【算法】三道算法题目单词拆分,填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针以及组合总和
算法
- 第一道算法题:单词拆分
- java解答参考
- 第二道算法题:填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- java 解答参考
- 第三道算法题:组合总和
- java解答参考
大家好,我是小冷。
今天还是继续学习算法技术知识吧
第一道算法题:单词拆分
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
说明:
分隔时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入:
s = "
catsanddog
"
wordDict =
[“cat”, “cats”, “and”, “sand”, “dog”]
输出:
[
“cats and dog”,
“cat sand dog”
]
示例 2:
输入:
s = “pineapplepenapple”
wordDict = [“apple”, “pen”, “applepen”, “pine”, “pineapple”]
输出:
[
“pine apple pen apple”,
“pineapple pen apple”,
“pine applepen apple”
]
解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入:
s = “catsandog”
wordDict = [“cats”, “dog”, “sand”, “and”, “cat”]
输出:
[]
可以根据提示思考
java解答参考
class Solution {public List<String> wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();int max = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();for (String word : wordDict) {set.add(word);max = Integer.max(max, word.length());min = Integer.min(min, word.length());}boolean f[] = new boolean[s.length() + 1];f[0] = true;for (int i = 1; i < s.length() + 1; i++) {for (int j = Math.max(i - max, 0); j <= i - min; j++) {if (f[j] && set.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {f[i] = true;break;}}}if (f[s.length()]) {dfs(s, res, new StringBuilder(), set, 0, max, min);}return res;}private void dfs(String s, List<String> res, StringBuilder sb, Set<String> set, int index, int max, int min) {if (index == s.length()) {sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);res.add(sb.toString());return;}String str;int size;for (int i = index + min; i <= s.length() && i <= index + max; i++) {if (set.contains(str = s.substring(index, i))) {size = sb.length();sb.append(str).append(' ');dfs(s, res, sb, set, i, max, min);sb.delete(size, sb.length());}}}
}
第二道算法题:填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个二叉树
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
进阶:
你只能使用常量级额外空间。
使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
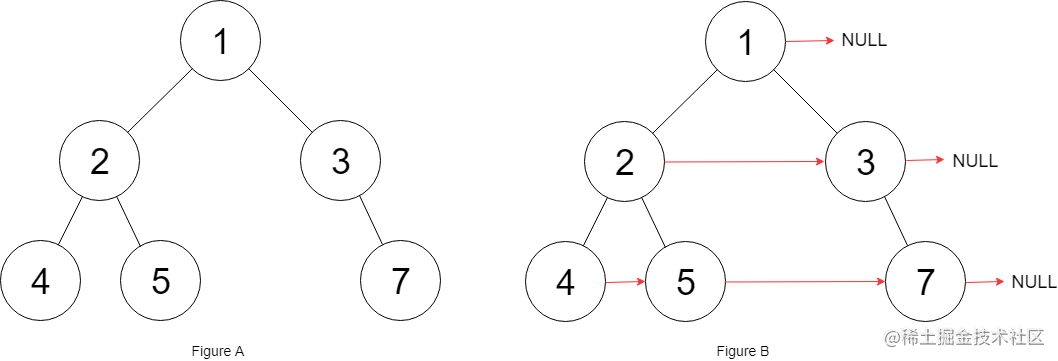
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化输出按层序遍历顺序(由 next 指针连接),‘#’ 表示每层的末尾。
提示:
树中的节点数小于 6000
-100 <= node.val <= 100
java 解答参考
class Node {public int val;public Node left;public Node right;public Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {val = _val;left = _left;right = _right;next = _next;}
};
class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {if (root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) {return root;}if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {root.left.next = root.right;root.next = getrightnext(root);}if (root.left != null) {root.left.next = getrightnext(root);}if (root.right != null) {root.right.next = getrightnext(root);}connect(root.right);connect(root.left);return root;}public static Node getrightnext(Node root) {while (root.next != null) {if (root.left != null) {return root.left;}if (root.right != null) {return root.right;}root = root.next;}return null;}
}
第三道算法题:组合总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
输出:[[7],[2,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
输出:[[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 30
1 <= candidates[i] <= 200
candidate 中的每个元素都是独一无二的。
1 <= target <= 500
java解答参考
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candiates, int target) {List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(candiates);dfs(candiates, resultList, result, 0, target);return resultList;}private void dfs(int[] candiates, List<List<Integer>> resultList, List<Integer> result, int start, int target) {if (target < 0) {return;}else if (target == 0) {resultList.add(new ArrayList<>(result));} else {for (int i = start; i < candiates.length; i++) {result.add(candiates[i]);dfs(candiates, resultList, result, i, target - candiates[i]);result.remove(result.size() - 1);}}}
}
写到最后,小冷一直在技术路上前行…你的关注,评论,收藏都是对我的支持。
昨天,删去;今天,争取;明天,努力。
