Go并发可视化解释 - Select语句
昨天,我发布了一篇文章,用可视化的方式解释了Golang中通道(Channel)的工作原理。如果你对通道的理解仍然存在困难,最好呢请在阅读本文之前先查看那篇文章。作为一个快速的复习:Partier、Candier 和 Stringer 经营着一家咖啡店。Partier 协助从顾客接收订单,然后将这些订单传递给厨房,Candier 和 Stringer 制作咖啡。
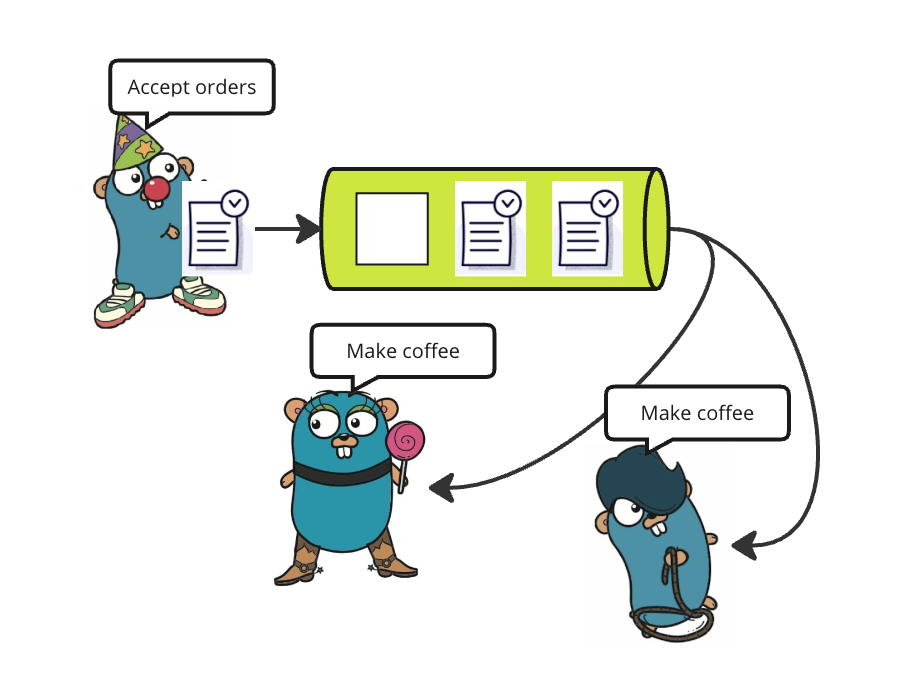
Gophers 咖啡馆
在本文中,我将以视觉方式解释 select 语句,这是另一个在Go应用程序中处理并发的强大工具。Gophers 和他们的想象中的咖啡馆仍然会是我的伙伴,但这次,让我们聚焦在 Partier 和订单部分。
场景
Gophers 咖啡馆意识到越来越多的顾客想通过食品外卖应用订购咖啡。因此,除了现场点餐外,他们还选择了一款食品外卖应用。Partier 同时监听来自这两个通道的订单,并将这些订单通过另一个通道 queue 转发给 Candier 和 Stringer。
select {
case order := <-appOrders:queue <- order
case order := <-inShopOrders:queue <- order
}当任何一个通道接收到订单时,Partier 会将其转发到 queue 通道。
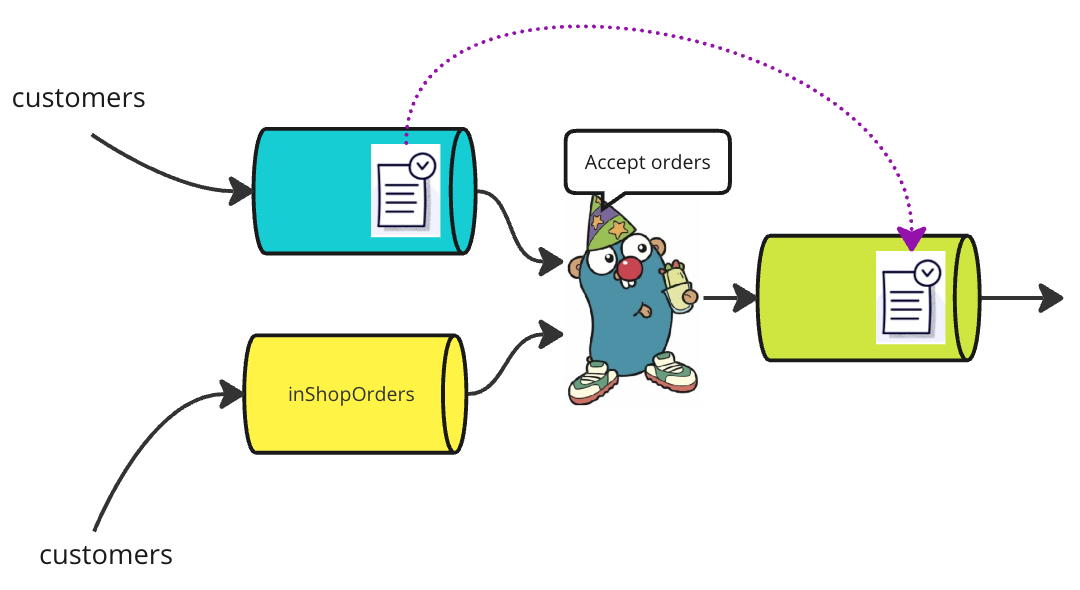
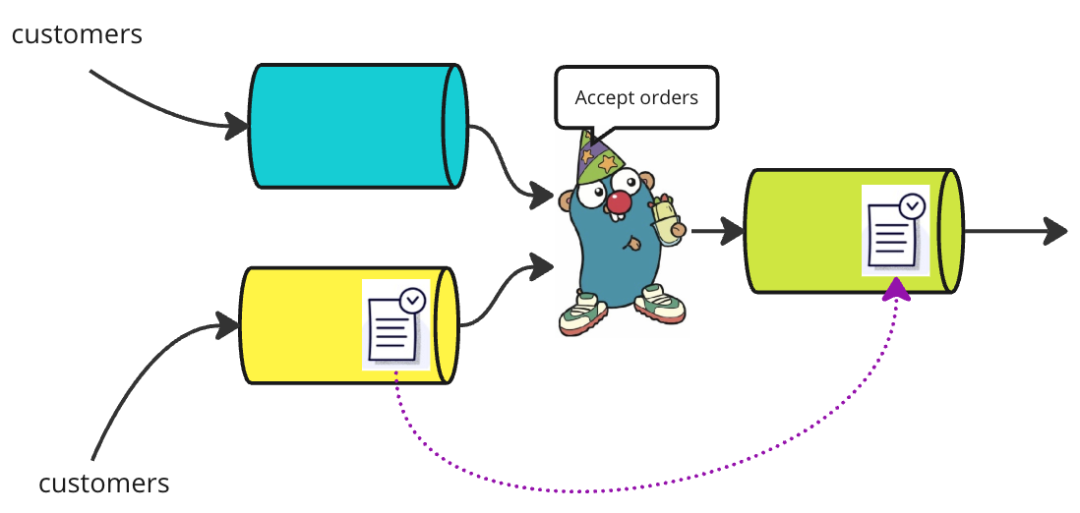
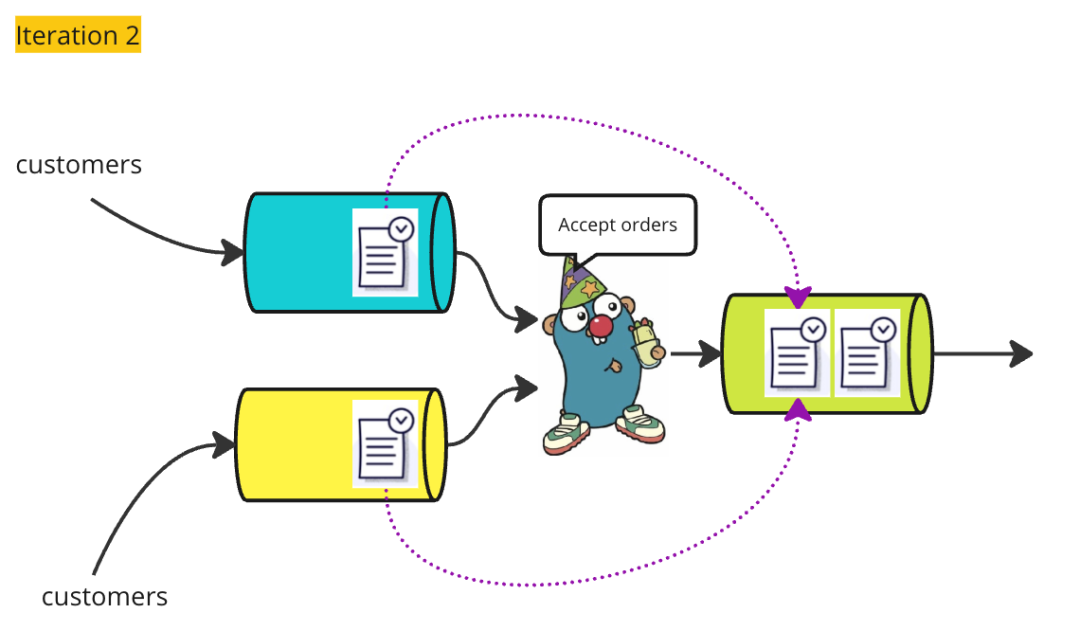
如果两个通道都有订单,其中之一将被选择。在真实的咖啡馆中,来自 inShopOrders 的订单可能会被优先处理。然而,在Go应用程序中,我们不能保证会选择哪个订单。还请注意,select 语句的每次执行只会选取一个订单,Partier 不会先选择一个订单,然后再选择另一个订单。尽管如此,在许多应用程序中,select 语句通常在 for 循环内部,使得前一次迭代中留下的订单在下一次迭代中有机会被选取。
for {select {case order := <-appOrders:queue <- ordercase order := <-inShopOrders:queue <- order}
}但是,如果两个通道都有订单,它们将再次进行公平竞争。
默认分支
在非高峰时段,订单不多,Partier 在等待上花费了大量时间。他认为,通过做其他事情,例如清洁桌子,他可以更有成效地利用时间。这可以通过 default 实现。
for {select {case order := <-appOrders:log.Println("There is an order coming from appOrders channel")queue <- ordercase order := <-inShopOrders:log.Println("There is an order coming from inShopOrders channel")queue <- orderdefault:log.Println("There is no order on both channels, I will do cleaning instead")doCleaning()}
}time.After()
通常,time.After(duration) 与 select 一起使用,以防止永远等待。与 default 立即在没有可用通道时执行不同,time.After(duration) 创建一个普通的 <-chan Time,等待 duration 过去,然后在返回的通道上发送当前时间。这个通道在 select 语句中与其他通道一样被处理。正如你所看到的,select 语句中的通道可以是不同类型的。
shouldClose := false
closeHourCh := time.After(8 * time.Hour)for !shouldClose {select {case order := <-appOrders:log.Println("There is an order coming from appOrders channel")queue <- ordercase order := <-inShopOrders:log.Println("There is an order coming from inShopOrders channel")queue <- ordercase now := <-closeHourCh:log.Printf("It is %v now, the shop is closing\n", now)shouldClose = truedefault:log.Println("There is no order on both channels, I will go cleaning instead")doCleaning()}
}log.Println("Shop is closed, I'm going home now. Bye!")在处理远程API调用时,这种技术非常常见,因为我们不能保证远程服务器何时返回或是否返回。有了 context,我们通常不需要这样做。
responseChannel := make(chan interface{})
timer := time.NewTimer(timeout)select {
case resp := <-responseChannel:log.Println("Processing response")processResponse(resp)timer.Stop()
case <-timer.C:log.Println("Time out, giving up")
}示例代码
让我们以一个完整的虚构咖啡馆代码结束本文。这里还有一件需要注意的事情,从关闭的通道中选择将总是立即返回。因此,如果您认为有必要,使用“comma ok”习惯用法。亲自动手编码是学习编程的最佳方式。因此,如果您对 select 不太熟悉,我建议您在IDE上复制并尝试修改此代码。
祝您编码愉快!
package mainimport ("fmt""log""time"
)func main() {appOrders := make(chan order, 3)inShopOrders := make(chan order, 3)queue := make(chan order, 3)go func() {for i := 0; i < 6; i++ {appOrders <- order(100 + i)time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)}close(appOrders)}()go func() {for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {inShopOrders <- order(200 + i)time.Sleep(15 * time.Second)}close(inShopOrders)}()go partier(appOrders, inShopOrders, queue)for o := range queue {log.Printf("Served %s\n", o)}log.Println("Done!")
}func partier(appOrders <-chan order, inShopOrders <-chan order, queue chan<- order) {shouldClose := falsecloseTimeCh := time.After(1 * time.Minute)for !shouldClose {select {case ord, ok := <-appOrders:if ok {log.Printf("There is %s coming from appOrders channel\n", ord)queue <- ord}case ord, ok := <-inShopOrders:if ok {log.Printf("There is %s coming from inShopOrders channel\n", ord)queue <- ord}case now := <-closeTimeCh:log.Printf("It is %v now, the shop is closing\n", now)shouldClose = truedefault:log.Println("There is no order on both channels, I will go cleaning instead")doCleaning()}}close(queue)log.Println("Shop is closed, I'm going home now. Bye!")
}func doCleaning() {time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)log.Println("Partier: Cleaning done")
}type order intfunc (o order) String() string {return fmt.Sprintf("order-%02d", o)
}感谢您一直阅读到文章末尾。请考虑关注下作者啦~
