Flink CEP(二) 运行源码解析
通过DemoApp学习一下,CEP的源码执行逻辑。为下一篇实现CEP动态Pattern奠定理论基础。
1. Pattern的定义
Pattern<Tuple3<String, Long, String>,?> pattern = Pattern.<Tuple3<String, Long, String>>begin("begin").where(new IterativeCondition<Tuple3<String, Long, String>>() {@Overridepublic boolean filter(Tuple3<String, Long, String> value, Context<Tuple3<String, Long, String>> ctx)throws Exception {return value.f2.equals("success");}}).followedByAny("middle").where(new IterativeCondition<Tuple3<String, Long, String>>() {@Overridepublic boolean filter(Tuple3<String, Long, String> value, Context<Tuple3<String, Long, String>> ctx)throws Exception {return value.f2.equals("fail");}}).followedBy("end").where(new IterativeCondition<Tuple3<String, Long, String>>() {@Overridepublic boolean filter(Tuple3<String, Long, String> value, Context<Tuple3<String, Long, String>> ctx)throws Exception {return value.f2.equals("end");}});
在执行中,我们可以看到pattern的几个属性,进入Pattern类中查看。
public class Pattern<T, F extends T> {/** Name of the pattern. */private final String name;/** Previous pattern. */private final Pattern<T, ? extends T> previous;/** The condition an event has to satisfy to be considered a matched. */private IterativeCondition<F> condition;/** Window length in which the pattern match has to occur. */private final Map<WithinType, Time> windowTimes = new HashMap<>();/*** A quantifier for the pattern. By default set to {@link Quantifier#one(ConsumingStrategy)}.*/private Quantifier quantifier = Quantifier.one(ConsumingStrategy.STRICT);/** The condition an event has to satisfy to stop collecting events into looping state. */private IterativeCondition<F> untilCondition;/** Applicable to a {@code times} pattern, and holds the number of times it has to appear. */private Times times;private final AfterMatchSkipStrategy afterMatchSkipStrategy;
}可以看到每一个Pattern都会存在以下属性:
- Name:Pattern的Name
- previous:之前的Pattern
- condition:Pattern的匹配逻辑
- windowTimes:限制窗口的时长
- Quantifier:Pattern的属性,包括配置Pattern的模式可以发生的循环次数,或者这个模式是贪婪的还是可选的。
-
/*** A quantifier describing the Pattern. There are three main groups of {@link Quantifier}.** <ol>* <li>Single* <li>Looping* <li>Times* </ol>** <p>Each {@link Pattern} can be optional and have a {@link ConsumingStrategy}. Looping and Times* also hava an additional inner consuming strategy that is applied between accepted events in the* pattern.*/ public class Quantifier {private final EnumSet<QuantifierProperty> properties;private final ConsumingStrategy consumingStrategy;private ConsumingStrategy innerConsumingStrategy = ConsumingStrategy.SKIP_TILL_NEXT; }
-
-
untilCondition:Pattern的循环匹配的结束条件
-
times:连续匹配次数
-
afterMatchSkipStrategy:匹配后的跳过策略
2.PatternStream的构建
对Pattern定义完成,会通过PatternStreamBuilder,将1中定义好的Pattern应用到输入流中,返回对应的PatternStream。
static <IN> PatternStreamBuilder<IN> forStreamAndPattern(final DataStream<IN> inputStream, final Pattern<IN, ?> pattern) {return new PatternStreamBuilder<>(inputStream, pattern, TimeBehaviour.EventTime, null, null);}PatternStream(final DataStream<T> inputStream, final Pattern<T, ?> pattern) {this(PatternStreamBuilder.forStreamAndPattern(inputStream, pattern));}继续执行代码,进入Select()。
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> select(final PatternSelectFunction<T, R> patternSelectFunction,final TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo) {final PatternProcessFunction<T, R> processFunction =fromSelect(builder.clean(patternSelectFunction)).build();return process(processFunction, outTypeInfo);}进入process可以看到PatternStream.select会调用builder.build函数。
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> process(final PatternProcessFunction<T, R> patternProcessFunction,final TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo) {return builder.build(outTypeInfo, builder.clean(patternProcessFunction));}在build函数中会完成NFAFactory的定义,随后构建CepOperator。inputstream随之运行CepOperator即pattern定义的处理逻辑,并返回结果流PatternStream。
<OUT, K> SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> build(final TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,final PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT> processFunction) {checkNotNull(outTypeInfo);checkNotNull(processFunction);final TypeSerializer<IN> inputSerializer =inputStream.getType().createSerializer(inputStream.getExecutionConfig());final boolean isProcessingTime = timeBehaviour == TimeBehaviour.ProcessingTime;final boolean timeoutHandling = processFunction instanceof TimedOutPartialMatchHandler;final NFACompiler.NFAFactory<IN> nfaFactory =NFACompiler.compileFactory(pattern, timeoutHandling);CepOperator<IN, K, OUT> operator = new CepOperator<>(inputSerializer,isProcessingTime,nfaFactory,comparator,pattern.getAfterMatchSkipStrategy(),processFunction,lateDataOutputTag);final SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> patternStream;if (inputStream instanceof KeyedStream) {KeyedStream<IN, K> keyedStream = (KeyedStream<IN, K>) inputStream;patternStream = keyedStream.transform("CepOperator", outTypeInfo, operator);} else {KeySelector<IN, Byte> keySelector = new NullByteKeySelector<>();patternStream =inputStream.keyBy(keySelector).transform("GlobalCepOperator", outTypeInfo, operator).forceNonParallel();}return patternStream;}3.CepOperator的执行
初始化。
@Overridepublic void open() throws Exception {super.open();timerService =getInternalTimerService("watermark-callbacks", VoidNamespaceSerializer.INSTANCE, this);nfa = nfaFactory.createNFA();nfa.open(cepRuntimeContext, new Configuration());context = new ContextFunctionImpl();collector = new TimestampedCollector<>(output);cepTimerService = new TimerServiceImpl();// metricsthis.numLateRecordsDropped = metrics.counter(LATE_ELEMENTS_DROPPED_METRIC_NAME);}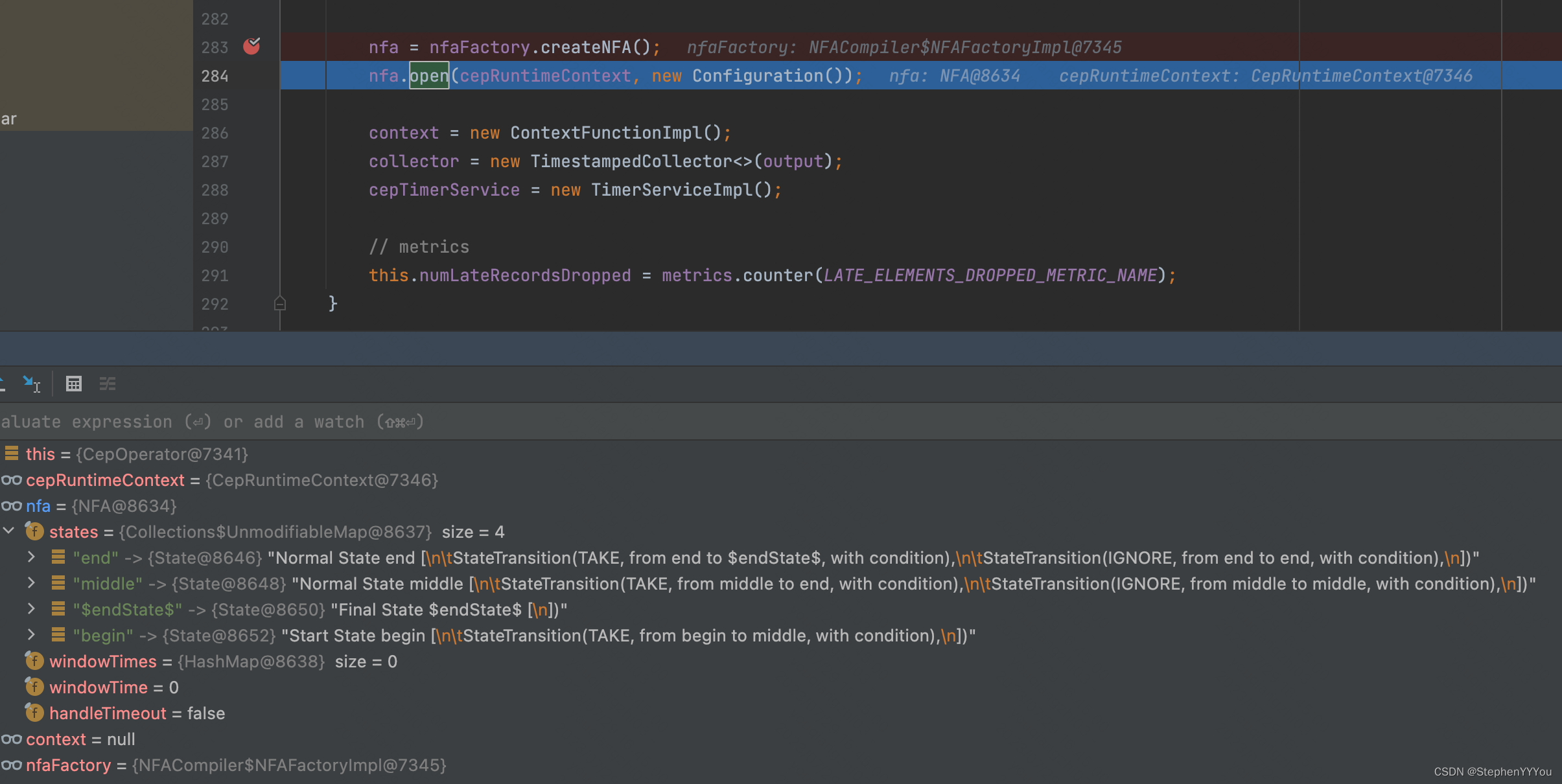
可以看到,nfaFactory.createNFA();会解析pattern组合,并为每一个pattern创建一个state。
CepOperator会在processElement中处理流中的每条数据。
@Overridepublic void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {if (isProcessingTime) {if (comparator == null) {// there can be no out of order elements in processing timeNFAState nfaState = getNFAState();long timestamp = getProcessingTimeService().getCurrentProcessingTime();advanceTime(nfaState, timestamp);processEvent(nfaState, element.getValue(), timestamp);updateNFA(nfaState);} else {long currentTime = timerService.currentProcessingTime();bufferEvent(element.getValue(), currentTime);}} else {long timestamp = element.getTimestamp();IN value = element.getValue();// In event-time processing we assume correctness of the watermark.// Events with timestamp smaller than or equal with the last seen watermark are// considered late.// Late events are put in a dedicated side output, if the user has specified one.if (timestamp > timerService.currentWatermark()) {// we have an event with a valid timestamp, so// we buffer it until we receive the proper watermark.bufferEvent(value, timestamp);} else if (lateDataOutputTag != null) {output.collect(lateDataOutputTag, element);} else {numLateRecordsDropped.inc();}}}可以看到,如果使用的是处理时间,需要先对数据根据当前处理时间将乱序的数据做一次处理,保证数据的有序。
如果使用的事件时间,如果事件时间戳小于等于watermark会被认为是迟到数据。
正常数据会先被缓存起来,等待处理。
private void bufferEvent(IN event, long currentTime) throws Exception {List<IN> elementsForTimestamp = elementQueueState.get(currentTime);if (elementsForTimestamp == null) {elementsForTimestamp = new ArrayList<>();registerTimer(currentTime);}elementsForTimestamp.add(event);elementQueueState.put(currentTime, elementsForTimestamp);}elementQueueState 会以时间戳为key保存对应的数据。在onEventTime()函数中通过processEvent中处理缓存的匹配数据。
@Overridepublic void onEventTime(InternalTimer<KEY, VoidNamespace> timer) throws Exception {// 1) get the queue of pending elements for the key and the corresponding NFA,// 2) process the pending elements in event time order and custom comparator if exists// by feeding them in the NFA// 3) advance the time to the current watermark, so that expired patterns are discarded.// 4) update the stored state for the key, by only storing the new NFA and MapState iff they// have state to be used later.// 5) update the last seen watermark.// STEP 1PriorityQueue<Long> sortedTimestamps = getSortedTimestamps();NFAState nfaState = getNFAState();// STEP 2while (!sortedTimestamps.isEmpty()&& sortedTimestamps.peek() <= timerService.currentWatermark()) {long timestamp = sortedTimestamps.poll();advanceTime(nfaState, timestamp);// 对事件按时间进行排序try (Stream<IN> elements = sort(elementQueueState.get(timestamp))) {elements.forEachOrdered(event -> {try {processEvent(nfaState, event, timestamp);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}});}elementQueueState.remove(timestamp);}// STEP 3advanceTime(nfaState, timerService.currentWatermark());// STEP 4updateNFA(nfaState);} private void processEvent(NFAState nfaState, IN event, long timestamp) throws Exception {try (SharedBufferAccessor<IN> sharedBufferAccessor = partialMatches.getAccessor()) {Collection<Map<String, List<IN>>> patterns =nfa.process(sharedBufferAccessor,nfaState,event,timestamp,afterMatchSkipStrategy,cepTimerService);if (nfa.getWindowTime() > 0 && nfaState.isNewStartPartialMatch()) {registerTimer(timestamp + nfa.getWindowTime());}processMatchedSequences(patterns, timestamp);}}private void processMatchedSequences(Iterable<Map<String, List<IN>>> matchingSequences, long timestamp) throws Exception {PatternProcessFunction<IN, OUT> function = getUserFunction();setTimestamp(timestamp);for (Map<String, List<IN>> matchingSequence : matchingSequences) {function.processMatch(matchingSequence, context, collector);}}nfa.process()最后会调用doProcess进行处理。
computer
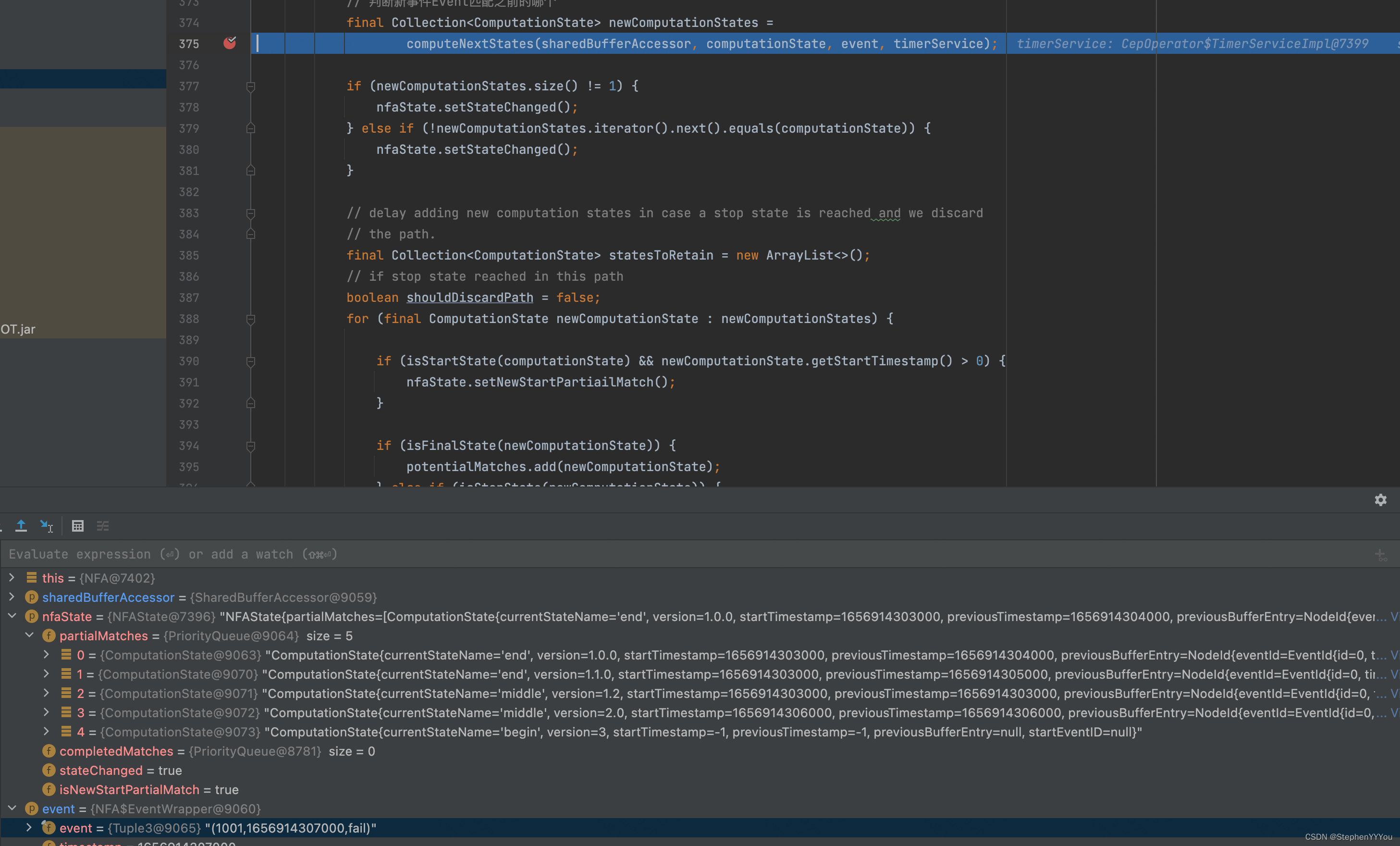
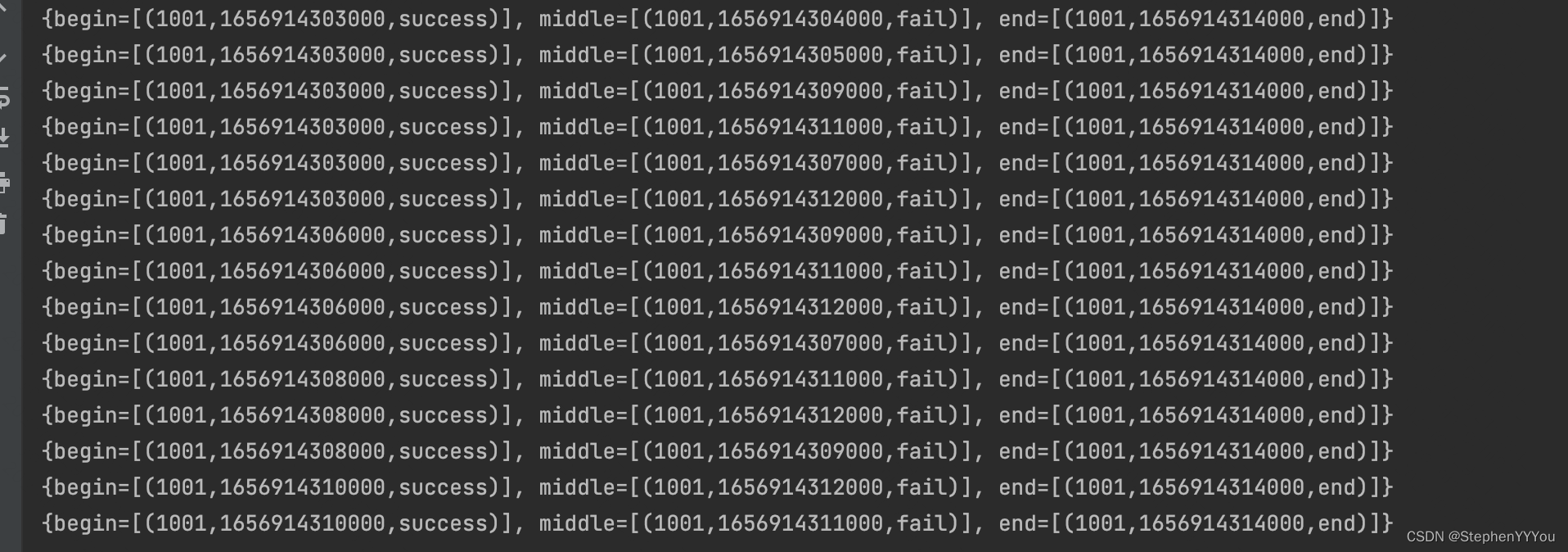
可以看到每来一个新的Event,就会从上一个数据停留的状态开始遍历。判断新事件Event匹配之前已经匹配过的哪个状态,并为其版本号+1
前5条数据是success->fail->fail->success->fail,我们可以观察到partialMatches的变化如下:
success事件到达,因为之前没有事件,所以当前停留的状态是 begin。success匹配,预期会停留在middle状态
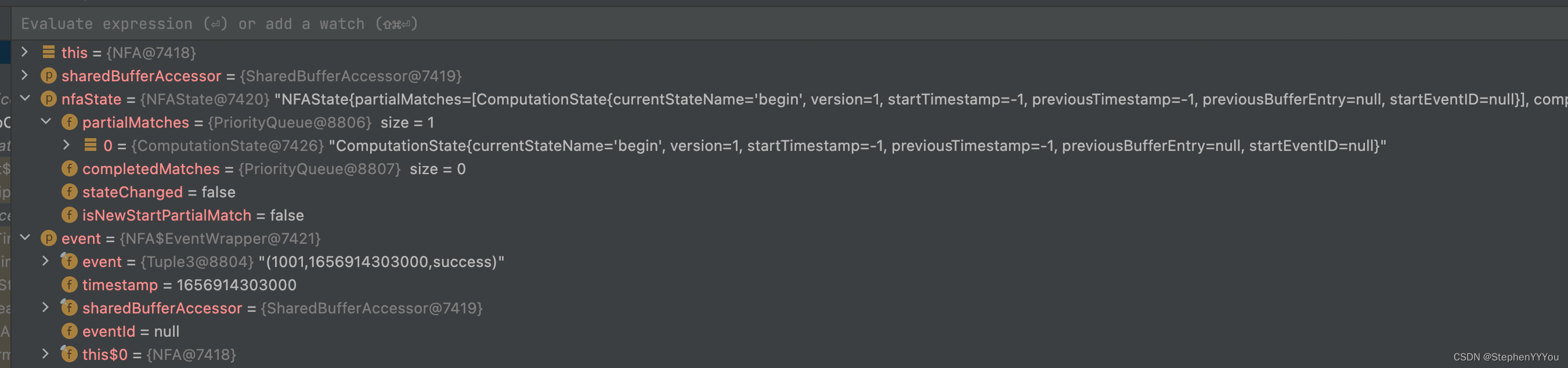
fail事件到达,可以看到上面的success事件停留在了middle状态,并且begin的版本+1.

判断这个fail事件可以匹配后续的patern,状态从middle转移到end。存在newComputationStates中。最终更新到partialMatch中。
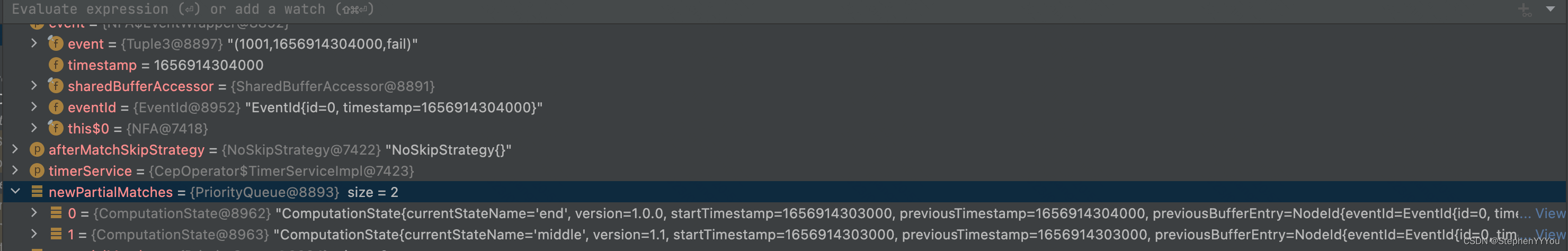
第二个fail事件到达,只能匹配之前的middle状态,所以partialMatch中会新增一个end状态,并且middle的版本+1;
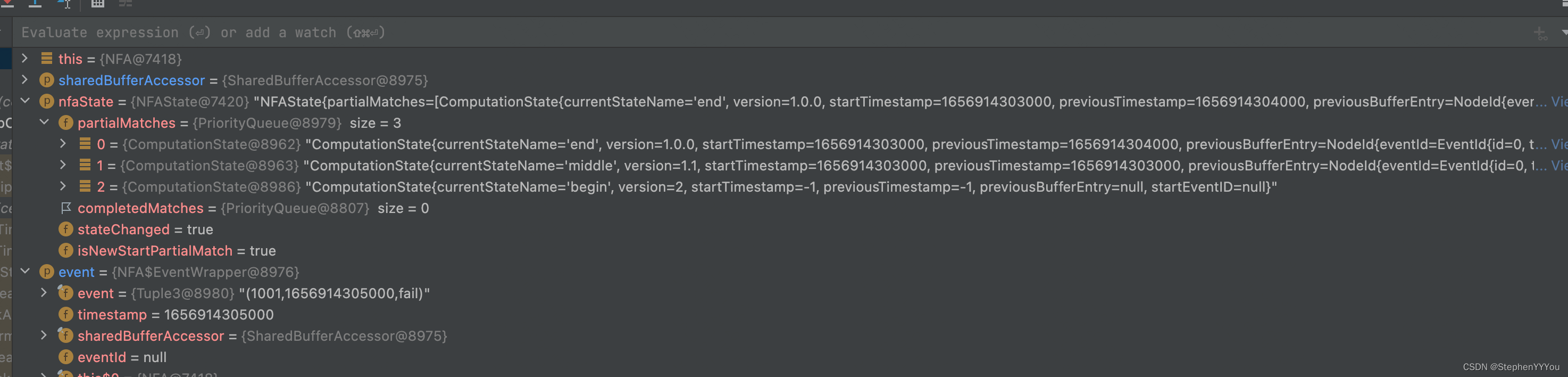
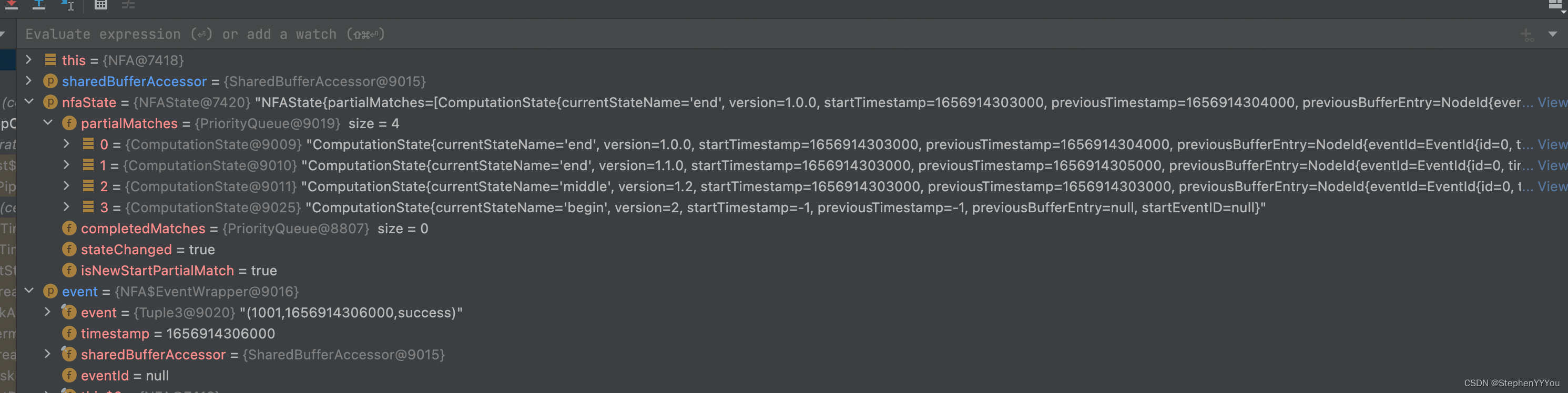
最后如果状态到达终态,输出到potentialMatches中存储。
打印结果,可以看到每个事件都会试图去匹配所有的历史状态,nfa会存储所有匹配上的历史状态,直到到达终态。