【Linix-Day12-线程同步和线程安全】
线程同步 和 线程安全
线程同步
除了信号量和互斥锁(互斥锁和条件变量上次介绍过),还有两种方式同步
1.读写锁
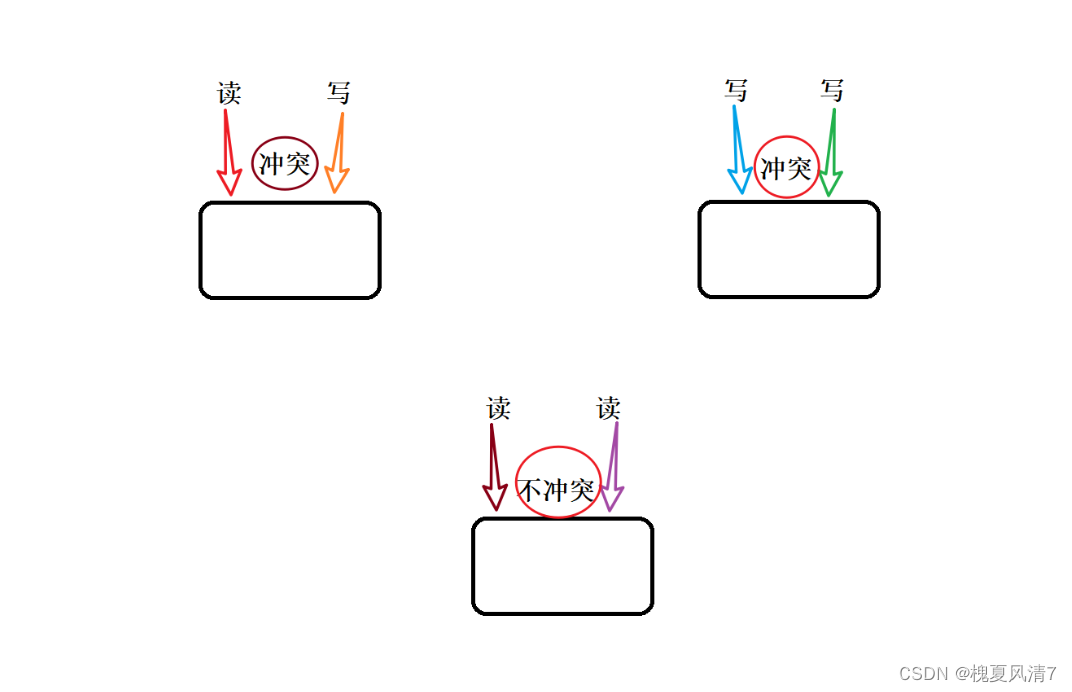
当同时对一块内存读写时,会出现下列问题,故而引入读写锁
接口介绍:
1.int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock, pthread_rwlockattr_t *attr);
函数功能:初始化读写锁
rwlock :传入定义的读写锁地址
attr : 读写锁的属性,一般默认为 NULL
返回值:如果成功,函数应返回零
2.int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
函数功能:加读锁,其他线程无法写入
rwlock :传入定义的读写锁地址
3.int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
函数功能:加写锁,其他线程无法写入,读取
rwlock :传入定义的读写锁地址
4.int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
函数功能:解锁,允许读和写
rwlock :传入定义的读写锁地址
5.int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
函数功能:销毁读写锁
rwlock :传入定义的读写锁地址
测试代码:
main.c
include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;void *fun1(void *arg)
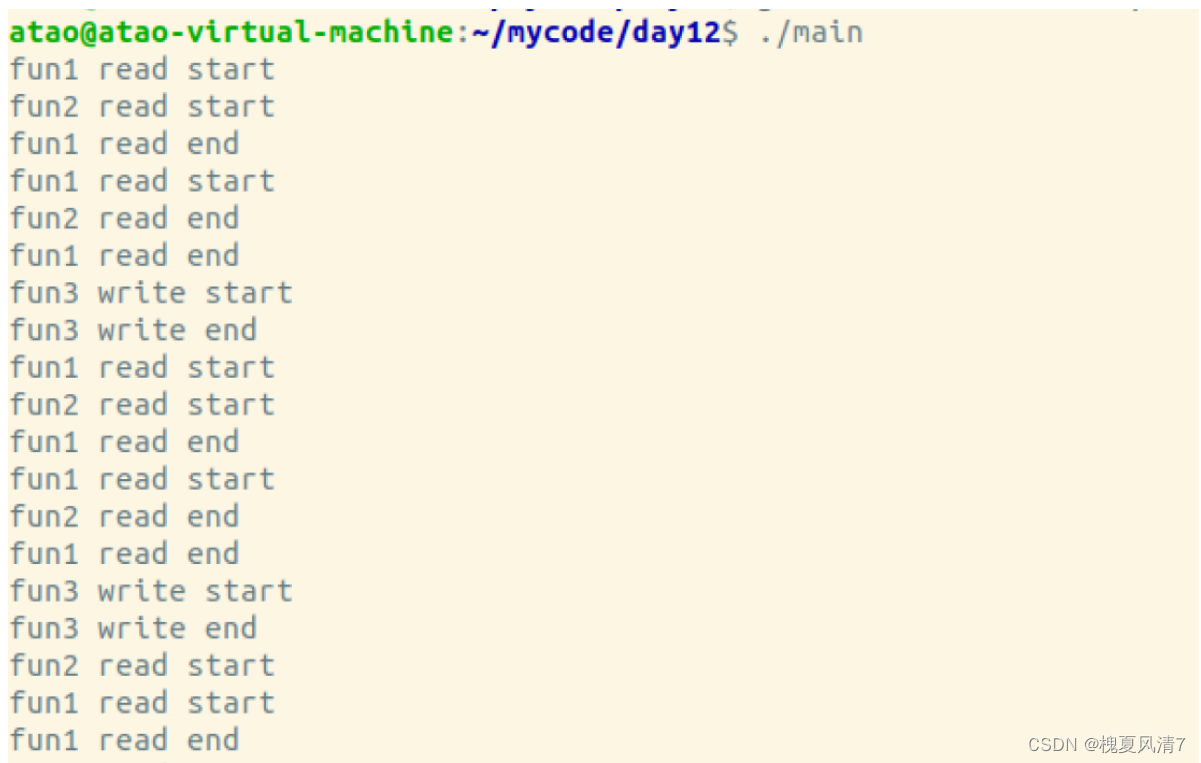
{for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i){pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);printf("fun1 read start\n");sleep(1);printf("fun1 read end\n");pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);sleep(1);}
}
void *fun2(void *arg)
{for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);printf("fun2 read start\n");sleep(3);printf("fun2 read end\n");pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);sleep(1);}
}
void *fun3(void *arg)
{for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);printf("fun3 write start\n");sleep(3);printf("fun3 write end\n");pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t id[3];pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, fun1, NULL);pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, fun2, NULL);pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, fun3, NULL);for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i){pthread_join(id[i], NULL);}pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);exit(0);
}
运行结果图:
2.条件变量
条件变量提供了一种线程间的通知机制:当某个共享数据达到某个值的时候,唤醒等待
这个共享数据的线程。
接口介绍:
1. int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *attr);
函数功能:初始化条件变量
cond:定义的条件变量的地址
attr:条件变量的属性,一般默认为 NULL
2. int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
函数功能:进入条件变量等待队列
cond:定义的条件变量的地址
mutex:定义的互斥锁的地址
3. int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
函数功能: 唤醒单个线程
cond:定义的条件变量的地址
4. int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
函数功能:唤醒所有等待的线程
cond:定义的条件变量的地址
5.int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
函数功能:摧毁条件变量
cond:定义的条件变量的地址
测试代码
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;void *fun1(void *arg)
{char *s = (char *)arg;while (1){// 阻塞,被唤醒pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);printf("fun1 read:%s\n", s);if (strncmp(s, "end", 3) == 0){break;}}
}
void *fun2(void *arg)
{char *s = (char *)arg;while (1){// 阻塞,被唤醒pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);printf("fun2 read:%s\n", s);if (strncmp(s,"end",3) == 0){break;}}
}int main()
{pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);pthread_t id[2];char buff[256]={0};pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, fun1, (void*)buff);pthread_create(&id[1], NULL, fun2, (void*)buff);while(1){printf("input: ");fflush(stdout);fgets(buff,255,stdin);printf("\n");if(strncmp(buff,"end",3) == 0){pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);break;}else{pthread_cond_signal(&cond);}sleep(1);}for(int i=0;i<2;++i){pthread_join(id[i],NULL);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);exit(0);
}
运行结果图

线程安全
在多线程运行的时候,不论线程的调度顺序怎样,最终的结果都是一样的、正确的。那么就说这些线程是安全的。
要保证线程安全需要做到:
1)对线程同步,保证同一时刻只有一个线程访问临界资源。
2)在多线程中使用线程安全的函数(可重入函数),所谓线程安全的函数指的是:如果一个函数能被多个线程同时调用且不发生竟态条件,则我们程它是线程安全的。
下面展示使用不安全的线程函数举例
实现在两个线程中分别打印 char buff[] = “a b c d e f g h i”; char buff[] = “1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9”;两个数组
测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>void *PthreadFun(void *arg)
{char buff[] = "a b c d e f g h i";char *p = strtok(buff, " ");while (p != NULL){printf("fun:: %c\n", *p);p = strtok(NULL, " ");sleep(1);}
}int main()
{pthread_t id;int res = pthread_create(&id, NULL, PthreadFun, NULL);assert(res == 0);char buff[] = "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9";char *p = strtok(buff, " ");while (p != NULL){printf("main:: %c\n", *p);p = strtok(NULL, " ");sleep(1);}exit(0);
}
运行结果
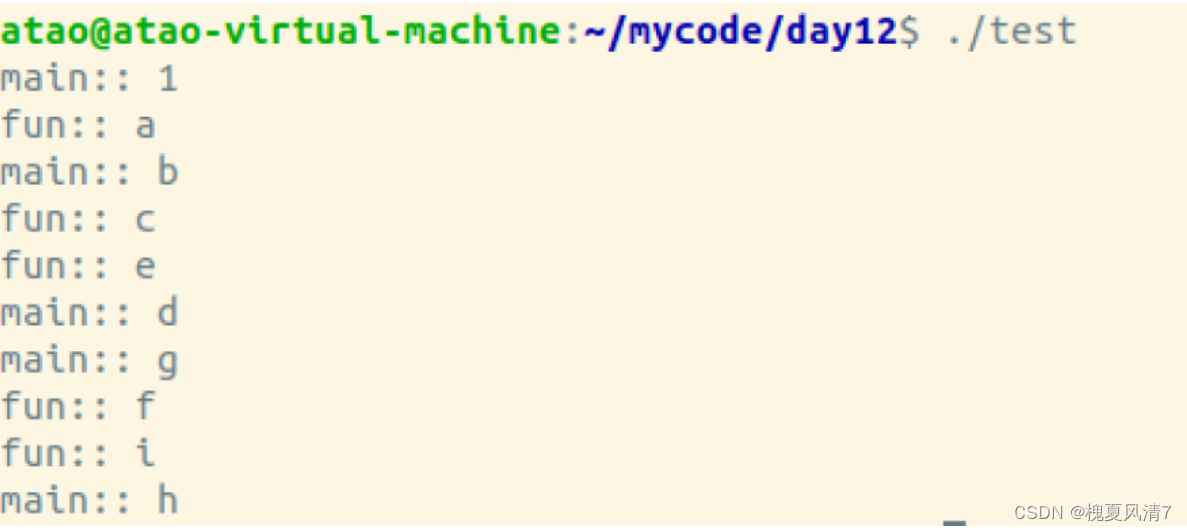
这是因为strtok()是线程不安全函数,内部实现使用了全局变量或静态变量,所以不能同时处理不同的字符串。
解决方法,使用线程安全版的 strtok_r();
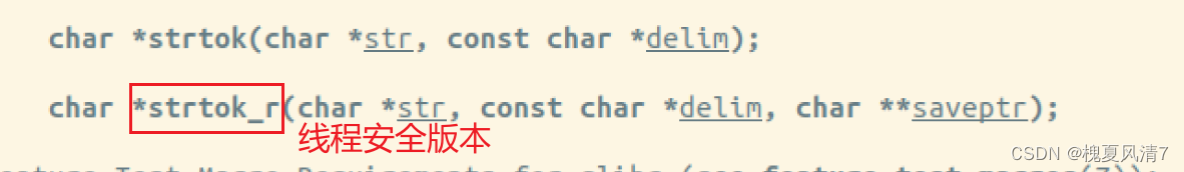
char *strtok_r(char *str, const char *delim, char **saveptr);
str : 数组
delim: 分隔符
saveptr:是指向char*变量的指针,用来维护连续解析相同字符串的调用
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>void *PthreadFun(void *arg)
{char *q = NULL;char buff[] = "a b c d e f g h i";char *p = strtok_r(buff, " ",&q);while (p != NULL){printf("fun:: %c\n", *p);p = strtok_r(NULL, " ",&q);sleep(1);}
}int main()
{pthread_t id;int res = pthread_create(&id, NULL, PthreadFun, NULL);assert(res == 0);char *q = NULL;char buff[] = "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9";char *p = strtok_r(buff, " ",&q);while (p != NULL){printf("main:: %c\n", *p);p = strtok_r(NULL, " ",&q);sleep(1);}exit(0);
}
运行结果

