【linux kernel】一文总结linux内核通知链
文章目录
- 1、通知链简介
- 2、通知链的类型
- 3、原理分析和API
- (1)注销通知器
- (2)注销通知器
- (3)通知链的通知
- 4、实例代码
- (1)定义一个通知链
- (2)实现观察者模块
- (3)事件发生模块
- (4)输出结果
内核源码中相关文件
- /kernel/notifier.c
- /include/linux/notifier.h
1、通知链简介
文本基于内核源码
4.19.4描述构成通知链的具体数据结构和API接口,同时描述四种通知链的具体应用场景,并对API接口进行简要分析。
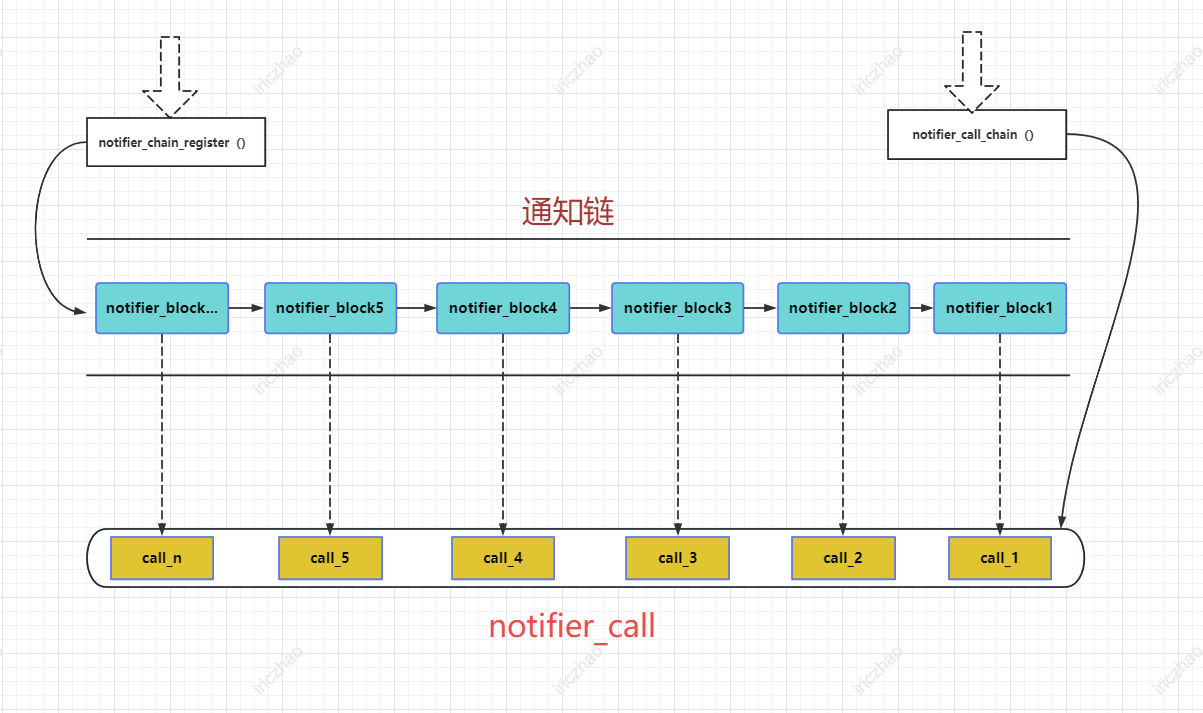
在Linux内核中,struct notifier_block 是一种数据结构,用于实现观察者模式。它允许内核的不同部分将自己注册为监听器(观察者)以侦听特定事件。当这些事件发生时,内核会通知所有注册的notifier block,它们可以对事件做出适当的响应。
struct notifier_block 在Linux内核头文件 include/linux/notifier.h 中定义,并具有以下结构:
struct notifier_block {int (*notifier_call)(struct notifier_block *nb, unsigned long action, void *data);struct notifier_block *next;int priority;
};
-
notifier_call:这个字段指向在通知事件发生时将被调用的回调函数。回调函数的函数签名定义为int (*notifier_call)(struct notifier_block *nb, unsigned long action, void *data)。nb参数是指向 notifier block 本身的指针,action包含通知类型,而data则是指向与事件相关的附加数据的指针。 -
next:这个字段是指向链中下一个 notifier block 的指针。Linux内核维护一个已注册的 notifier block 的链表,该字段使得可以遍历整个链表。 -
priority:这个字段决定了该 notifier block 相对于其他已注册 notifier block 的优先级。当多个块为同一事件注册时,内核按照优先级降序通知它们。具有较高优先级值的 notifier block 将在具有较低优先级值的之前收到通知。
要使用 struct notifier_block,内核模块可以使用Linux内核提供的函数进行注册,例如register_inotifier() 或 register_netdevice_notifier(),具体取决于特定的事件类别。
一些常见的利用 struct notifier_block 的事件包括:
- 文件系统事件,如文件创建、删除和修改。
- 网络设备事件,如接口的启用或禁用。
- 内存管理事件,如页面分配和释放。
通过使用 struct notifier_block,内核开发人员可以更好地设计模块化和可扩展的系统,让不同的组件以解耦的方式对事件做出响应。这种模式有助于更好地组织代码,并且在不影响现有代码的情况下更容易添加新功能到内核中。
整个结构如下图所示:
2、通知链的类型
在linux内核中,定义了四种类型的通知链。
- (1)原子(Atomic)通知链
定义如下:

原子通知链在内核中广泛应用,特别是在一些基本的通知机制中。这种通知链的处理是原子的,意味着在处理链上的通知时,不会被中断或其他并发操作干扰。原子通知链的应用场景包括进程退出通知、进程停止通知、以及内核调试和跟踪事件通知等。
- (2)阻塞(Block)通知链
定义如下:

阻塞通知链用于一些需要等待通知链中所有处理器完成后才能继续执行的场景。当某个处理器在链上发起通知后,阻塞通知链将等待所有处理器都完成其任务后才返回。阻塞通知链的应用场景包括内核模块的初始化,其中一个模块可能需要等待其他模块完成初始化后才能继续执行。
- (3)原始(RAW)通知链
定义如下:

原始通知链是一种特殊类型的通知链,它没有任何同步机制。这意味着在处理通知链时,不进行任何锁定或同步操作,这可能会导致并发问题。原始通知链主要用于一些低层的底层通知机制,通常需要使用者自己确保线程安全性。原始通知链的应用场景相对较少,可能只在一些特定的高性能场景中使用。
- (4)SRCU通知链
定义如下:

SRCU通知链是通过Linux内核中的SRCU(Synchronize RCUs)机制来实现的。SRCU通知链提供了更高级的同步机制,以确保在删除或释放通知处理器时,不会出现竞态条件。这允许在通知链上安全地添加和删除处理器。SRCU通知链的应用场景包括网络设备事件通知,其中多个处理器可能对事件做出响应,并且需要在处理器安全删除时保持同步。
3、原理分析和API
(1)注销通知器
在使用通知链之前,需要创建对应类型的通知链,并使用注册进行注册,从源码角度,每种类型的通知链都一一对应着一个注册函数:
-
原子通知链注册函数:
int atomic_notifier_chain_register(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb)。 -
阻塞通知链注册函数:
int atomic_notifier_chain_register(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb)。 -
原始通知链注册函数:
int atomic_notifier_chain_register(struct raw_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb)。 -
srcu通知链注册函数:
int atomic_notifier_chain_register(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb)。
上述四种类型的注册函数本质上是调用notifier_chain_register()函数实现核心功能,该函数实现如下:
static int notifier_chain_register(struct notifier_block **nl,struct notifier_block *n)
{while ((*nl) != NULL) {if (n->priority > (*nl)->priority)break;nl = &((*nl)->next);}n->next = *nl;rcu_assign_pointer(*nl, n);return 0;
}
上述代码是一个根据优先级进行循环遍历的操作,如果n的优先级比*nl的优先级高那么循环结束,接着就将n插入到*nl的前面。形成通知链。
(2)注销通知器
有注册函数,则对应着注销函数,四种通知链的注销函数是:
- 原子通知链注销函数:
int atomic_notifier_chain_unregister(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb); - 阻塞通知链注销函数:
int blocking_notifier_chain_unregister(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb); - 原始通知链注销函数:
int raw_notifier_chain_unregister(struct raw_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb); - srcu通知链注销函数:
int srcu_notifier_chain_unregister(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh,struct notifier_block *nb);
上述四种类型的注册函数本质上是调用notifier_chain_unregister()函数实现核心功能,该函数实现如下:
static int notifier_chain_unregister(struct notifier_block **nl,struct notifier_block *n)
{while ((*nl) != NULL) {if ((*nl) == n) {rcu_assign_pointer(*nl, n->next);return 0;}nl = &((*nl)->next);}return -ENOENT;
}
循环判断找到了要注销的然后执行注销,将其从链表中移除。
(3)通知链的通知
通常,通知链的注册是由各个模块在内核初始化阶段进行的。当特定事件发生时,内核会调用相应的notifier_call_chain()函数,以通知所有注册的模块或组件。这样,不同的模块可以根据事件类型和参数进行自定义处理,而无需显式地知道其他模块的存在。
四种通知链分别对应不同的函数:
- 原子通知链通知函数:
int atomic_notifier_call_chain(struct atomic_notifier_head *nh,unsigned long val, void *v); - 阻塞通知链通知函数:
int blocking_notifier_call_chain(struct blocking_notifier_head *nh,unsigned long val, void *v); - 原始通知链通知函数:
int raw_notifier_call_chain(struct raw_notifier_head *nh, unsigned long val, void *v); - srcu通知链通知函数:
int srcu_notifier_call_chain(struct srcu_notifier_head *nh, unsigned long val, void *v);
上述四个函数最后都会调用notifier_call_chain()实现核心功能,该函数实现如下:
static int notifier_call_chain(struct notifier_block **nl,unsigned long val, void *v,int nr_to_call, int *nr_calls)
{int ret = NOTIFY_DONE;struct notifier_block *nb, *next_nb;nb = rcu_dereference_raw(*nl);while (nb && nr_to_call) {next_nb = rcu_dereference_raw(nb->next);#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_NOTIFIERSif (unlikely(!func_ptr_is_kernel_text(nb->notifier_call))) {WARN(1, "Invalid notifier called!");nb = next_nb;continue;}
#endifret = nb->notifier_call(nb, val, v);if (nr_calls)(*nr_calls)++;if ((ret & NOTIFY_STOP_MASK) == NOTIFY_STOP_MASK)break;nb = next_nb;nr_to_call--;}return ret;
}
- nl:指向通知链头的指针。这是一个指向指针的指针,指向通知链的头节点。
- val:事件类型。链本身标识的一组事件,val明确标识一种事件类型
- v:一个指针,指向携带更多事件相关信息的数据结构。
- nr_to_call:记录发送的通知数量。如果不需要这个字段的值可以是NULL
- nr_calls:通知程序调用链返回最后一个被调用的通知程序函数返回的值。
在notifier_chain_unregister()的while循环结构中会调用:
ret = nb->notifier_call(nb, val, v);
依次执行注册到该通知链中的所有函数。
4、实例代码
本小节通过原子通知链给出实例代码,原子通知链可用于实现观察者模式的通信机制。
(1)定义一个通知链
#include <linux/notifier.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() *///定义原子通知链
static ATOMIC_NOTIFIER_HEAD(my_notifier_list);//通知事件
static int call_notifiers(unsigned long val, void *v)
{return atomic_notifier_call_chain(&my_notifier_list, val, v);}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(call_notifiers);//向通知链注册通知block
static int register_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb)
{int err;err = atomic_notifier_chain_register(&my_notifier_list, nb);if(err)return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(register_notifier);//从通知链中注销通知block
static int unregister_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb)
{int err;err = atomic_notifier_chain_unregister(&my_notifier_list, nb);if(err)return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(unregister_notifier);static int __init myNotifier_init(void)
{printk("myNotifier init finish\n");return 0;
}static void __exit myNotifier_exit(void)
{printk("myNotifier exit finish\n");
}module_init(myNotifier_init);
module_exit(myNotifier_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("iriczhao");
(2)实现观察者模块
/*** 模块1,用于创建通知block,并注册
*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/notifier.h>extern int register_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb);
extern int unregister_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb);static int notifier_one_call_fn(struct notifier_block *nb,unsigned long action, void *data)
{printk(">>this is notifier_one_call_fn\n");printk("recv action = %d data = %p\n",action,data);return 0;
}static int notifier_two_call_fn(struct notifier_block *nb,unsigned long action, void *data)
{printk(">>this is notifier_two_call_fn\n");return 0;
}/* define a notifier_block */
static struct notifier_block notifier_one = {.notifier_call = notifier_one_call_fn,
};static struct notifier_block notifier_two = {.notifier_call = notifier_two_call_fn,
};static int __init module_1_init(void)
{register_notifier(¬ifier_two);register_notifier(¬ifier_one);return 0;
}static void __exit module_1_exit(void)
{unregister_notifier(¬ifier_two);unregister_notifier(¬ifier_one);
}module_init(module_1_init);
module_exit(module_1_exit);//定义模块相关信息
MODULE_AUTHOR("iriczhao");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
(3)事件发生模块
/** 事件通知模块
*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/notifier.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>extern int call_notifiers(unsigned long val, void *v);static int event_module_init(void)
{printk("Event module initialized\n");unsigned long event = 123;void *data = (void *)0xDEADBEEF;call_notifiers(event, data);return 0;
}static void event_module_exit(void)
{printk("Event module exiting\n");
}module_init(event_module_init);
module_exit(event_module_exit);//定义模块相关信息
MODULE_AUTHOR("iriczhao");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
(4)输出结果
将上述三份代码以模块方式构建,并加载进内核,首先加载自定义的通知链my_notifier_list,接着加载module_1.ko注册两个事件订阅者,最后加载module_2.ko通知事件,并向module_1发送两个参数:action和data,并通过module_1打印出来。输出结果如下:

