Spring 框架源码(六) Bean的生命周期全流程源码解析
Spring框架作为Java王国的地基,我觉得它包含了很多精妙的设计,例如Bean工厂设计、Bean的生命周期、tx、aop、web、mvc等,最核心基本的Bean设计是Spring 的框架的灵魂,本文就Bean的生命周期全流程做源码程度上的解析,欢迎各位大佬指点江山。
先上一张DefaultListableBeanFactory的UML图来来感受Spring 框架设计的强大,跟着DefaultListableBeanFactory去揭开Spring框架的核心面纱。
一、DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory掌管了Bean生命周期的大权,Bean的创建、初始化、销毁,添加BeanPostProcessor等功能,可以说是Spring框架最全的Bean工厂, 掌握DefaultListableBeanFactory 是非常有必要的。
1. 创建并注册BeanDefinition
我们可以使用DefaultListableBeanFactory 对象注册一个BeanDefition, 使用registerBeanDefinition()方法, 如果想要加入一个BeanPostProcessor, 可以使用addBeanPostProcessor()方法。
private DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanByDefaultListableBeanFactory(final Class<?> beanClass) {DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass);beanDefinition.setInitMethodName("testMethod");beanDefinition.setDestroyMethodName("testDestroy");beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("testBean", beanDefinition);//添加BeanPostProcessorbeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessor() {@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {//System.out.println("执行前..");return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("执行后..");return bean;}});return beanFactory;}public static class User {public void testMethod(){System.out.println("初始化..");}public void testDestroy(){System.out.println("销毁..");}}@Testpublic void testDefaultListableBeanFactory() {final Class<?> beanClass = User.class;DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanByDefaultListableBeanFactory(beanClass);User user = beanFactory.getBean("testBean", User.class);System.out.println("user= " + user);}
打印结果:
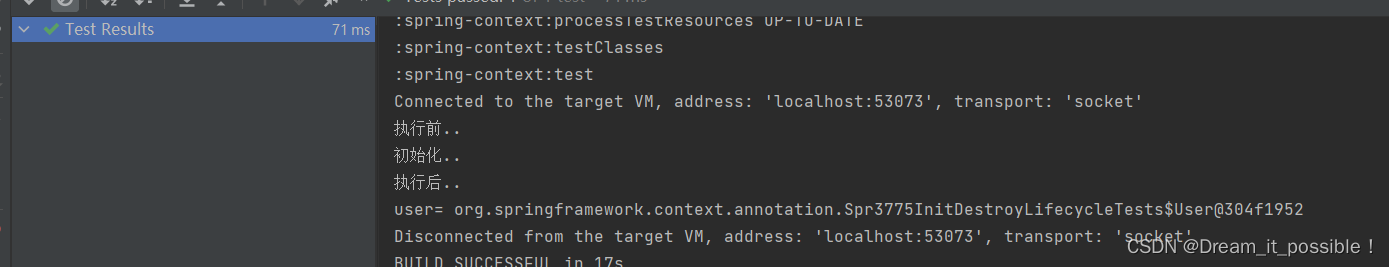
从打印结果可以知道User这个Bean的三个方法的执行顺序:
postProcessBeforeIntialization()> init-method()>postProcessAfterInitialization()
为了进一步理解Bean的生命周期,下面我们继续看Aware、BeanPostProcessor、InitialzingBean接口的执行顺序。
二、Bean的生命周期
BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、BeanClassLoaderAware
BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、BeanClassLoaderAware接口分别是在初始化Bean之前调用的,我们可以利用BeanName、BeanFactory、ClassLoader去开发一些业务。
/*** 执行BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware的接口。* @param beanName* @param bean*/private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {if (bean instanceof Aware) {if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);}if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();if (bcl != null) {((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);}}if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);}}}BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor接口里有2个默认方法,分别为PostProcessBeforeInitialization和PostProcessAfterInitialization。
public interface BeanPostProcessor {/*** Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.* @param bean the new bean instance* @param beanName the name of the bean* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet*/@Nullabledefault Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}/*** Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.* @param bean the new bean instance* @param beanName the name of the bean* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean*/@Nullabledefault Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}}
InitializingBean
InitializingBean接口官方解释: 当所有的Bean属性被BeanFactory设置完后允许你用afterPropertieSet()方法做一次调。
/*** Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their* properties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custom* initialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set.** <p>An alternative to implementing InitializingBean is specifying a custom* init-method, for example in an XML bean definition.* For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the* {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.** @author Rod Johnson* @see BeanNameAware* @see BeanFactoryAware* @see BeanFactory* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware*/
public interface InitializingBean {/*** Invoked by a BeanFactory after it has set all bean properties supplied* (and satisfied BeanFactoryAware and ApplicationContextAware).* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform initialization only* possible when all bean properties have been set and to throw an* exception in the event of misconfiguration.* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such* as failure to set an essential property) or if initialization fails.*/void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;}该接口一般可以用来做属性实例的校验,比如当前Bean依赖了哪些Bean, 如果依赖的Bean没有初始化,就应该抛出异常,例如DataSourceTransactionManager里用该方法去校验DataSource有没有被初始化。
public class DataSourceTransactionManager extends AbstractPlatformTransactionManagerimplements ResourceTransactionManager, InitializingBean {@Nullableprivate DataSource dataSource;private boolean enforceReadOnly = false;/*** Create a new DataSourceTransactionManager instance.* A DataSource has to be set to be able to use it.* @see #setDataSource*/public DataSourceTransactionManager() {setNestedTransactionAllowed(true);}/*** Create a new DataSourceTransactionManager instance.* @param dataSource JDBC DataSource to manage transactions for*/public DataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {this();setDataSource(dataSource);afterPropertiesSet();}@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() {if (getDataSource() == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'dataSource' is required");}}}
InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactoryinvokeInitMethods方法里被调用。
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)throws Throwable {boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);// 执行InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");}if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {try {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();return null;}, getAccessControlContext());}catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {throw pae.getException();}}else {// 执行InitialingBean的afterProperties()接口。((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();}}if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);}}}三、DefaultListableBeanFactory的父类AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
AbstarctAutowireCapableBeanFactory 是一个抽象类,实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory和AbstarctBeanFactory接口,initializeBean方法实现了实例化Bean的整个流程。
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);return null;}, getAccessControlContext());}else {// 1. 执行所有的BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware接口,把对象塞入到参数里交给开发者使用。invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);}// 2. 执行所有的BeanPostProcessor里的postProcessBeforeInitialization()Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}try {// 3. 执行Init方法, 其中包含InitializingBean接口里的AfterPropertiesSet()方法和自定义的init()方法invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException((mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);}//4. 执行所有的BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}return wrappedBean;}
