cuda编程002—流
没有使用同步的情况:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>__global__ void test_kernel(){printf("Message from Device.\n");
}
void test(){test_kernel<<<1, 1>>>();
}#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <stdio.h>void test();
int main(){test();printf("Message from Host.\n");getchar();return 0;
}先调用的核函数,结果是先输出的Host:
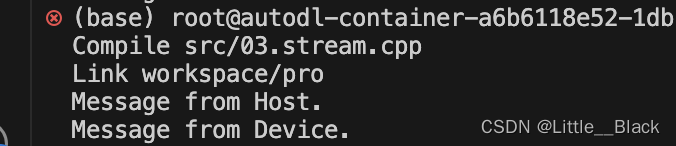
进行同步,代码如下:
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <stdio.h>void test();
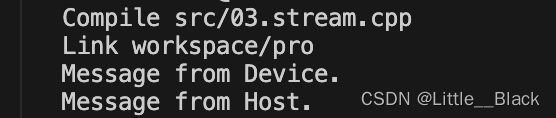
int main(){test();// cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // 设备同步,整个GPU设备的同步等待任务完成cudaStreamSynchronize(nullptr); // 流同步printf("Message from Host.\n");getchar();return 0;
}输出结果:
cuda流整体笔记和代码
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>// 核函数
__global__ void test_kernel(float* array, int edge){int position = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;if(position >= edge) return;array[position] *= 0.5f;
}void test(cudaStream_t stream, float* array, int num){int threads = 512;int blocks = ceil(num / (float)threads);test_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, stream>>>(array, num);
}#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <stdio.h>// C++ 文件
void test(cudaStream_t stream, float* array, int num);int main(){cudaStream_t stream;cudaEvent_t start, stop;// cudaEvent 是事件, 通常可以用来观察队列的执行情况// 比如,统计执行时间等操作cudaEventCreate(&start);cudaEventCreate(&stop);// 是重操作,不要随便创建太多,会消耗资源的// GPU计算的基本原则,是尽可能的使得计算密集,如果使用同步的话就是算一坨,等一会儿,算一坨,等一会。费劲吧啦的// 通过stream使得计算连续化、密集化,这样最好// GPU有个使用率,跟CPU使用了一样的,以GPU使用率越高越好cudaStreamCreate(&stream);cudaEventRecord(start, stream);int num = 10000;float* a = new float[num];for(int i=0; i < num; ++i)a[i] = i;float* a_device = nullptr;size_t a_bytes = sizeof(float) * num;cudaMalloc(&a_device, a_bytes);// 异步依赖的指针数据,必须在执行完成前一直存在,否则会造成例外结果// 并且异步执行时,对指针数据的修改,也需要合理的理解cudaMemcpyAsync(a_device, a, a_bytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream);// 如果异步复制加上下面这段代码。会导致GPU边复制,CPU边修改,结果是a_device的内容不可控// 因此不要这么做,或者合理的去做你想做的// for(int i=0; i < num; ++i)// a[i] = 500-i;test(stream, a_device, num);cudaMemcpyAsync(a, a_device, a_bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);cudaEventRecord(stop, stream);cudaEventSynchronize(stop);float ms = 0;cudaEventElapsedTime(&ms, start, stop);printf("核的执行时间是:%.8f ms\n", ms);// 打印前10个结果for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){printf(i == 0 ? "%.2f" : ", %.2f", a[i]);}printf("\n");// cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);// cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // 设备同步,整个GPU设备的同步等待任务完成// cudaStreamSynchronize(nullptr); // 流同步/* 流的概率,stream, 类型全称是cudaStream_t1. 认为流是一个线程,任务级别的线程2. 认为流是一个任务队列3. 把异步执行的任务管理起来,在需要的时候等待或者做更多处理4. 默认流,指nullptr,如果给定为nullptr,就会使用默认流cuda核的执行都是异步的, 通过流来实现需要的同步任务队列队列特性:先进先出,后进后出cudaMemcpy 属于同步版本的内存拷贝等价于干了 -> 发送指令(任务队列中增加一个任务),我要复制了, cudaMemcpyAsync-> 等待复制完成,cudaDeviceSynchronize*/printf("Message from Host.\n");// 符合栈的方式分配和释放,就不用担心有bugdelete [] a;cudaFree(a_device);cudaStreamDestroy(stream);cudaEventDestroy(start);cudaEventDestroy(stop);// getchar();return 0;
}
