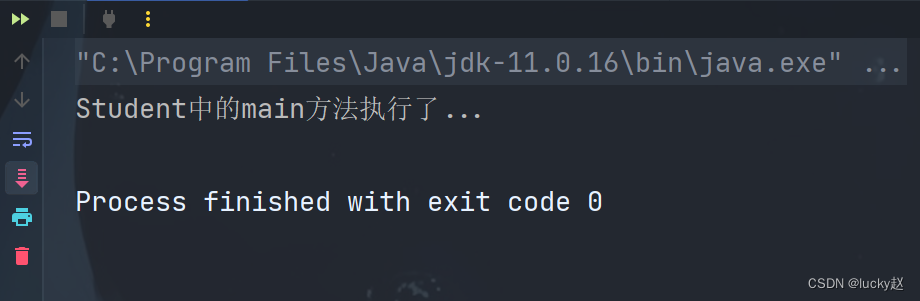
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1、获取Student的字节码文件Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.reflection.Student");//2、获取main方法Method main = clazz.getMethod("main", String[].class);//3、调用main方法// 第一个参数:对象类型,因为方法时静态的,所有为null可以// 第二个参数:String数组,这里要注意在JDK1.4之后是数组,JDK1.5之后为可变参数// 这里拆的时候将new String[]{"a","b","c"}拆成3个对象所有需要强制转换main.invoke(null, (Object) new String[]{"a", "b", "c"});
// main.invoke(null,new Object[]{new String[]{"a","b","c"}}); //这样也可以} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
运行结果:
6、通过反射运行配置文件内容
利用反射和配置文件,可以使应用程序更新时,对源码无需进行修改,只需将类发送给客户端,修改配置文件即可
application.properties
classname=com.example.reflection.Student
methodName=test3
Student
package com.example.reflection;public class Student {/*** 无参构造方法*/public Student() {System.out.println("无参构造方法执行了...");}public void test1(String str) {System.out.println("调用了公有的、String参数的方法" + str + "...");}
}
测试类
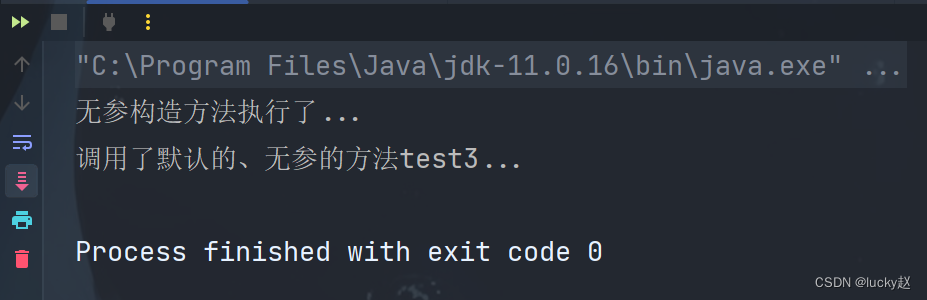
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {Properties prop = new Properties();InputStream is = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("application.properties");try {prop.load(is);//获取类String classname = prop.getProperty("classname");Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classname);//获取方法名String methodName = prop.getProperty("methodName");Method test2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName);test2.invoke(clazz.getConstructor().newInstance());} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
运行结果:
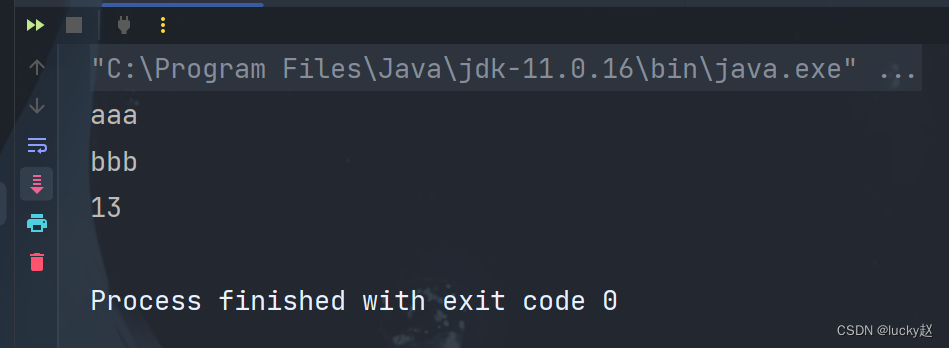
7、通过反射越过泛型检查
需求:有一个List list,向其中添加Integer类型的数据
测试类
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args){List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("aaa");list.add("bbb");//获取ArrayList的Class对象,反向调用add()方法Class<? extends List> clazz = list.getClass();try {Method add = clazz.getMethod("add", Object.class);add.invoke(list, 13);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}for (Object obj : list) {System.out.println(obj);}}
}
运行结果: