Linux系统编程_文件编程第1天:打开、写入、读取、关闭文件等编程
1. 文件编程概述(399.1)
- 内容超多:
- 文件系统原理及访问机制
- 文件在内核中的管理机制
- 什么是文件信息节点inode
- 文件的共享
- 文件权限,各种用户对其权限
- 。。。。。。
- 应用为王,如:
- 账单
- 游戏进度
- 配置文件等
- 关心如何用代码操作文件,实现文件创建、打开、编辑等自动化执行
- Windows 如何手动修改文件,比如写一个 word 文档:
- 打开/创建文档、编辑文档、保存文档、关闭文档
- 计算机如何帮助我们自动化完成以上操作?
- 操作系统提供了一系列的 API,如 Linux 系统:
- 打开 open
- 读写 write /read
- 光标定位 lseek
- 关闭 close
2. 文件打开及创建(400.2)
打开/创建文件
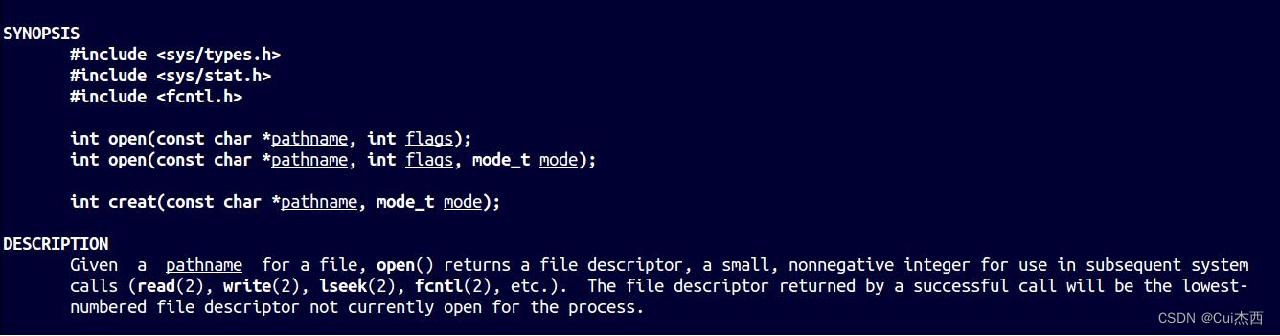
参数说明
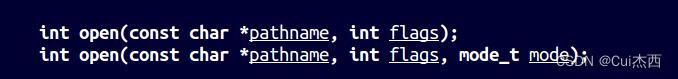
- int 返回值:文件描述符,应为小的非负整数
- Pathname:要打开的文件名(含路径,缺省为当前路径)
- Flags:
- O_RDONLY 只读打开
- O_WRONLY 只写打开
- O_RDWR 可读可写打开
- 当我们附带了权限后,打开的文件就只能按照这种权限来操作。
- 以上这三个常数中应当指定一个。
- 下列常数是可选择的:
- O_CREAT:若文件不存在则创建它。使用此选项时,需要同时说明第三个参数 mode(0600),用其说明该新文件的存取许可权限
- O_EXCL:如果同时指定了O_CREAT,而文件已经存在,则出错
- O_APPEND:每次写时都加到文件的尾端
- O_TRUNC:属性去打开文件时,如果这个文件中本来是有内容的,而且为只读或只写成功打开,则将其长度截短为 0。
- Mode:一定是在 flags 中使用了 O_CREAT 标志,mode 记录待创建的文件的访问权限
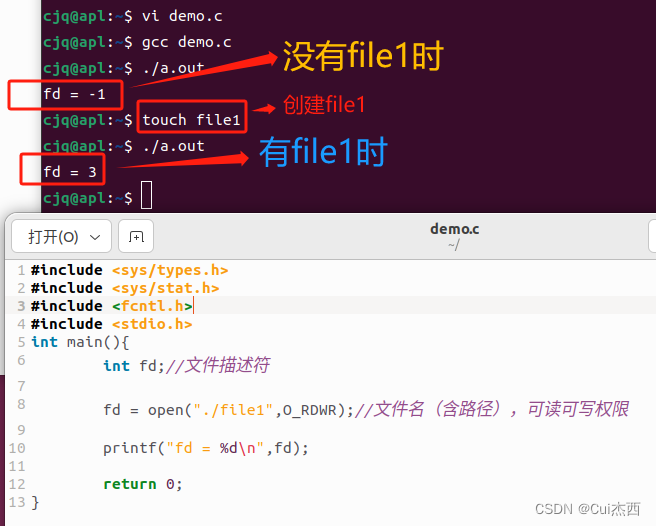
- FILE/demo.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
int main(){int fd;//文件描述符,索引值fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);//文件名(含路径),可读可写权限printf("fd = %d\n",fd);return 0;
}
- FILE/demo2.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件int main(){int fd;fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);printf("fd = %d\n",fd);if(fd == -1){printf("open file1 failed\n");fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600);//若文件不存在则创建if(fd > 0){printf("fd = %d\n",fd);printf("create file1 success!\n");}}return 0;
}
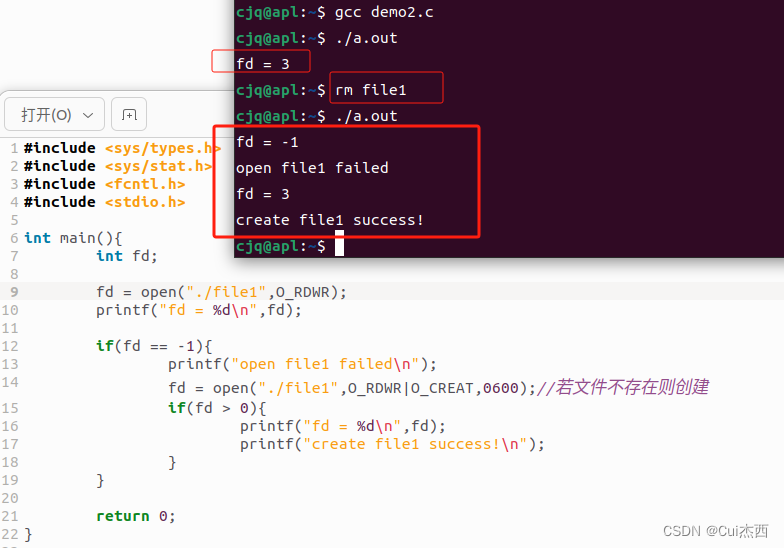
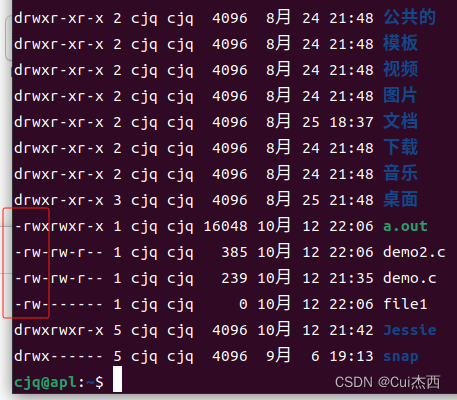
- -rwx:
- -:普通文件
- r:可读
- w:可写
- x:可执行

3. 文件写入操作编程(401.3)
- 查看函数原型
写入文件
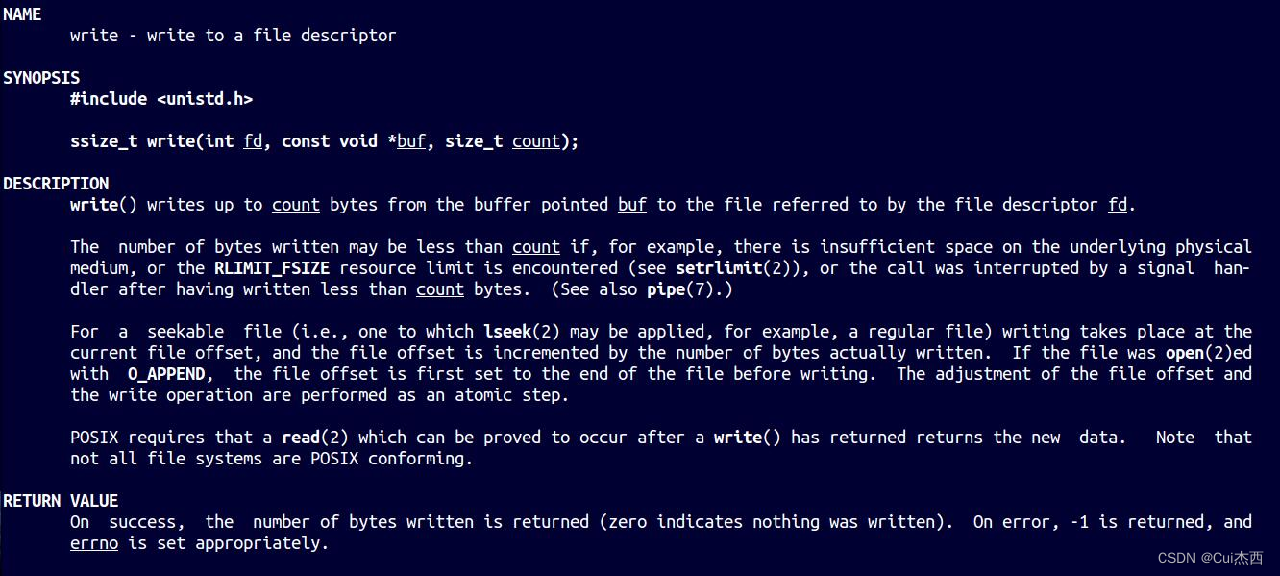
- write 返回的是写入的字节数
- FILE/demo3.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
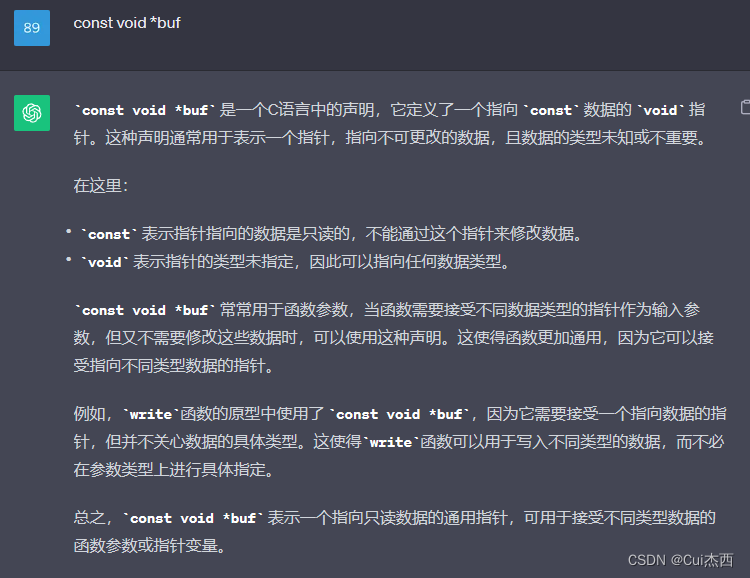
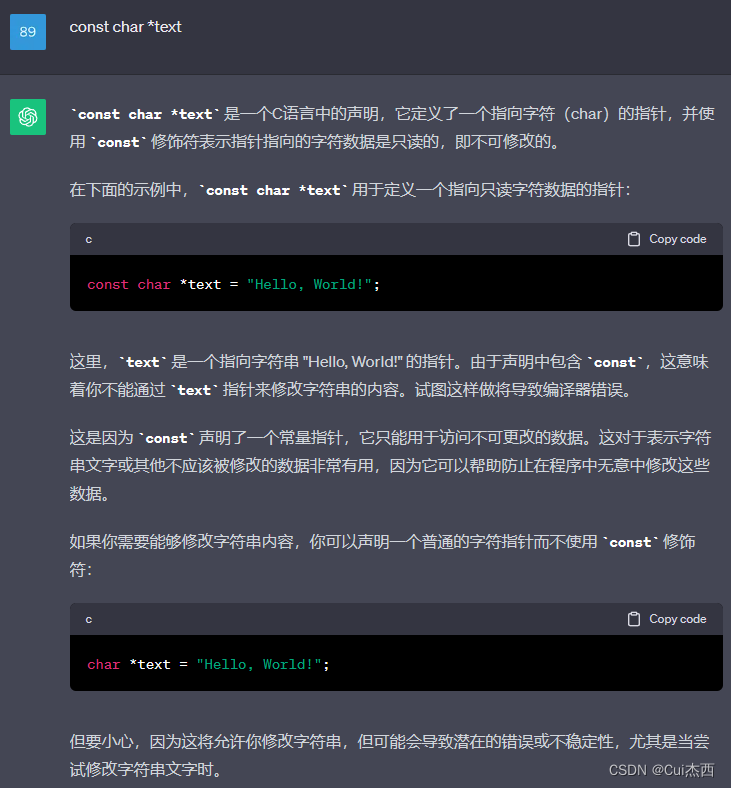
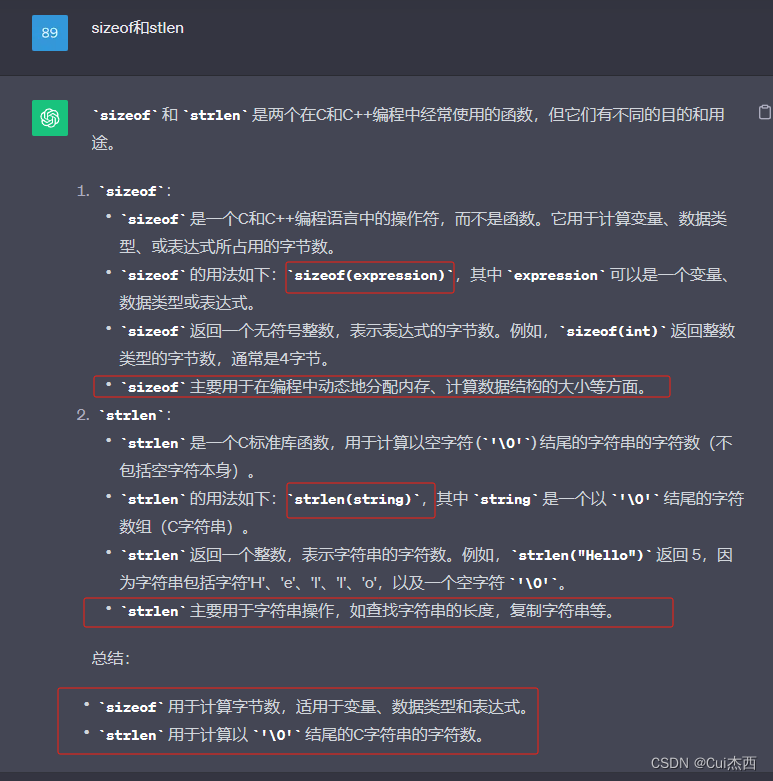
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie is very kind.";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);printf("fd = %d\n",fd);if(fd == -1){printf("open file1 failed\n");fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600);//若文件不存在则创建if(fd > 0){printf("fd = %d\n",fd);printf("create file1 success!\n");}}printf("open success : fd = %d\n",fd);//打开文件//ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);//write的函数原型write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));//写入文件//在Linux中指针是固定8个字节,所以不能用sizeof//stlen计算字符串长度close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}
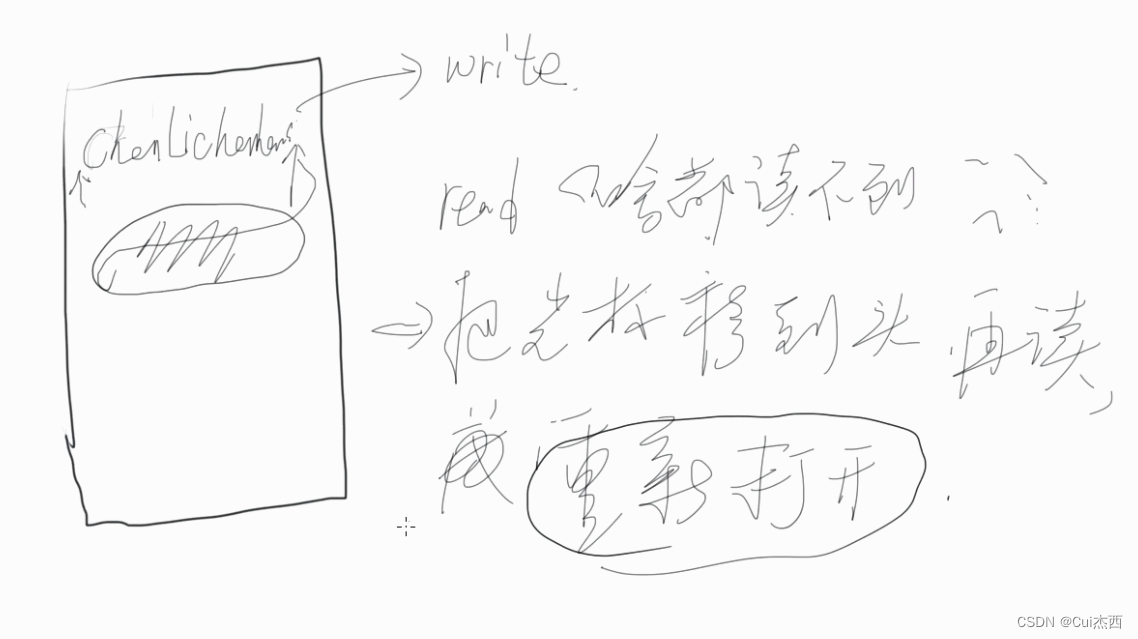
4. 文件读取操作(402.4)
读取文件
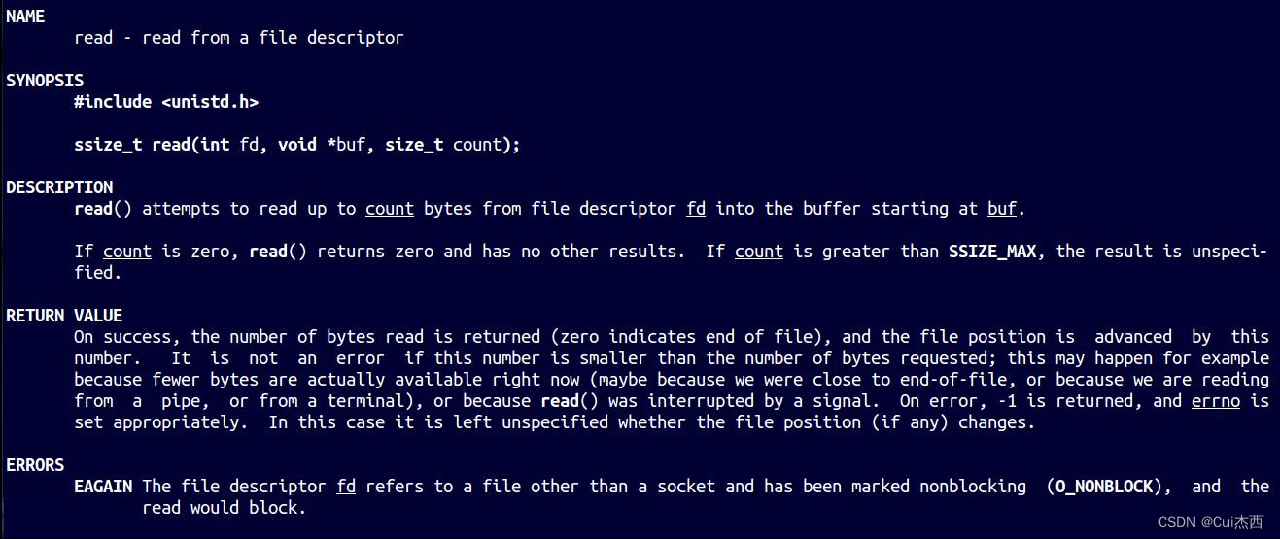
- read 返回的是读取的字节数
- FILE/demo4.c
- FILE/demo5.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie is very kind.";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);printf("fd = %d\n",fd);if(fd == -1){printf("open file1 failed\n");fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600);//若文件不存在则创建if(fd > 0){printf("fd = %d\n",fd);printf("create file1 success!\n");}}printf("open success : fd = %d\n",fd);//打开文件//ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));//存储在fd中写入所有的buf后的字节数if(n_write != -1){printf("write %d byte to file1\n",n_write);}close(fd);fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);//重新打开文件,光标移至头char *readBuf;readBuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*n_write + 1); //ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);//read的函数原型int n_read = read(fd,readBuf,n_write);//存储从fd中读出的readBuf的所有的字节数printf("read %d ,context:%s\n",n_read,readBuf);close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}
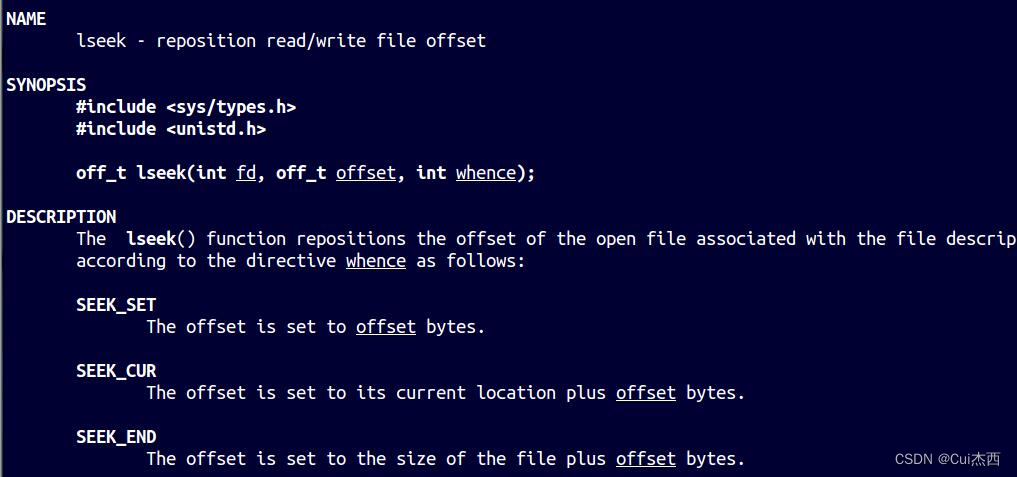
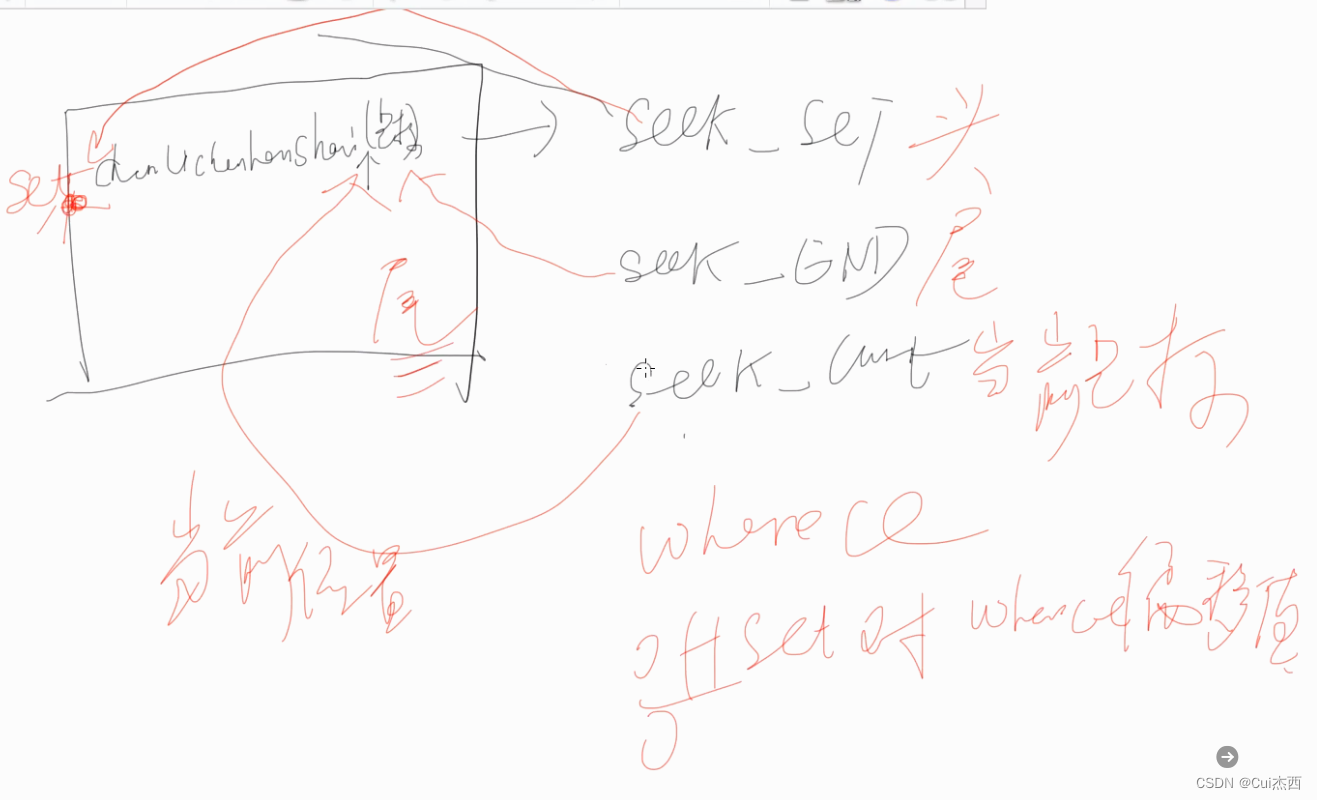
5. 文件光标移动操作(403.5)
将文件读写指针相对whence移动offset个字节
- FILE/demo6.c(打开、写入、定位光标、读取数据)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie is very kind.";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);printf("fd = %d\n",fd);if(fd == -1){printf("open file1 failed\n");fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600);//若文件不存在则创建if(fd > 0){printf("fd = %d\n",fd);printf("create file1 success!\n");}}printf("open success : fd = %d\n",fd);//打开文件//ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);//write的函数原型int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));//存储在fd中写入所有的buf后的字节数if(n_write != -1){printf("write %d byte to file1\n",n_write);}//close(fd);//fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);//重新打开文件,光标移至头char *readBuf;readBuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*n_write + 1); //ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);//read的函数原型//off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);//lseek的函数原型//lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);lseek(fd,-20,SEEK_CUR);//lseek(fd,-20,SEEK_END);int n_read = read(fd,readBuf,n_write);//存储从fd中读出的readBuf的所有的字节数printf("read %d ,context:%s\n",n_read,readBuf);close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}- FILE/demo7.c(lseek返回有多少个字节)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie is very kind.";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);int filesize = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);//lseek返回多少个字节printf("file's size is :%d\n",filesize);close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}关闭文件
6. 文件打开创建的补充(404.6)
O_EXCL:如果同时指定了 OCREAT,而文件已经存在,则出错(即返回-1)
- FILE/demo8.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int fd;fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_EXCL,0600);//若文件不存在则创建,已存在则出错if(fd == -1){printf("File1 exists.\n");}return 0;
}O_APPEND:每次写时都加到文件的尾端(另起一行)
- FILE/demo9.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie is very kind.";//fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_APPEND);//另起一行添加字符printf("open success : fd = %d\n",fd);//打开文件int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));//存储在fd中写入所有的buf后的字节数if(n_write != -1){printf("write %d byte to file1\n",n_write);}close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}- 有 O_APPEND 时:另起一行添加
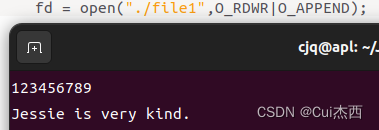
- 无 O_APPEND 时:覆盖原先对应位置的字符,保留后边的字符
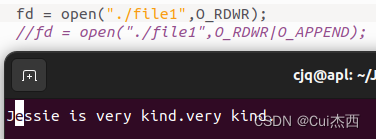
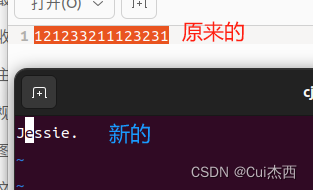
O_TRUNC:去打开文件时,如果这个文件中本来是有内容的,而且为只读或只写成功打开,则将其长度截短为0(即删除原来的所有字符)
- FILE/demo10.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;char *buf = "Jessie.";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_TRUNC);//打开已有文件时,清空字符printf("open success : fd = %d\n",fd);//打开文件int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));//存储在fd中写入所有的buf后的字节数if(n_write != -1){printf("write %d byte to file1\n",n_write);}close(fd);//关闭文件return 0;
}
创建文件creat函数
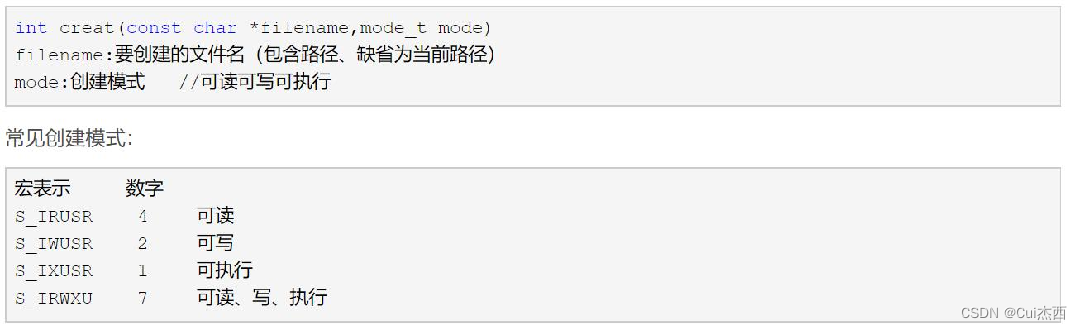
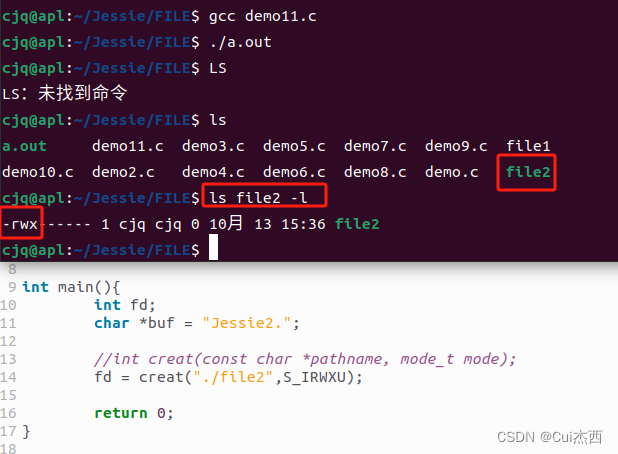
- FILE/demo11.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>//以上三行为open函数需包含的头文件
#include <stdio.h>//printf函数需包含的头文件
#include <unistd.h>//write函数需包含的头文件
#include <string.h>//strlen的头文件
#include <stdlib.h>//malloc的头文件int main(){int fd;//int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);fd = creat("./file2",S_IRWXU);return 0;
}
7. 文件操作原理简述(审核不过./7)
文件描述符

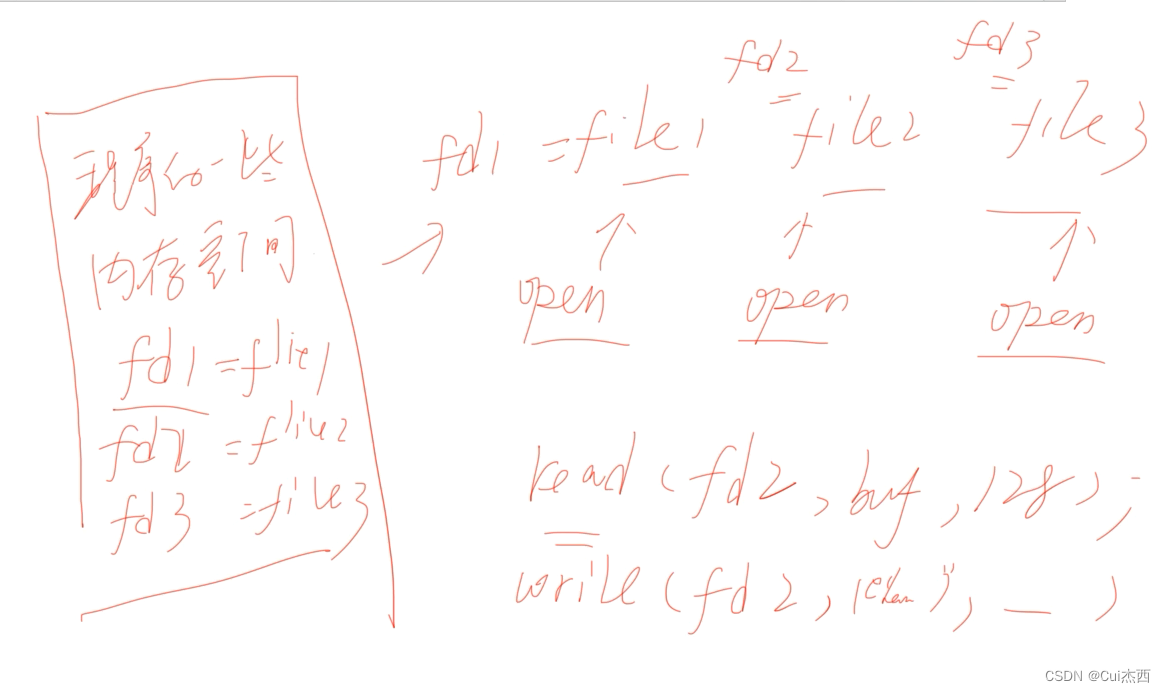

- FILE/demo12.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(){int fd;char readBuf[128];int n_read = read(0,readBuf,5);//从标准输入(键盘)读int n_write = write(1,readBuf,strlen(readBuf));//写到标准输出(UNIX shell)printf("\ndone!\n");return 0;
}
文件编程的一般步骤
- 打开/创建文件、读取文件/写入文件、关闭文件

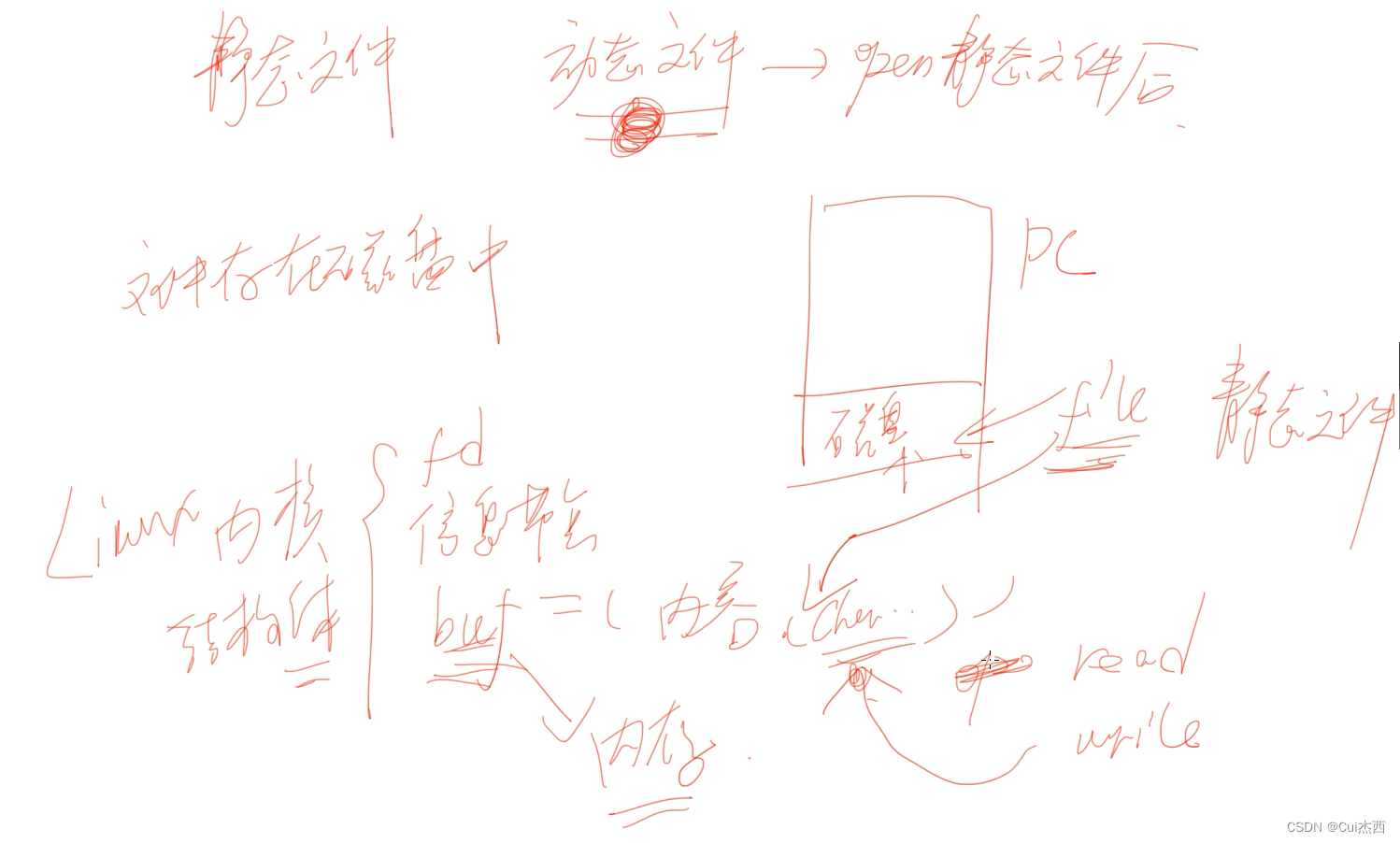
Linux文件管理简述
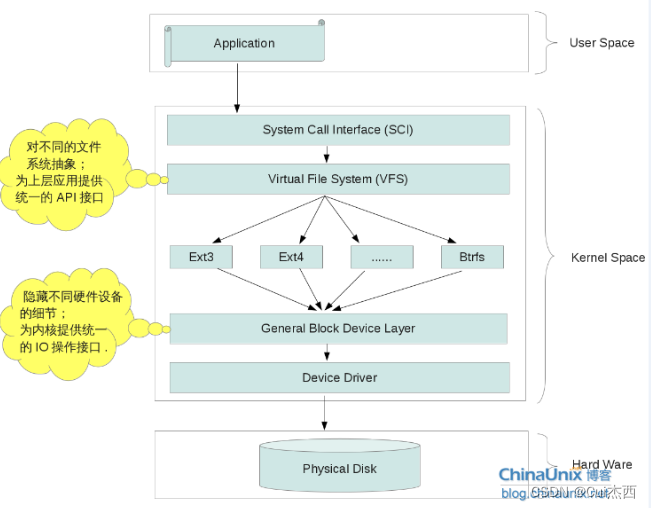
8. 文件操作小应用之实现cp指令(405.8)

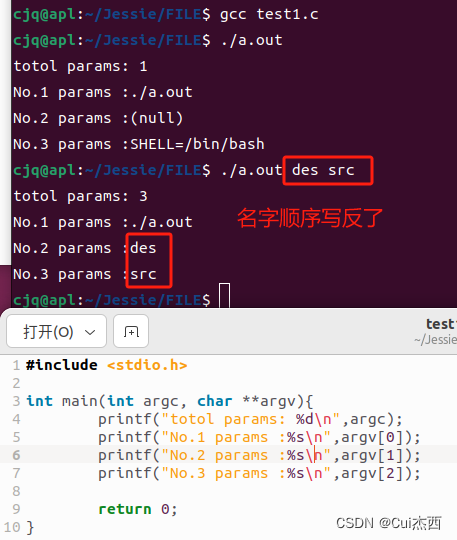
- FILE/test1.c(先做测试)
#include <stdio.h>int main(int argc, char **argv){printf("totol params: %d\n",argc);//参数总数printf("No.1 params :%s\n",argv[0]);//参数名称,数组的形式//a.outprintf("No.2 params :%s\n",argv[1]);//srcprintf("No.3 params :%s\n",argv[2]);//des()return 0;
}
- FILE/demo13.c( 实现linux cp命令的代码)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(int argc, char **argv){int fdSrc;//源文件描述符int fdDes;//目标文件描述符char *readBuf=NULL;if(argc != 3){//对参数个数的判断printf("pararm error\n");exit(-1);}fdSrc = open(argv[1],O_RDWR);//打开源文件int size = lseek(fdSrc,0,SEEK_END);//算出源文件的字节大小readBuf=(char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*size + 8);//开辟比源文件多8个字节的大小lseek(fdSrc,0,SEEK_SET);//光标移至源文件内容的头int n_read = read(fdSrc, readBuf, size);//读源文件到readBuf,要用sizefdDes = open(argv[2],O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0600);//打开/创建目标文件,目标文件已存在时清空内容int n_write = write(fdDes,readBuf,strlen(readBuf));//将readBuf写入目标文件close(fdSrc);//关闭源文件close(fdDes);//关闭目标文件return 0;
}
9. 解决上节课中的隐藏bug(406.9)
- FILE/demo13.c( 实现linux cp命令的代码)
int n_read = read(fdSrc, readBuf, size);//读源文件到readBuf,要用sizefdDes = open(argv[2],O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0600);//打开/创建目标文件,目标文件已存在时清空内容
