DRM全解析 —— plane详解(1)
本文参考以下博文:
Linux内核4.14版本——drm框架分析(5)——plane分析
特此致谢!
1. 简介
一个plane代表一个image layer(硬件图层),最终的image由一个或者多个plane(s)组成。plane和 Framebuffer 一样是内存地址。plane主要包括以下3种类型:
- DRM_PLANE_TYPE_PRIMARY:主要图层,通常用于仅支持RGB格式的简单图层
- DRM_PLANE_TYPE_OVERLAY:叠加图层,通常用于YUV格式的视频图层
- DRM_PLANE_TYPE_CURSOR:光标图层,一般用于pc系统,用于显示鼠标
2. 核心结构
在Linux内核的DRM中,plane对应的核心结构体为:struct drm_plane。该结构体在include/drm/drm_plane.h中定义,代码如下(Linux内核版本:6.1):
/*** struct drm_plane - central DRM plane control structure** Planes represent the scanout hardware of a display block. They receive their* input data from a &drm_framebuffer and feed it to a &drm_crtc. Planes control* the color conversion, see `Plane Composition Properties`_ for more details,* and are also involved in the color conversion of input pixels, see `Color* Management Properties`_ for details on that.*/
struct drm_plane {/** @dev: DRM device this plane belongs to */struct drm_device *dev;/*** @head:** List of all planes on @dev, linked from &drm_mode_config.plane_list.* Invariant over the lifetime of @dev and therefore does not need* locking.*/struct list_head head;/** @name: human readable name, can be overwritten by the driver */char *name;/*** @mutex:** Protects modeset plane state, together with the &drm_crtc.mutex of* CRTC this plane is linked to (when active, getting activated or* getting disabled).** For atomic drivers specifically this protects @state.*/struct drm_modeset_lock mutex;/** @base: base mode object */struct drm_mode_object base;/*** @possible_crtcs: pipes this plane can be bound to constructed from* drm_crtc_mask()*/uint32_t possible_crtcs;/** @format_types: array of formats supported by this plane */uint32_t *format_types;/** @format_count: Size of the array pointed at by @format_types. */unsigned int format_count;/*** @format_default: driver hasn't supplied supported formats for the* plane. Used by the non-atomic driver compatibility wrapper only.*/bool format_default;/** @modifiers: array of modifiers supported by this plane */uint64_t *modifiers;/** @modifier_count: Size of the array pointed at by @modifier_count. */unsigned int modifier_count;/*** @crtc:** Currently bound CRTC, only meaningful for non-atomic drivers. For* atomic drivers this is forced to be NULL, atomic drivers should* instead check &drm_plane_state.crtc.*/struct drm_crtc *crtc;/*** @fb:** Currently bound framebuffer, only meaningful for non-atomic drivers.* For atomic drivers this is forced to be NULL, atomic drivers should* instead check &drm_plane_state.fb.*/struct drm_framebuffer *fb;/*** @old_fb:** Temporary tracking of the old fb while a modeset is ongoing. Only* used by non-atomic drivers, forced to be NULL for atomic drivers.*/struct drm_framebuffer *old_fb;/** @funcs: plane control functions */const struct drm_plane_funcs *funcs;/** @properties: property tracking for this plane */struct drm_object_properties properties;/** @type: Type of plane, see &enum drm_plane_type for details. */enum drm_plane_type type;/*** @index: Position inside the mode_config.list, can be used as an array* index. It is invariant over the lifetime of the plane.*/unsigned index;/** @helper_private: mid-layer private data */const struct drm_plane_helper_funcs *helper_private;/*** @state:** Current atomic state for this plane.** This is protected by @mutex. Note that nonblocking atomic commits* access the current plane state without taking locks. Either by going* through the &struct drm_atomic_state pointers, see* for_each_oldnew_plane_in_state(), for_each_old_plane_in_state() and* for_each_new_plane_in_state(). Or through careful ordering of atomic* commit operations as implemented in the atomic helpers, see* &struct drm_crtc_commit.*/struct drm_plane_state *state;/*** @alpha_property:* Optional alpha property for this plane. See* drm_plane_create_alpha_property().*/struct drm_property *alpha_property;/*** @zpos_property:* Optional zpos property for this plane. See* drm_plane_create_zpos_property().*/struct drm_property *zpos_property;/*** @rotation_property:* Optional rotation property for this plane. See* drm_plane_create_rotation_property().*/struct drm_property *rotation_property;/*** @blend_mode_property:* Optional "pixel blend mode" enum property for this plane.* Blend mode property represents the alpha blending equation selection,* describing how the pixels from the current plane are composited with* the background.*/struct drm_property *blend_mode_property;/*** @color_encoding_property:** Optional "COLOR_ENCODING" enum property for specifying* color encoding for non RGB formats.* See drm_plane_create_color_properties().*/struct drm_property *color_encoding_property;/*** @color_range_property:** Optional "COLOR_RANGE" enum property for specifying* color range for non RGB formats.* See drm_plane_create_color_properties().*/struct drm_property *color_range_property;/*** @scaling_filter_property: property to apply a particular filter while* scaling.*/struct drm_property *scaling_filter_property;
};3. drm_plane结构释义
(0)总述
DRM全解析 —— plane详解(1)
struct drm_plane —— 核心的DRM plane控制结构。
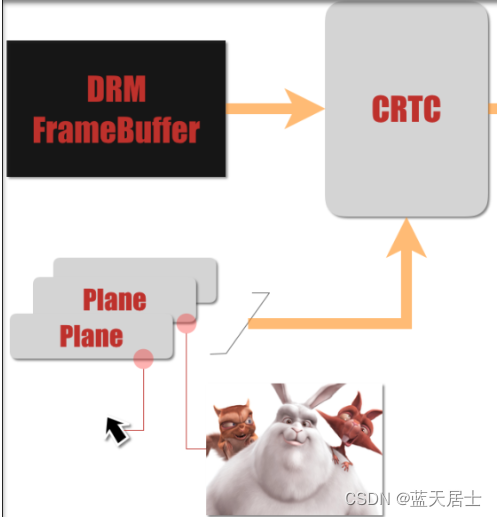
planes表示显示块的扫描输出硬件。它们从drm_framebuffer中接收输入数据,并将其提供给drm_crtc。planes控制颜色转换(有关详细信息,请参见“平面合成属性”),并且还参与输入像素的颜色转换(请参见“颜色管理属性”以了解详细信息)。
作用如下图示:

(1)struct drm_device *dev
/** @dev: DRM device this plane belongs to */struct drm_device *dev;此plane所属的DRM设备。
(2)struct list_head head
/*** @head:** List of all planes on @dev, linked from &drm_mode_config.plane_list.* Invariant over the lifetime of @dev and therefore does not need* locking.*/struct list_head head;@dev上所有平面的列表,链接自&drm_mode_config.plane_List。在@dev的生命周期内保持不变,因此不需要锁定。
(3)char *name
/** @name: human readable name, can be overwritten by the driver */char *name;人类可读的名称(名字),可以被驱动程序覆盖。
下一篇文章继续深入释义drm_plane结构中其余成员。
