IO进程线程day8(2023.8.6)
一、Xmind整理: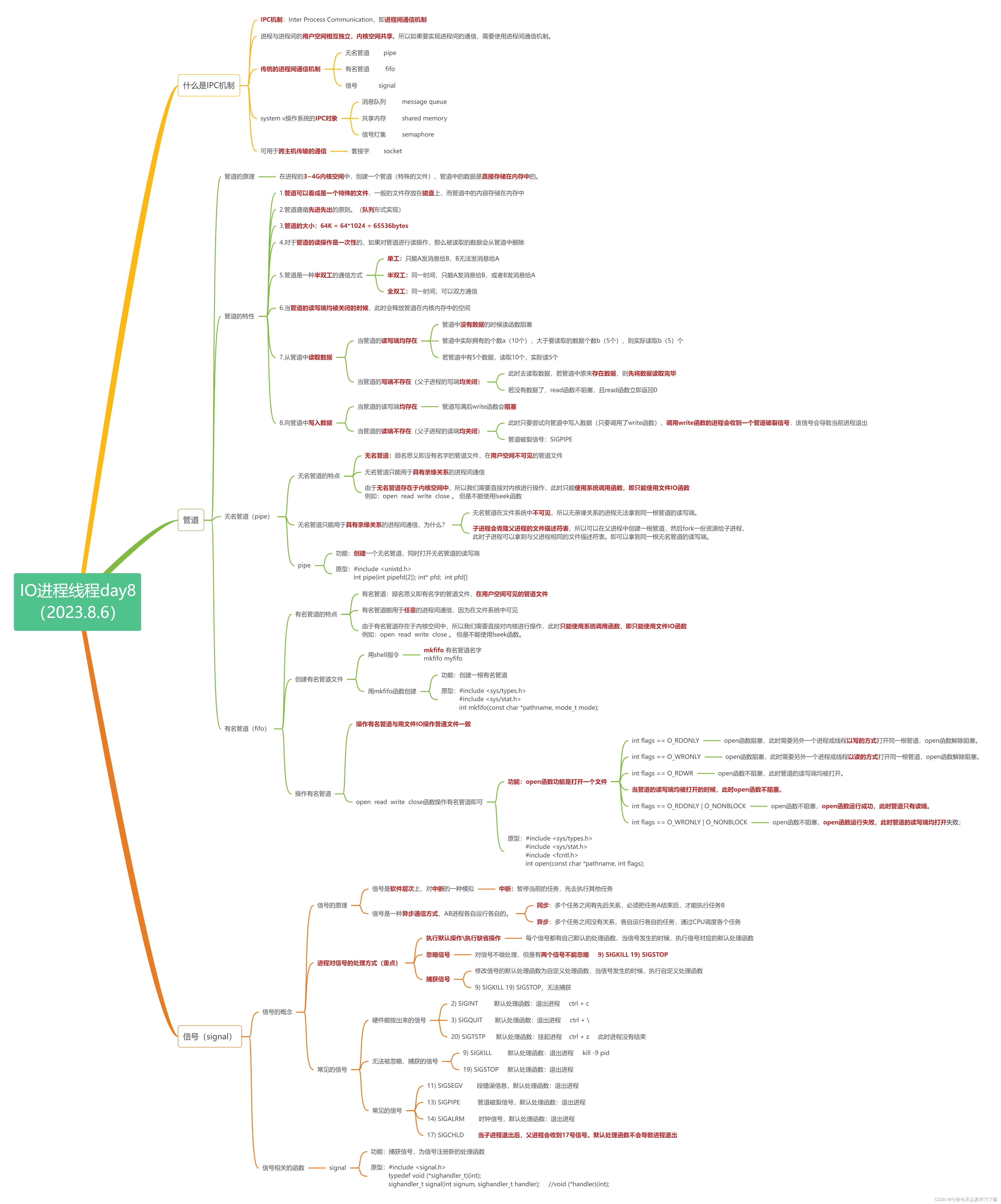
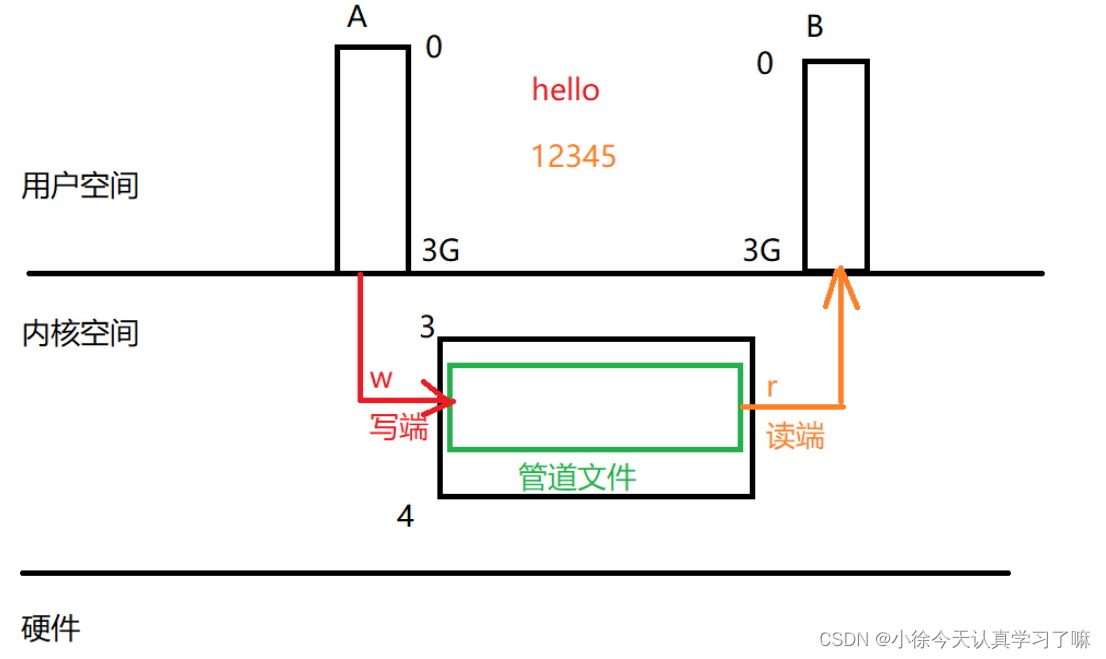
管道的原理:
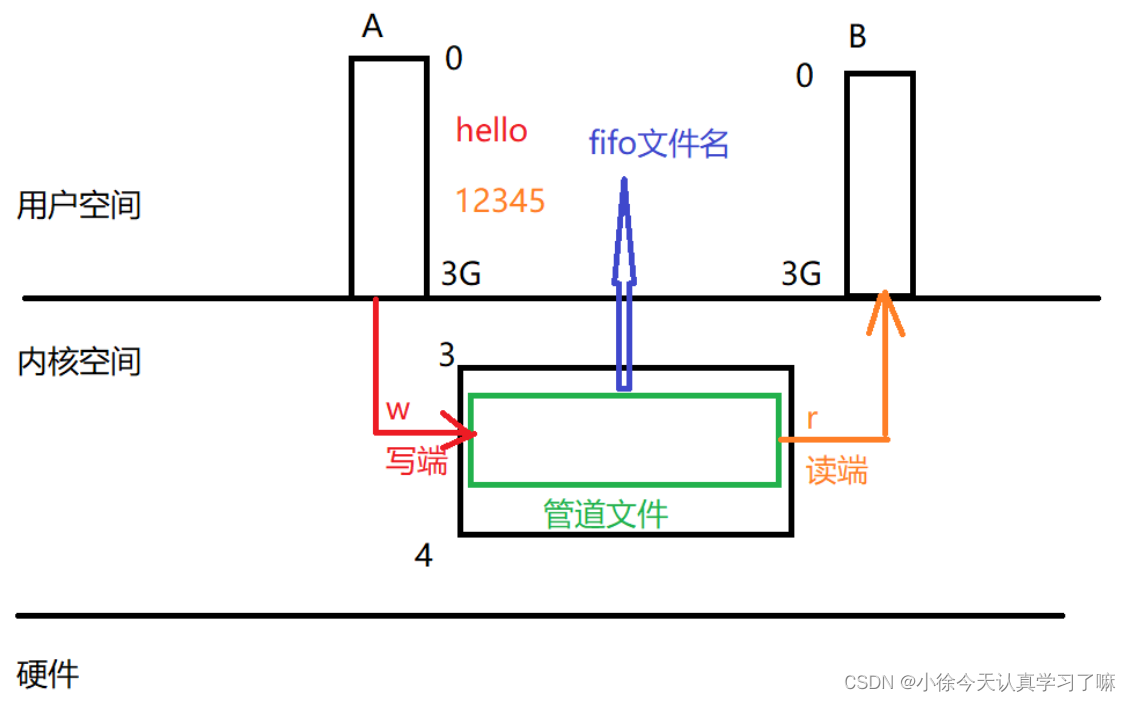
有名管道的特点:
信号的原理:

二、课上练习:
练习1:pipe
功能:创建一个无名管道,同时打开无名管道的读写端
原型:
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]); int* pfd; int pfd[]参数:
int pipefd[2]:函数运行完毕后,该参数指向的数组中会存储两个文件描述符;
pipefd[0]: 读端文件描述符;
pipefd[1]: 写端文件描述符;返回值:
成功,返回0;
失败,返回-1,更新errno;小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道的创建必须放在fork函数前//若放在fork函数后,会导致父子进程各自创建一根管道//此时会导致父子进程各自操作各自的管道,无法进行通信int pfd[2] = {0};if(pipe(pfd) < 0){perror("pfd");return -1;}printf("pipe success pfd[0]=%d pfd[1]=%d\n",pfd[0],pfd[1]);pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0) //父进程中为真{//父进程发送数据给子进程char buf[128]="";while(1){fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0; //从终端获取数据,最后会拿到\n字符,将\n字符修改成0//将数据写入到管道文件中if(write(pfd[1],buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入成功\n");}}else if(0 == cpid) //子进程中为真{//子进程读取父进程发送过来的数据char buf[128] = "";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));printf("__%d__\n",__LINE__);//当管道中没有数据的时候,read函数阻塞res = read(pfd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));printf("res=%ld : %s\n",res,buf); }}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}

练习2:mkfifo
功能:创建一根有名管道
原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);参数:
char *pathname:指定要创建的有名管道的路径以及名字;
mode_t mode:有名管道的权限:0664 0777,真实的权限 (mode & ~umask)
the permissions of the created file are (mode & ~umask)返回值:
成功,返回0;
失败,返回-1,更新errno;
errno == 17,文件已经存在的错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误练习3:操作有名管道
功能:操作有名管道与用文件IO操作普通文件一致
原型:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);参数:
int flags:O_RDONLY 只读O_WRONLY 只写O_RDWR 读写---上述三种必须,且只能包含一种---O_NONBLOCK 非阻塞1.int flags == O_RDONLY
open函数阻塞,此时需要另外一个进程或线程以写的方式打开同一根管道,open函数解除阻塞
2.int flags == O_WRONLY
open函数阻塞,此时需要另外一个进程或线程以读的方式打开同一根管道,open函数解除阻塞
3.int flags == O_RDWR
open函数不阻塞,此时管道的读写端均被打开
当管道的读写端均被打开的时候,此时open函数不阻塞
4.int flags == O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK
open函数不阻塞,open函数运行成功,此时管道只有读端
5.int flags == O_WRONLY | O_NONBLOCK
open函数不阻塞,open函数运行失败,此时管道的读写端均打开失败
示例:
读端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{umask(0);if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0777) < 0){//printf("errno = %d\n", errno);if(errno != 17) //17 == EEXIST{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("create FIFO success\n");//open函数阻塞int fd = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open FIFO rdonly success fd=%d\n", fd);char buf[128] = "";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));res = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1; }else if(0 == res){printf("对端关闭\n");break;}printf("%ld :%s\n", res, buf);}close(fd);return 0;
}写端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{umask(0);if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0777) < 0){ //printf("errno = %d\n", errno);if(errno != 17) //17 == EEXIST{perror("mkfifo");return -1; }} printf("create FIFO success\n");//open函数阻塞int fd = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY);if(fd < 0){ perror("open");return -1; } printf("open FIFO wronly success fd=%d\n", fd);char buf[128] = ""; while(1){ printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1; }printf("写入成功\n");} close(fd);return 0;
}小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");/*int fd = open("./fifo",O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd = %d\n",fd);
*/int fd_r = open("./fifo",O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK);if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);int fd_w = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY|O_NONBLOCK);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w = %d\n",fd_w);return 0;
}

练习4:常见的信号
练习5:signal
功能:捕获信号,为信号注册新的处理函数
原型:
#include <signal.h>
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler); //void (*handler)(int);参数:
int signum:指定要捕获的信号对应的编号。可以填编号,也可以填对应的宏。2) SIGINT
sighandler_t handler:函数指针,回调函数;
1) SIG_IGN:忽略信号; 9) 19)号信号无法忽略;
2) SIG_DFL:执行默认操作;
3) 传入一个函数的首地址,代表捕获信号,且该函数的返回值必须是void类型,参数列表必须是int类型,例如:void handler(int sig){ }typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int); typedef void (*)(int) sighandler_t;
typedef 旧的类型名 新的类型名;
typedef int uint32_t; int a ----> uint32_t a;
typedef int* pint; int* pa ---> pint pa;
typedef void (*)(int) sighandler_t; void (*ptr)(int) ----> sighandler_t ptr;返回值:
成功,返回该信号的上一个信号处理函数的首地址; 默认处理函数的首地址获取不到,返回NULL;
失败,返回SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t)-1),更新errno; 小练:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <head.h>
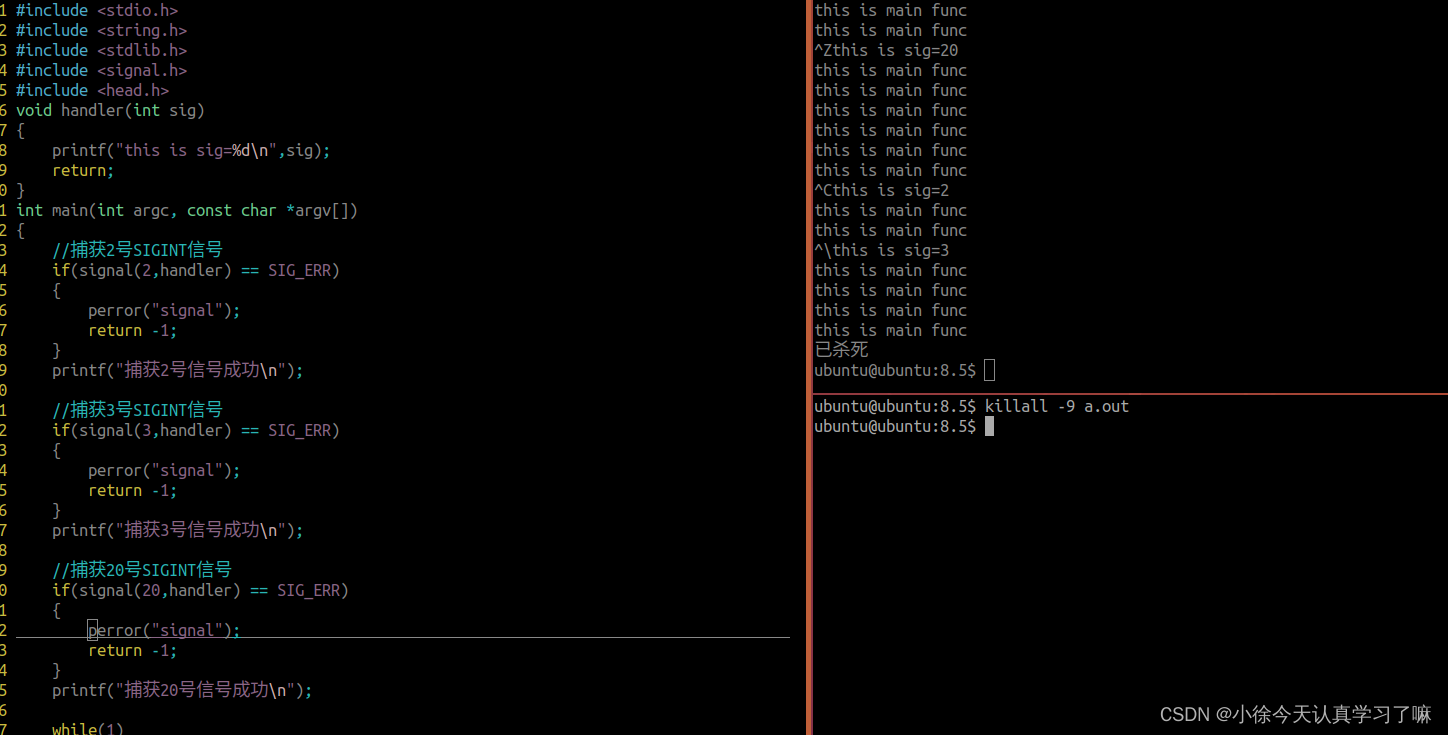
void handler(int sig)
{printf("this is sig=%d\n",sig);return;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//捕获2号SIGINT信号if(signal(2,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获2号信号成功\n");//捕获3号SIGINT信号if(signal(3,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获3号信号成功\n");//捕获20号SIGINT信号if(signal(20,handler) == SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("捕获20号信号成功\n");while(1){printf("this is main func\n");sleep(1);}return 0;
}
三、课后作业:
1.要求实现AB进程对话
A进程先发送一句话给B进程,B进程接收后打印
B进程再回复一句话给A进程,A进程接收后打印
重复1.2步骤,当收到quit后,要结束AB进程
提示:两根管道
A进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo1 success\n");int fd_r= open("./fifo",O_RDONLY);if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);int fd_w = open("./fifo1",O_WRONLY);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w= %d\n",fd_w);//从管道中读取数据,打印到终端上char buf[128]="";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//当管道的读写端均存在,若管道中没有数据,则read函数阻塞res = read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0){write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf));break;}if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}if(0 == res){printf("写端关闭\n");break;}printf("res =%ld\n输出:%s\n",res,buf);bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));printf("请输入:");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';if(write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf))< 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入数据成功 res =%ld\n",res);}close(fd_r);close(fd_w);return 0;
}
B进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <head.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//创建有名管道if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1",0664) < 0){//printf("%d\n",errno);if(errno != 17) //17:文件已经存在错误,这是一个允许存在的错误,忽略该错误{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo1 success\n");int fd_w = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY);if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_w= %d\n",fd_w);int fd_r= open("./fifo1",O_RDONLY); if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open success fd_r = %d\n",fd_r);//从终端获取数据,写到管道中char buf[128]="";ssize_t res = 0;while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));printf("请输入:");fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0){write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf));break;}if(write(fd_w,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}printf("写入数据成功 res =%ld\n",res);bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//当管道的读写端均存在,若管道中没有数据,则read函数阻塞res = read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}if(0 == res){printf("写端关闭\n");break;}printf("res =%ld\n输出:%s\n",res,buf);}close(fd_w);close(fd_r);return 0;
}
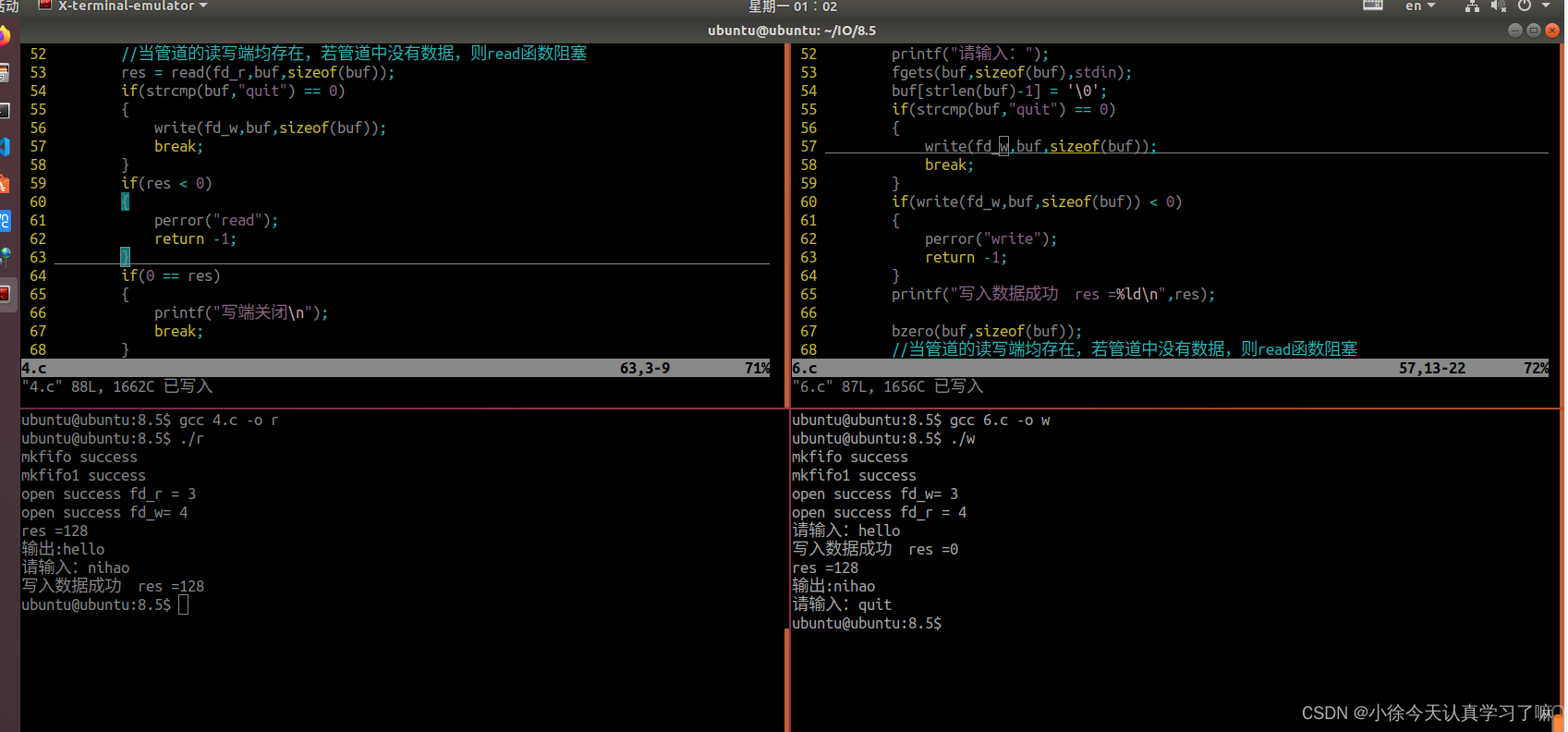
2.在第1题的基础上实现,A能随时发信息给B,B能随时接收A发送的数据,反之亦然。
A进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0775) < 0) //当前进程写该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo create success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1", 0775) < 0) //当前进程读该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo1 create success\n");//创建一个子进程pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0){//读 fifo1int fd_r = open("./fifo1", O_RDONLY); //阻塞if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo rdonly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//读写段均存在,且管道中没有数据,该函数阻塞res = read(fd_r, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("对端进程退出\n");break; }printf("res=%ld : buf=%s\n", res, buf);if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_r);kill(cpid, 9);wait(NULL);}else if(0 == cpid){//写 fifoint fd_w = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY); //阻塞if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo wronly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));// printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd_w, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}// printf("写入成功\n");if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_w);kill(getppid() , 9);}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}
B进程:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./fifo", 0775) < 0) //当前进程写该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo create success\n");if(mkfifo("./fifo1", 0775) < 0) //当前进程读该管道{if(17 != errno) //#define EEXIST 17{perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("fifo1 create success\n");//创建一个子进程pid_t cpid = fork();if(cpid > 0){//读 fifoint fd_r = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY); //阻塞if(fd_r < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo rdonly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//读写段均存在,且管道中没有数据,该函数阻塞res = read(fd_r, buf, sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("对端进程退出\n");break; }printf("res=%ld : buf=%s\n", res, buf);if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_r);kill(cpid, 9);wait(NULL);}else if(0 == cpid){//写 fifo1int fd_w = open("./fifo1", O_WRONLY); //阻塞if(fd_w < 0){perror("open");return -1;}printf("open fifo wronly success __%d__\n", __LINE__);char buf[128] = "";while(1){bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));//printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd_w, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}// printf("写入成功\n");if(!strcmp(buf, "quit"))break;}close(fd_w);kill(getppid() , 9);}else{perror("fork");return -1;}return 0;
}


