Springboot扩展点之CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
Springboot扩展点系列:
Springboot扩展点之ApplicationContextInitializer
Springboot扩展点之BeanFactoryPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之BeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
Springboot扩展点之@PostConstruct
Springboot扩展点之InitializingBean
Springboot扩展点之SmartInitializingSingleton
Springboot扩展点之CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
Springboot扩展点之FactoryBean
Springboot扩展点之DisposableBean
Springboot扩展点系列之终结篇:Bean的生命周期
前言
大家都知道Springboot简化了Spring的开发,因此从某种意义来说,Spring的扩展点也是Springboot的扩展点,而这篇文章主角是CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner,而这两个是Springboot中新增的扩展点,之所以将这两个扩展点放在一起,是因为它两个功能特性高度相似,不同的只是名字、扩展方法形参数类型、执行先后的一些小的不同,那么下面就直接进入正题吧。
功能特性
1、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner都有一个扩展方法run(),但是run()形参数类型不同;
2、CommandLineRunner.run()方法的形参数类型是String... args,ApplicationRunner.run()的形参数类型是ApplicationArguments args;
3、CommandLineRunner.run()的执行时机要晚于ApplicationRunner.run()一点;
4、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner触发执行时机是在Spring容器、Tomcat容器正式启动完成后,可以正式处理业务请求前,即项目启动的最后一步;
5、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner可以应用的场景:项目启动前,热点数据的预加载、清除临时文件、读取自定义配置信息等;
实现方式
1、定义MyCommandLineRunner和MyCommandLineRunner2,实现 CommandLineRunner, ApplicationRunner接口,并用@Order标记执行顺序,数字越小,执行知先级越高;
@Component
@Slf4j
@Order(value = 1)
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner, ApplicationRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("----CommandLineRunner.run()触发执行,实现类是:"+this.getClass().getName());}@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {log.info("----ApplicationRunner.run()触发执行,实现类是:"+this.getClass().getName());}
}@Component
@Slf4j
@Order(value = 2)
public class MyCommandLineRunner2 implements CommandLineRunner, ApplicationRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("----CommandLineRunner.run()触发执行,实现类是:"+this.getClass().getName());}@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {log.info("----ApplicationRunner.run()触发执行,实现类是:"+this.getClass().getName());}
}2、使用SpringApplication.run()启动SprIngboot项目;
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class FanfuApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {log.info("----Springboot开始启动....");SpringApplication.run(FanfuApplication.class, args);log.info("----Springboot启动完成");}
}3、启动完成,日志结果如图:
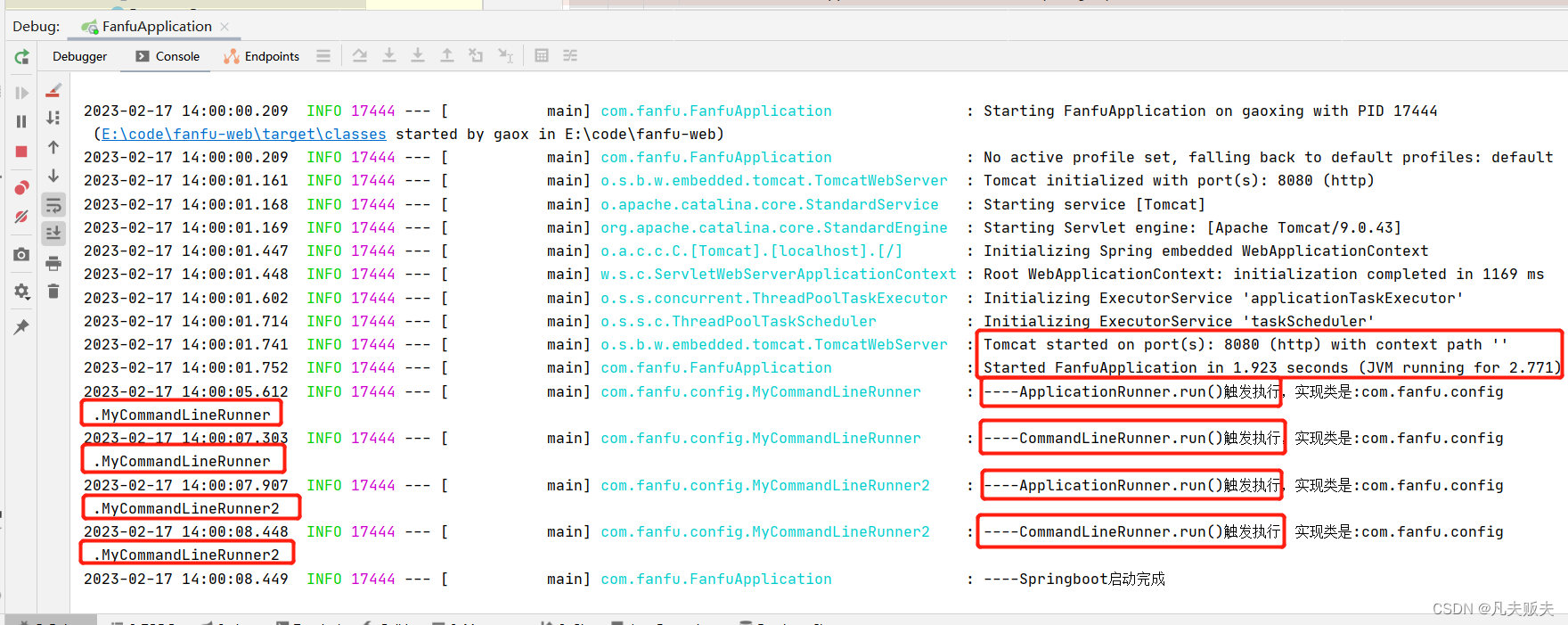
工作原理
之前基他的扩展点的执行时机大部分是在Spring容器实例化前后、Spring容器刷新中,CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner与之前其他的扩展点不同的是,其执行时机最晚,即在Spring容器、Tomcat容器正式启动完成的最后一步。
1、顺着SpringApplication.run(FanfuApplication.class, args)进入到run(String... args)中,CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner的执行入口就在这里,之前在其他分享其他扩展点时,经常遇到的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh(),其实是第25行 refreshContext(context)中触发的。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {//springboot启动前的准备工作StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();stopWatch.start();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();configureHeadlessProperty();//启动要开始的时候触发了SpringApplicationRunListenersSpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);listeners.starting();try {//启动参数args包装ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);//准备系统环境ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);//打印启动时标志图形Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);//创建Spring的上下文环境context = createApplicationContext();exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);//刷新Spring容器refreshContext(context);//容器启动后的一些后置处理afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);stopWatch.stop();if (this.logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);}//触发了Spring容器启动完成的事件listeners.started(context);//开始调用CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner的扩展点方法callRunners(context, applicationArguments);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}try {listeners.running(context);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}return context;
}2、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner的扩展点方法的调用逻辑,其实也是简单易懂,先把所有CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner的实现类汇总到一个集合,然后循环遍历这个集合,在集合里判断,如果ApplicationRunner的实现类,则先执行;如果是CommandLineRunner的实现类,则后执行;非常的朴实无华。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {//汇总CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner的实现类到runners集合List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);//循环遍历runners 集合for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {//如果ApplicationRunner的实现类,则先执行if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);}//如果是CommandLineRunner的实现类,则后执行;if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);}}
}
private void callRunner(ApplicationRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {try {(runner).run(args);}catch (Exception ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute ApplicationRunner", ex);}
}
private void callRunner(CommandLineRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {try {(runner).run(args.getSourceArgs());}catch (Exception ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute CommandLineRunner", ex);}
}总结
如果面试过程中,有面试官这样问你:”对业务上一些热点数据需要在项目启动前进行预加载,你有什么好的办法吗?“
你可以这么回答他:”我了解Springboot有两个扩展点:CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner,其触发执行时机是在Spring容器、Tomcat容器正式启动完成后,可以正式处理业务请求前,刚好可以做一些热点数据预先加载完全可以使用这个方法,实现方式也很简单,实现CommandLineRunner或ApplicationRunner接口即可,非常优雅。“
如果你这么回答他,相信他会满意的。
