设计模式 - 行为型模式考点篇:迭代器模式(概述 | 案例实现 | 优缺点 | 使用场景)
目录
一、行为型模式
一句话概括行为型模式
1.1、迭代器模式
1.1.1、概述
1.1.2、案例实现
1.1.3、优缺点
1.1.4、使用场景
一、行为型模式
一句话概括行为型模式
行为型模式:类或对象间如何交互、如何划分职责,从而更好的完成任务.
1.1、迭代器模式
1.1.1、概述
提供一个聚合对象,内部通过迭代器来访问聚合对象中的一系列数据,而不暴露聚合对象的内部实现.
例如,现在有一个班级的学生(包装在一个 List 容器中的聚合元素),我需要按照学号拿到每一个学生,此时就需要把遍历这个班级的学生(List 容器)交给迭代器完成.
迭代器模式主要包含以下角色:
- 抽象迭代器:定义访问和遍历聚合元素的接口,通常包含 hasNext()、next() 等方法.
- 具体迭代器:实现抽象迭代器接口中定义的方法,完成聚合对象的遍历,记录遍历的当前位置.
- 抽象聚合:定义存储、添加、删除聚合元素以及创建迭代器对象接口.
- 具体聚合:实现抽象聚合类,返回一个具体的迭代器实例.
1.1.2、案例实现
实现上述学生案例.
/*** 学生类*/
public class Student {private String name;private int id;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int id) {this.name = name;this.id = id;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", id=" + id +'}';}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}
}
/*** 抽象迭代器: 学生迭代器接口*/
public interface StudentIterator {boolean hasNext();Student next();}
/*** 具体迭代器: 学生迭代器*/
public class StudentIteratorImpl implements StudentIterator{private List<Student> list;private int position;public StudentIteratorImpl(List<Student> list) {this.list = list;}@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return position < list.size();}@Overridepublic Student next() {Student current = list.get(position);position++;return current;}}
/*** 抽象聚合: 学生聚合接口*/
public interface StudentAggregation {void addStudent(Student student);void removeStudent(Student student);StudentIterator getStudentIterator();}
/*** 具体聚合: 学生聚合*/
public class StudentAggregationImpl implements StudentAggregation{private List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();@Overridepublic void addStudent(Student student) {list.add(student);}@Overridepublic void removeStudent(Student student) {list.remove(student);}@Overridepublic StudentIterator getStudentIterator() {return new StudentIteratorImpl(list);}}
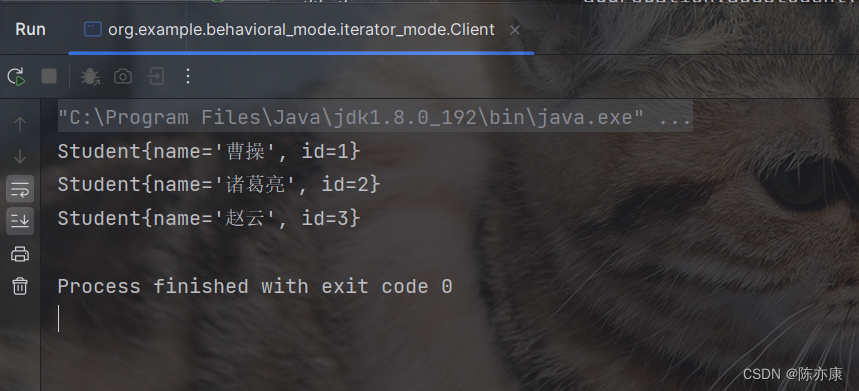
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {StudentAggregationImpl aggregation = new StudentAggregationImpl();aggregation.addStudent(new Student("曹操", 1));aggregation.addStudent(new Student("诸葛亮", 2));aggregation.addStudent(new Student("赵云", 3));StudentIterator studentIterator = aggregation.getStudentIterator();while(studentIterator.hasNext()) {Student student = studentIterator.next();System.out.println(student);}}}
执行结果如下:
1.1.3、优缺点
优点:
定义多种遍历方式:支持不同方式遍历一个聚合对象,可以在同一个聚合对象上顶一个多种遍历方式.
满足开闭原则:引入抽象层,增加新的聚合类和迭代器,都无需修改原有代码.
缺点:
增加了类的个数,一定程度上增加了系统复杂度.
1.1.4、使用场景
- 当需要为聚合对象提供多种遍历方式.
- 当需要为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口时.
- 当访问的聚合对象的内容无需要暴露其内部实现细节.
