解读Spring-context的property-placeholder
在spring中,如果要给程序定义一些参数,可以放在application.properties中,通过<context:property-placeholder>加载这个属性文件,然后就可以通过@value给我们的变量自动赋值,如果你们的程序可能运行在多个环境中(比如开发、测试和生产)你也可以定义多套属性文件。这些用法我们早已司空见惯,今天我们就来理一下来龙去脉。
context:property-placeholder
用法
<context:property-placeholder>的主要属性:
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| location | 文件位置,多个之间通过如逗号/分号等分隔; |
| file-encoding | 文件编码 |
| ignore-resource-not-found | 如果属性文件找不到,是否忽略,默认false,即不忽略,找不到将抛出异常 |
| ignore-unresolvable | 是否忽略解析不到的属性,如果不忽略,找不到将抛出异常 |
| properties-ref | 本地java.util.Properties配置 |
| local-override | 是否本地覆盖模式,即如果true,本地属性文件的优先级高于环境变量 |
| system-properties-mode | 系统属性模式 ENVIRONMENT(默认), FALLBACK(环境变量兜底) NEVER(不使用环境变量) OVERRIDE(环境变量覆盖) |
历史渊源
要说清楚这个标签,涉及spring3.1这个重要版本,从这个版本起,spring抽象了Environment接口,这个标签的处理器也从PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer被过渡到PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer(下面细讲)。
关于system-properties-mode属性
在3.1之前,只有三个取值,当时的处理器还是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,这个处理现在已经不推荐使用,这个变量的作用是:声明对系统属性和环境变量的使用方式。
| 属性值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NEVER | 不使用系统属性和环境变量 |
| OVERRIDE | 使用系统属性和环境变量覆盖属性文件 即系统属性和环境变量优先 |
| FALLBACK | 使用系统属性和环境变量来做兜底 即属性文件优先 |
在3.1之后,多了一个新的取值Environment,spring从这个版本起引入了Environment接口,如果system-properties-mode属性被配置为Environment,则使用采用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer进行占位符处理,这也是3.1之后的默认处理方式。
见PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser:
@Overrideprotected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {//system-properties-mode设置为ENVIRONMENT,则走PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurerif (SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT.equals(element.getAttribute(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIBUTE))) {return PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class;}//否则走PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(兼容处理)return PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class;}各种配置的优化级
由于system-properties-mode只推荐使用ENVIRONMENT,其它三种方式只是保持对老版本spring的兼容,这里主要分析在ENVIRONMENT模式下,属性文件,properties-ref,系统属性,环境变量的优先级
| local-override属性值 | 优先级 |
|---|---|
| false | System.getProperty()>System.getenv()> location属性文件>properties-ref |
| true | properties-ref>location属性文件>System.getProperty()>System.getenv() |
默认情况下,系统属性和环境变量一起构成StandardEnvironment,系统属性优先于环境变量。
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {/** System environment property source name: {@value}. */public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value}. */public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";//加入(定义)两个PropertySource:这个是系统属性,一个是环境变量@Overrideprotected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {propertySources.addLast(new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));}}PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer维护一个MutablePropertySources,该对象放着两个PropertySource,一个对Environment做了一个包装,一个是合并本地的属性文件配置。并local-override的配置的不同,决定这两个PropertySource的优先级:
#postProcessBeanFatcory
作为一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,该方法会在Bean实例化之前被spring容器调用
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {if (this.propertySources == null) {this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();if (this.environment != null) {this.propertySources.addLast(//将Environment封装成一个新的PropertySource,后面的占位符处理将委托给Environment对象new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {@Override@Nullablepublic String getProperty(String key) {return this.source.getProperty(key);}});}try {//合并properties-ref和location的属性合并,并统称为localPropertiesPropertySource<?> localPropertySource =new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());if (this.localOverride) {//如果本地覆盖,则将本地属性放在首位(优先)this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);}else {//否则将本地属性放在未位this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);}}catch (IOException ex) {throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);}}//处理属性占位符,这里只是将占位符处理器注入给到BeanFactoryprocessProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources));this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources;}#mergeProperties
mergeProperties方法:合并location指向的属性文件和properties-ref指向的配置对象。如果全地覆盖,则使用properties-ref覆盖location的配置,否则相反。其中loadProperties是加载location指定的属性文件,并解析代析Properties对象,代码略
protected Properties mergeProperties() throws IOException {Properties result = new Properties();if (this.localOverride) {// 如果本地覆盖,则先加载location指定的属性文件loadProperties(result);}if (this.localProperties != null) {//如果定义了properties-ref属性,则进行属性合并for (Properties localProp : this.localProperties) {CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(localProp, result);}}if (!this.localOverride) {//如果非本地覆盖,则最后加载location指定的属性文件loadProperties(result);}return result;}#processProperties
进入processProperties方法:ConfigurablePropertyResolver 最终被转换成StringValueResolver,然后调用doProcessProperties。
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));if (this.trimValues) {resolved = resolved.trim();}return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved);};doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);}#doProcessProperties
进入doProcessProperties,该方法进行处理BeanDefinition中的各种占位符,最后把StringValueResolver注入给beanFactory,供属性代替使用,后面会讲到。
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,StringValueResolver valueResolver) {BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();for (String curName : beanNames) {if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);try {//处理BeanDefinition中的各种占位符(注意:不是bean本身)visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);}catch (Exception ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);}}}beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);//在这里把StringValueResolver注入给beanFactory,供属性代替使用beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);}相关接口说明
PropertyResolver接口
在PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer中会创建PropertyResolver接口对象,该对象持有配置属性源的引用,并提供获取属性值,处理占位符等功能。详见:PropertySourcesPropertyResolver这里只列出接口的定义:
public interface PropertyResolver {boolean containsProperty(String key);@NullableString getProperty(String key);//获取属性值String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);@Nullable<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;String resolvePlaceholders(String text);//处理占位符String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}Environment
Environment接口是Spring体系里一个既熟悉又陌生的接口。
Spring 3.1 开始引入 Environment 抽象,它统一 Spring 配置属性的存储、占位符处理和类型转换,支持更丰富的配置属性源(PropertySource)。
条件化 Spring Bean 装配管理:
通过 Environment Profiles 信息,帮助 Spring 容器提供条件化地装配 Bean。
@Profile
在spring应用中,通常会通过变量spring.profiles.active去指定当前环境,而注解@Profile可以加上Bean上,让Bean在某个环境中生效,其实现通过@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class),这里不展开。
Environment接口继承自PropertyResolver,同时扩展了对profile的操作,通过profile来标识当前处于哪个环境(开发、测试或生产)
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {//获取当前profile(环境)String[] getActiveProfiles();String[] getDefaultProfiles();@Deprecatedboolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);//判断当前环境是否与给定profiles一致boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}AbstractEnvironment
结合抽象类AbstractEnvironment,可以更好地理解Environment的行为
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {//维护当前活动的profile环境private final Set<String> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>();private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(getReservedDefaultProfiles());//维护各种配置属性源private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();//持有占位符处理器private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
}AbstractEnvironment由于知道当前是哪个环境,就知道需要装载哪些配置文件,而MutablePropertySources是可变的PropertySources,它允许用户动态地添加各种PropertySource,比如来自配置中心的配置。最后由propertyResolver完成最后的占位符处理操作。
PropertySource
属性源就是对一类配置(可以是属性配置文件,系统属性,环境变量等)的封装,同时给这个配置一个名称
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {protected final String name;//名称protected final T source;//配置,存放键值对...}MapPropertySource:一种基于Map实现的简单的PropertySource。
public class MapPropertySource extends EnumerablePropertySource<Map<String, Object>> {public MapPropertySource(String name, Map<String, Object> source) {super(name, source);}@Override@Nullablepublic Object getProperty(String name) {return this.source.get(name);}@Overridepublic boolean containsProperty(String name) {return this.source.containsKey(name);}@Overridepublic String[] getPropertyNames() {return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.source.keySet());}}只要你喜欢,你可以把Map当做你的配置源,也就是说你可以把创建一个Map作为应用程序的配置。一些主要的PropertySource.
| PropertySource 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| org.springframework.core.env.CommandLinePropertySource | 命令行配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.jndi.JndiPropertySource | JDNI 配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource | 基于Map对象的配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource | 扩展自MapPropertySource, Properties 配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletConfigPropertySource | Servlet 配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextPropertySource | ServletContext 配置属性源 |
| org.springframework.core.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySource | 环境变量配置属性源 |
其中PropertiesPropertySource扩展自MapPropertySource,我们的系统属性,以及我们属性配置文件,最终会被封装成PropertiesPropertySource,其它配置属性源请自行脑补。
PropertySources
PropertySources是PropertySource的集合,是一个继承自Iterable的接口,提供了一些方便操作属性源的方法:
- addFirst():将属性源放在首位,即优先级最高
- addLast():将属性源放在未位,即优先级最低
MutablePropertySources
PropertySources有一个唯一的实现:MutablePropertySources。该实现就是Environment对象里的可变属性源,基于该对象,可以实现PropertySource的动态地添加,并按需对属性源进行优先级排序。
注:在spring中有对应的注解,如@PropertySource和@PropertySources可以以注解的形成来配置属性源,随着applicationContext.xml慢慢被摈弃,正逐渐代替<context:property-placeholder>,这里不展开。
如何动态添加属性源
通过调用ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment可以获得到Environment引用,再把自己扩展的PropertySource添加到它的MutablePropertySources里面。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = context.getEnvironment();
MapPropertySource mapPropertySource = new MapPropertySource("my-map-properties", new HashMap<>());
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
propertySources.addFirst(mapPropertySource);@Value的实现
上面讲了Enviroment抽象以及属性源优先级,下面讲@Value注释如何实现属性值的替换。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
多数人对@Value这一块并不陌生,主要的实现就是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,该BeanPostProcessor主要处理@Value和@Autowired注解。这里就不贴代码了,大概流程如下:
spring容器在创建完Bean对象实现实例之后,进入属性注入阶段会回postProcessPropertyValues方法(BeanPostProcessor的回调机制),进而会调用beanFactory.resolveDependency(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,持有beanFactory对象引用)
DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);try {Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);if (shortcut != null) {return shortcut;}Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);if (value != null) {if (value instanceof String) {//这里处理属性值String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);}//对属性值做类型转换TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());try {return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());}catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...return (descriptor.getField() != null ?converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));}}
...
}
2)beanFactory.resolveDependency的主要作用是处理属性依赖,可以处理对象的注入也可以处理属性值的注入。如果是@Value属性值注入,则进行占位符处理,而在BeanFactory里,处理占位符的对象是StringValueResolver,BeanFactory维护多个StringValueResolver:
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {if (value == null) {return null;}String result = value;//这里的StringValueResolver有一个是PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer注入的for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);if (result == null) {return null;}}return result;}BeanFactory对属性值的处理就是交给多个StringValueResolver去循环处理,这里的StringValueResolver有一个是PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer注入的,可回头看PlaceholderConfigurerSupport#doProcessProperties。
StringValueResolver接口
回到StringValueResolver接口,该接口只做一件事,那就是做占位符处理(将一个字符串转成另一个字符串)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface StringValueResolver {@NullableString resolveStringValue(String strVal);}那问题来了,为何BeanFactory不直接持有PropertyResolver对象,而要使用新的接口呢?
这里要说明的是PropertyResolver接口是spring3.1才引入的,而StringValueResolver则在spring2.5就已经存在,一方面BeanFactory原先持有的就是StringValueResolver,另一个方面这突显了接口设计的单一原则,因为对于BeanFactory而言,就仅仅是想得到目标的属性值。因而也就没有必要换成PropertyResolver接口。
总结
回顾<context:property-placeholder>和@Value的整个过程:
1)自spring3.1起,采用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer维护一个聚合了Environment(环境变量和系统属性)和本地属性文件的配置,将Environment包装成一个新的PropertySource中。
2)PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer维护一个MutablePropertySources,该对象放着两个PropertySource,一个对Environment做了一个包装,一个是合并本地的属性文件配置。并local-override的配置的不同,决定这两个PropertySource的优先级
3)PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer创建了PropertyResolver接口对象,并适配成StringValueResolver接口,传递给BeanFactory,由于PropertyResolver对象持有MutablePropertySources引用,因此这个MutablePropertySources对BeanFactory可见。
4)BeanFactory维护着一系列StringValueResolver对象,并提供处理对象依赖(包括属性值)的能力。
5)属性值注入阶段,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor通过调用BeanFactory的doResolveDependency实现属性注入,内部调用StringValueResolver进行属性值处理,而本质上就是调用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的PropertyResolver,最终使用的也是PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer中的的MutablePropertySources。
6)得益于Environment的MutablePropertySources,应用可以更灵活地管理各种配置及其优先级。
最后献上一个类图:
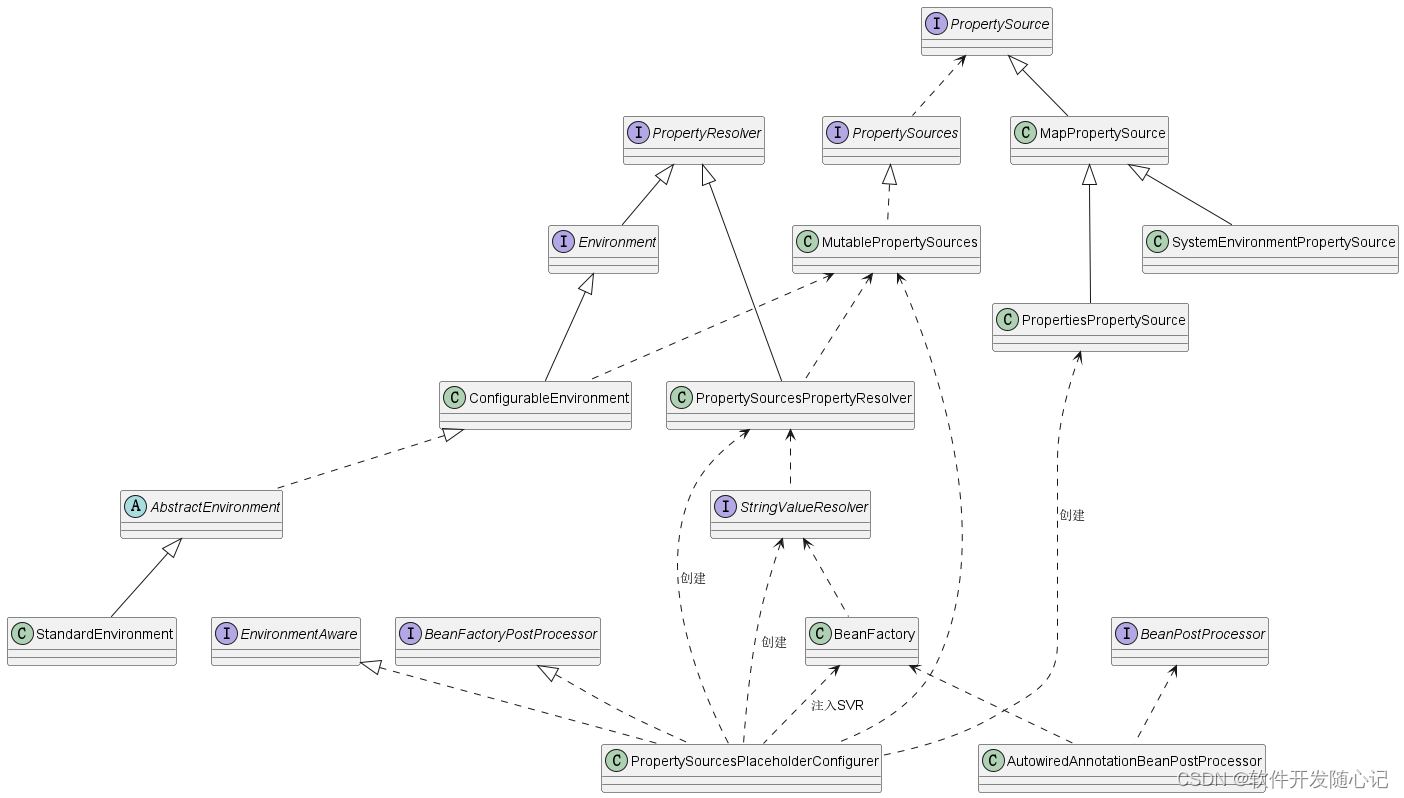
by simple
