【基础篇】7 # 队列:队列在线程池等有限资源池中的应用
说明
【数据结构与算法之美】专栏学习笔记
什么是队列?
队列是一种操作受限的线性表数据结构,特点是先进先出,最基本的操作有:入队 enqueue(),放一个数据到队列尾部;出队 dequeue(),从队列头部取一个元素。

顺序队列和链式队列
- 用数组实现的队列叫作顺序队列
- 用链表实现的队列叫作链式队列
基于数组的队列实现方法
队列需要两个指针:
- 一个是 head 指针,指向队头;
- 一个是 tail 指针,指向队尾。
用 Java 语言实现:
// 用数组实现的队列
public class ArrayQueue {// 数组:items,数组大小:nprivate String[] items;private int n = 0;// head表示队头下标,tail表示队尾下标private int head = 0;private int tail = 0;// 申请一个大小为capacity的数组public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {items = new String[capacity];n = capacity;}// 入队操作,将item放入队尾public boolean enqueue(String item) {// tail == n表示队列末尾没有空间了if (tail == n) {// tail ==n && head==0,表示整个队列都占满了if (head == 0) return false;// 数据搬移for (int i = head; i < tail; ++i) {items[i-head] = items[i];}// 搬移完之后重新更新head和tailtail -= head;head = 0;}items[tail] = item;++tail;return true;}// 出队public String dequeue() {// 如果head == tail 表示队列为空if (head == tail) return null;// 为了让其他语言的同学看的更加明确,把--操作放到单独一行来写了String ret = items[head];++head;return ret;}
}
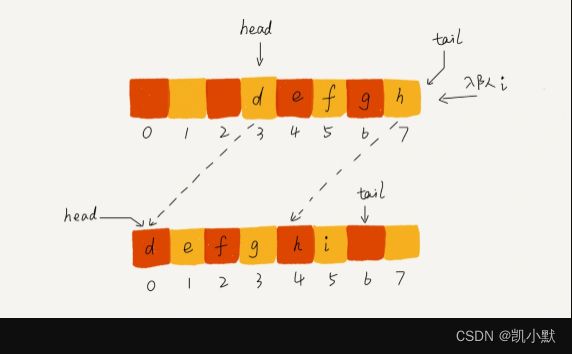
当 tail 移动到最右边,即使数组中还有空闲空间,也无法继续往队列中添加数据,针对这种情况,只需要在入队时,再集中触发一次数据的搬移操作。示意图如下:
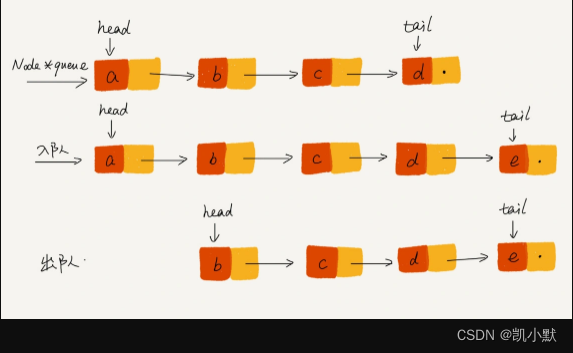
基于链表的队列实现方法
- 入队时:
tail->next= new_node;tail = tail->next - 出队时:
head = head->next
入队出队示意图:
/*** 基于链表实现的队列。** Author: nameczz*/class Node {constructor(element) {this.element = elementthis.next = null}
}export class QueueBasedOnLinkedList {constructor() {this.head = nullthis.tail = null}enqueue(value) {if (this.head === null) {this.head = new Node(value)this.tail = this.head} else {this.tail.next = new Node(value)this.tail = this.tail.next}}dequeue() {if (this.head !== null) {const value = this.head.elementthis.head = this.head.nextreturn value} else {return -1}}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>07.基于链表实现的队列</title></head><body><script type="module">import { QueueBasedOnLinkedList } from './js/07/QueueBasedOnLinkedList.js';const newQueue = new QueueBasedOnLinkedList();// 元素入队newQueue.enqueue(1);newQueue.enqueue(2);newQueue.enqueue(3);console.log('入队--->', newQueue);// 获取元素let res = 0;console.log("-------获取dequeue元素------");while (res !== -1) {res = newQueue.dequeue();console.log(res);}</script></body>
</html>
循环队列
循环队列就是普通队列首尾相连形成了一个环。
比如:下面队列的大小为 8,当前 head=4,tail=7。
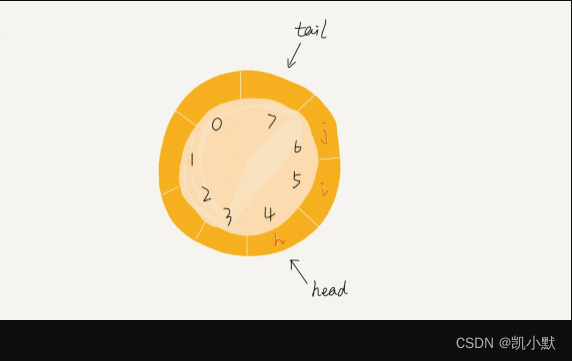
当有一个新的元素 a 入队时,放入下标为 7 的位置。将 tail 更新为 0 ,而不是 8。
如何判断循环队列队空和队满呢?
- 队空:队列为空的判断条件是
head == tail - 队满:当队满时,
(tail + 1)%n = head
基于数组的循环队列实现方式
public class CircularQueue {// 数组:items,数组大小:nprivate String[] items;private int n = 0;// head表示队头下标,tail表示队尾下标private int head = 0;private int tail = 0;// 申请一个大小为capacity的数组public CircularQueue(int capacity) {items = new String[capacity];n = capacity;}// 入队public boolean enqueue(String item) {// 队列满了if ((tail + 1) % n == head) return false;items[tail] = item;// 取余运算保证,数组队列的循环插入效果tail = (tail + 1) % n;return true;}// 出队public String dequeue() {// 如果head == tail 表示队列为空if (head == tail) return null;String ret = items[head];// 因为要保持一个环状,必须通过取余运算才能得到保障!head = (head + 1) % n;return ret;}
}
基于链表实现的循环队列
/*** 基于链表实现的循环队列。** Author: nameczz*/class Node {constructor(element) {this.element = elementthis.next = null}
}export class CircularQueue {constructor() {this.head = nullthis.tail = null}// 入队enqueue(value) {if (this.head === null) {this.head = new Node(value)this.head.next = this.headthis.tail = this.head} else {const flag = this.head === this.tailthis.tail.next = new Node(value)this.tail.next.next = this.headthis.tail = this.tail.nextif (flag) {this.head.next = this.tail}}}// 出队dequeue() {if(this.head == null) return -1if (this.head === this.tail) {const value = this.head.elementthis.head = nullreturn value} else {const value = this.head.elementthis.head = this.head.nextthis.tail.next = this.headreturn value} }display() {let res = 0console.log('-------获取dequeue元素------')while (res !== -1) {res = this.dequeue()console.log(res)}}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>07.基于链表实现的循环队列</title></head><body><script type="module">import { CircularQueue } from "./js/07/CircularQueue.js";const newCircularQueue = new CircularQueue();// 插入元素newCircularQueue.enqueue(1);newCircularQueue.enqueue(2);newCircularQueue.enqueue(3);console.log(newCircularQueue);// 获取元素newCircularQueue.display();newCircularQueue.enqueue(1);newCircularQueue.display();</script></body>
</html>
阻塞队列
阻塞队列就是在队列基础上增加了阻塞操作。
- 在队列为空的时候,从队头取数据会被阻塞。直到队列中有了数据才能返回
- 如果队列已经满了,那么插入数据的操作就会被阻塞。直到队列中有空闲位置后再插入数据,然后再返回
可以使用阻塞队列实现一个生产者 - 消费者模型,有效地协调生产和消费的速度。
如何实现一个线程安全的队列呢?
线程安全的队列叫作并发队列。在多线程情况下,会有多个线程同时操作队列,这个时候就会存在线程安全问题,最简单的解决方式就是直接在 enqueue()、dequeue() 方法上加锁,但是锁粒度大并发度会比较低,同一时刻仅允许一个存或者取操作。
如何实现一个高效的并发队列:
- 基于数组的循环队列:避免数据搬移
- CAS原子操作:避免真正的去OS底层申请锁资源
队列的应用
基于链表的实现方式,可以实现一个支持无限排队的无界队列(unbounded queue),但是可能会导致过多的请求排队等待,请求处理的响应时间过长。所以,针对响应时间比较敏感的系统,基于链表实现的无限排队的线程池是不合适的。而基于数组实现的有界队列(bounded queue),队列的大小有限,所以线程池中排队的请求超过队列大小时,接下来的请求就会被拒绝,这种方式对响应时间敏感的系统来说,就相对更加合理。
队列可以应用在任何有限资源池中,用于排队请求,比如数据库连接池等。对于大部分资源有限的场景,当没有空闲资源时,基本上都可以通过队列这种数据结构来实现请求排队。
