训练营day17
110.平衡二叉树
力扣题目链接
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]

返回 true 。
示例 2:
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]

返回 false 。
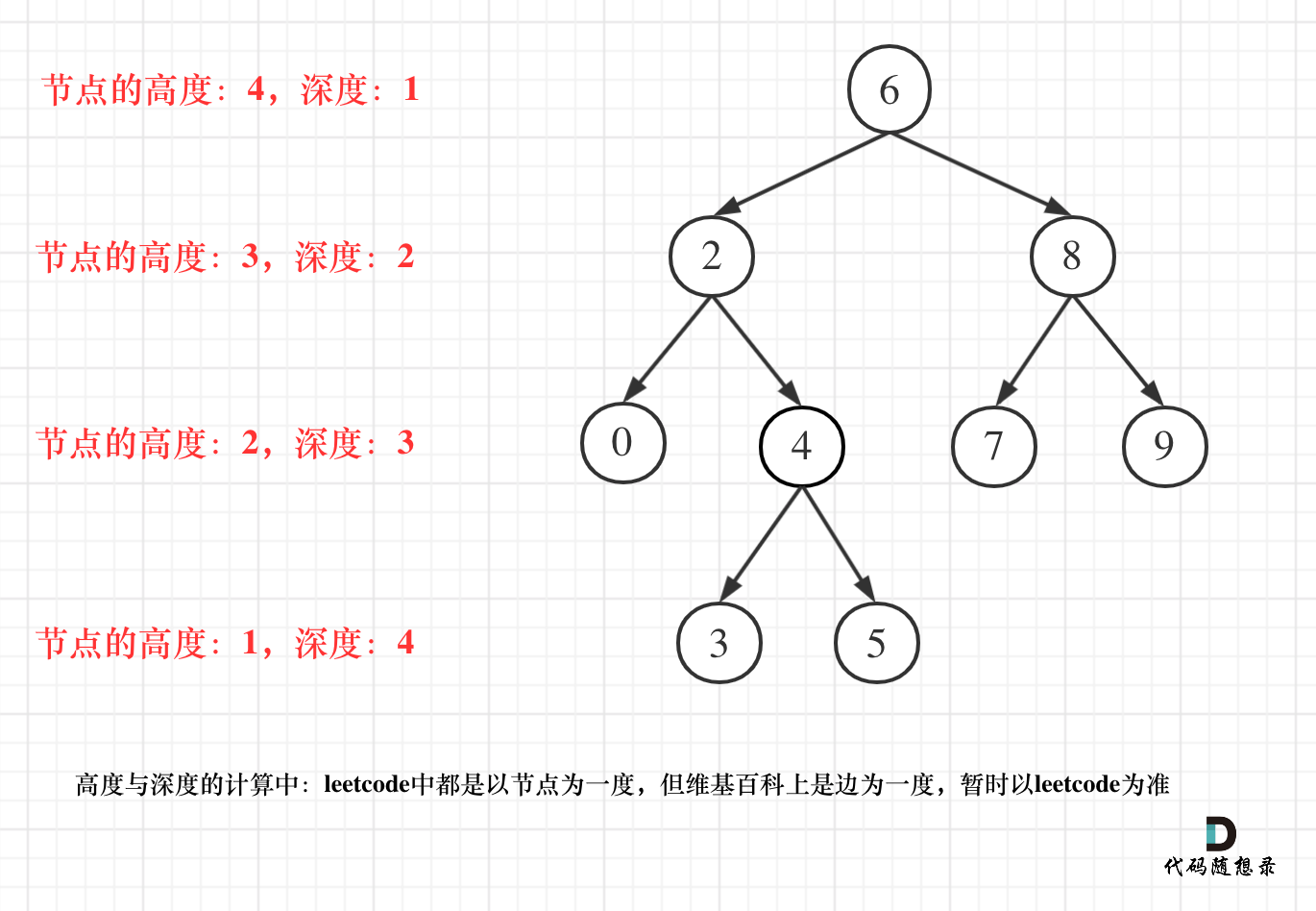
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
var isBalanced=function(root){if(root===null) return true;if(Math.abs(getHeight(root.left)-getHeight(root.right))>1) return false;return isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right);
}
var getHeight=function(root){if(root===null) return 0;return Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right))+1;
}
// 代码随想录
// 递归法:
var isBalanced = function(root) {//还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1// 1. 确定递归函数参数以及返回值const getDepth = function(node) {// 2. 确定递归函数终止条件if(node === null) return 0;// 3. 确定单层递归逻辑let leftDepth = getDepth(node.left); //左子树高度// 当判定左子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1if(leftDepth === -1) return -1;let rightDepth = getDepth(node.right); //右子树高度// 当判定右子树不为平衡二叉树时,即可直接返回-1if(rightDepth === -1) return -1;if(Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1) {return -1;} else {return 1 + Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);}}return !(getDepth(root) === -1);
};
// 迭代法:
// 获取当前节点的高度
//getHeight函数的作用是获取当前节点的高度
var getHeight = function (curNode) {let queue = [];if (curNode !== null) queue.push(curNode); // 压入当前元素let depth = 0, res = 0;while (queue.length) {let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶if (node !== null) {queue.pop();queue.push(node); // 中queue.push(null);depth++;node.right && queue.push(node.right); // 右node.left && queue.push(node.left); // 左} else {queue.pop();node = queue[queue.length - 1];queue.pop();depth--;}res = res > depth ? res : depth;}return res;
}
var isBalanced = function (root) {if (root === null) return true;let queue = [root];while (queue.length) {let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶queue.pop(); if (Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) > 1) {return false;}node.right && queue.push(node.right);node.left && queue.push(node.left);}return true;
};257. 二叉树的所有路径
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。

var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {if(root===null) return [];if(root.left===null&&root.right===null) return [root.val.toString()];let left_paths=binaryTreePaths(root.left);let right_paths=binaryTreePaths(root.right);let paths=[];for(let path of left_paths){paths.push(root.val.toString()+"->"+path);}for(let path of right_paths){paths.push(root.val.toString()+"->"+path);}return paths;
}
// 代码随想录
// 递归法
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {//递归遍历+递归三部曲let res = [];//1. 确定递归函数 函数参数const getPath = function(node,curPath) {//2. 确定终止条件,到叶子节点就终止if(node.left === null && node.right === null) {curPath += node.val;res.push(curPath);return;}//3. 确定单层递归逻辑curPath += node.val + '->';node.left && getPath(node.left, curPath);node.right && getPath(node.right, curPath);}getPath(root, '');return res;};
// 迭代法:
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const stack = [root], paths = [''], res = [];while (stack.length) {const node = stack.pop();let path = paths.pop();if (!node.left && !node.right) { // 到叶子节点终止, 添加路径到结果中res.push(path + node.val);continue;}path += node.val + '->';if (node.right) { // 右节点存在stack.push(node.right);paths.push(path);}if (node.left) { // 左节点存在stack.push(node.left);paths.push(path);}}return res;}; -
#404.左叶子之和
力扣题目链接
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。

var sumOfLeftLeaves=function(root){if(root===null) return 0;let sum=0;if(root.left!==null&&root.left.left===null&&root.left.right===null){sum+=root.left.val;}sum+=sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);sum+=sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);return sum;
}
// 代码随想录
// 递归法
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {//采用后序遍历 递归遍历// 1. 确定递归函数参数const nodesSum = function(node) {// 2. 确定终止条件if(node === null) {return 0;}let leftValue = nodesSum(node.left);let rightValue = nodesSum(node.right);// 3. 单层递归逻辑let midValue = 0;if(node.left && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {midValue = node.left.val;}let sum = midValue + leftValue + rightValue;return sum;}return nodesSum(root);
};
// 迭代法
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {//采用层序遍历if(root === null) {return null;}let queue = [];let sum = 0;queue.push(root);while(queue.length) {let node = queue.shift();if(node.left !== null && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {sum+=node.left.val;}node.left && queue.push(node.left);node.right && queue.push(node.right);}return sum;};