c++运算符重载
目录
运算符重载的基本概念
重载加号运算符(+)
类内实现
类外实现
运算符重载碰上友元函数
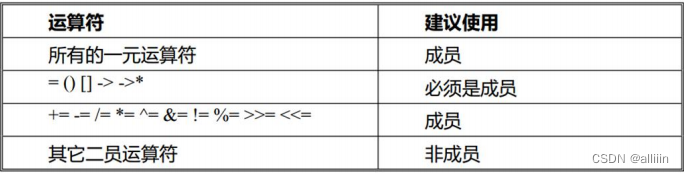
可重载和不可重载的运算符
可重载的运算符
不可重载的运算符
重载自加自减运算符(a++ ++a)
智能指针
重载等号运算符(=)
重载等于和不等运算符(== !=)
运算符重载的基本概念
概念:
运算符重载与函数重载比较类似,相当于让一个运算符具有另外一种含义;
语法:
定义重载的运算符就像定义函数,只是该函数的名字是 operator@,这里的@代表了被重载的运算符。函数的参数中参数个数取决于两个因素。运算符是一元(一个参数)的还是二元(两个参数);运算符被定义为全局函数(对于一元是一个参数,对于二元是两个参数)还是成员函数(对于一元没有参数,对于二元是一个参数-此时该类的对象用作左耳参数)
重载加号运算符(+)
类内实现
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class person
{public:person(int age){this->age = age;}person operator+(person &p2)//{person p = (this->age+p2.age);return p;}int age;
};
void test01()
{person p1(10);person p2(20);person p3 = p1 + p2;cout << p3.age << endl;}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}类外实现
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class person
{public:person(int age){this->age = age;}int age;
};person operator+(person &p1,person &p2)//
{person p = (p1.age+p2.age);return p;
}void test01()
{person p1(10);person p2(20);person p3 = p1 + p2;cout << p3.age << endl;}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
运算符重载碰上友元函数
将左移运算符的重载函数声明为类的友元函数 就可以访问类的成员
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class person
{friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,person &p);public:person(int age){this->age = age;}private:int age;
};ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,person &p)
{cout << p.age;return cout;
}void test01()
{person p1(10);cout << p1 << endl;}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}可重载和不可重载的运算符
可重载的运算符

不可重载的运算符

重载自加自减运算符(a++ ++a)
a++是先把a赋值到一个临时空间,再对a+1赋值给临时变量,等运算结束后才返回临时变量给a (参与运算的是自加之前的值)
++a是先给a+1,直接对a赋值,不需要开辟临时空间(参与运算的是返回值的引用)
前置++返回的是引用
后置++返回的是对象
前置++调用void operator++()
后置++调用myint operator++(int) 后置++多了一个占位参数
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class myint
{public:myint &operator++(){this->num = this->num+1;return *this;}myint(int num){this->num = num;}myint operator++(int){myint tmp = *this;this->num = this->num+1;return tmp;}int num;
};ostream &operator<<(ostream& cout,myint &p)
{cout << p.num;return cout;
}#include <iostream>using namespace std;class myint
{public:myint &operator++(){this->num = this->num+1;return *this;}myint(int num){this->num = num;}myint operator++(int){myint tmp = *this;this->num = this->num+1;return tmp;}int num;
};ostream &operator<<(ostream& cout,myint &p)
{cout << p.num;return cout;
}void test01()
{myint p1(10);cout << p1 << endl;++p1;//调用operator++(p1)或者p1.operator()cout << ++p1 << endl;p1++;//cout << p1++ << end; //有些编译器会报错cout << p1 << endl;
}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
智能指针
我们经常new出一个对象,忘记释放,所以我们使用智能指针来维护
智能指针实质上是一个局部对象 这个局部对象维护了new出来的对象的地址,在局部对象的析构函数中,会帮忙释放new出来的对象
对于智能指针我们重载了->和* 让智能指针和普通指针一样使用
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class person
{public:person(int age ){this->age = age;}int age;
};class SmartPointer
{public:SmartPointer(person *p1){this->p = p1;}~SmartPointer(){delete p;cout << "释放了p" << endl;}person *p;
};void test01()
{//局部对象 在释放之前可以帮助释放pperson *p = new person(10);SmartPointer s1(p);cout << p->age <<endl;cout <<
}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
重载等号运算符(=)
编译器默认给每个类加上了四个函数
默认的无参构造
默认的拷贝构造
析构函数
operator=()
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;class person
{public:person(){}person(int agel,char *namel){age = agel;name = new char[strlen(namel)+1];strcpy(name,namel);}person& operator=(person &p1){this->age = p1.age;this->name = new char[strlen(p1.name)+1];strcpy(this->name,p1.name);return *this;//返回p2 为什么不返回p1?可以连续赋值 p3 = p2 = p1}~person(){delete []name;}int age;char *name;
};void test01()
{person p1(10,(char *)"bob");person p2;p2 = p1;//p2.operator(person &p1)cout << p2.age << " " << p2.name <<endl;
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
重载等于和不等运算符(== !=)
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;class person
{public:person(){}bool operator==(person &p2){return this->age == p2.age && this->name == p2.name;}bool operator!=(person &p2){return this->age != p2.age || this->name != p2.name;}person(int age,string name){this->age = age;this->name = name;}int age;string name;
};void test01()
{person p1(10,"lucy");person p2(10,"bob");if(p1 == p2){cout << "p1 = p2" << endl;}if(p1 != p2){cout << "p1 != p2" << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}函数调用符号()重载
一个类中重载了()的类,那么类的定义出来的对象可以像函数一样使用,本质是调用了operator()这个函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;class Myadd
{public:int add(int a,int b){return a + b;}int operator()(int x,int y){return x + y;}
};void test01()
{Myadd p;cout << p.add(3,5) << endl;//p() 可以像函数一样调用的对象 函数对象cout << p(3,4) << endl;//p.operator()(3,4)cout << Myadd()(3,4) << endl;//定义一个匿名对象 Myadd().operator()(3,4)
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}尽量不要重载 || &&
class Complex{public :Complex( int flag){this ->flag = flag;}Complex& operator +=(Complex& complex){this ->flag = this ->flag + complex.flag;return * this ;}bool operator &&(Complex& complex){return this ->flag && complex.flag;}public :int flag;};int main(){Complex complex1( 0 ); //flag 0Complex complex2( 1 ); //flag 1//原来情况,应该从左往右运算,左边为假,则退出运算,结果为假//这边却是,先运算( complex1+complex2 ),导致, complex1 的 flag 变为 complex1+complex2 的值,complex1.a = 1// 1 && 1//complex1.operator&&(complex1.operator+=(complex2))if (complex1 && (complex1 += complex2)){//complex1.operator+=(complex2)cout << " 真 !" << endl;}else {cout << " 假 !" << endl;}return EXIT_SUCCESS;}
符号重载总结