数据结构(六)—— 二叉树(4)回溯
文章目录
- 一、题
- 1 257 二叉树的所有路径
- 1.1 写法1
- 1.2 写法2
一、题
1 257 二叉树的所有路径
1.1 写法1
递归+回溯:回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯
首先考虑深度优先搜索;而题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历,这样才方便让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径。
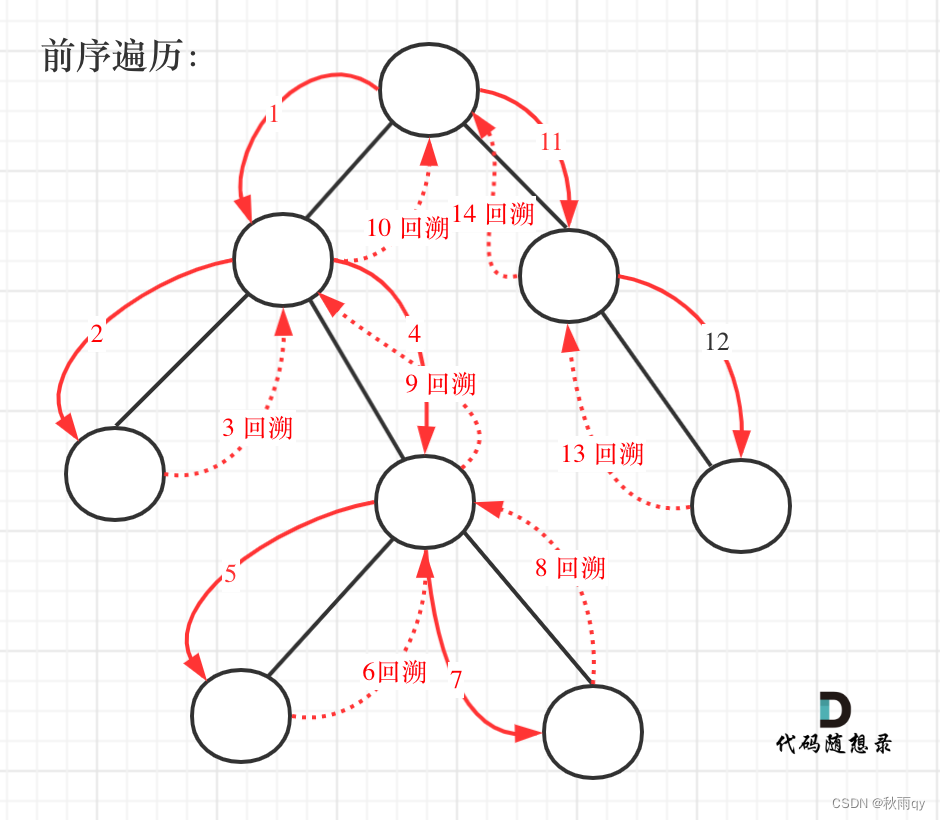
递归和回溯就是一家的,本题也需要回溯。
1、确定递归函数输入输出
要传入根节点,记录每一条路径的vector<int>&,和存放结果集的vector<string>&,这里递归不需要返回值,
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& path, vector<string>& result)
2、确定递归终止条件
一般来说都是if(cur == NULL) return,但是本题要找到叶子节点,就开始结束的处理逻辑了(把路径放进result里)。
那么什么时候算是找到了叶子节点? 是当 cur不为空,其左右孩子都为空的时候,就找到叶子节点。
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) { // 遇到叶子节点string sPath;for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) { // 将path里记录的路径转为string格式sPath += to_string(path[i]);sPath += "->";}sPath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]); // 记录最后一个节点(叶子节点)result.push_back(sPath); // 收集一个路径return;
}
3、确定单层递归逻辑
因为是前序遍历,需要先处理中间节点,中间节点就是我们要记录路径上的节点,先放进path中。
path.push_back(cur->val);
然后是递归和回溯的过程,上面说过没有判断cur是否为空,那么在这里递归的时候,如果为空就不进行下一层递归了。
所以递归前要加上判断语句,下面要递归的节点是否为空,如下
if (cur->left) traversal(cur->left, path, result);
此时还没完,递归完,要做回溯啊,因为path 不能一直加入节点,它还要删节点,然后才能加入新的节点。
if (cur->left) {traversal(cur->left, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
if (cur->right) {traversal(cur->right, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
4、整合traversal()
class Solution {
private:void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& path, vector<string>& result) {path.push_back(cur->val); // 中,中为什么写在这里,因为最后一个节点也要加入到path中 // 这才到了叶子节点if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {string sPath;for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {sPath += to_string(path[i]);sPath += "->";}sPath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);result.push_back(sPath);return;}if (cur->left) { // 左 traversal(cur->left, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}if (cur->right) { // 右traversal(cur->right, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}}public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> result;vector<int> path;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, path, result);return result;}
};
1.2 写法2
1、确定输入输出
输入:节点、每条路径string、每条路径组成的vector<string>&
输出:空
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, string path, vector<string>& result)
注意:函数输出定义的是string,每次都是复制赋值,没使用引用,否则就无法做到回溯的效果。(这里涉及到C++语法知识)
2、确定退出条件
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {result.push_back(path);return;
}
3、确定单层逻辑
中左右
path += to_string(cur->val); // 中
... // 退出条件
if (cur->left) traversal(cur->left, path + "->", result); // 左
if (cur->right) traversal(cur->right, path + "->", result); // 右
4、整合
class Solution {
private:void traversal(TreeNode* cur, string path, vector<string>& result) {path += to_string(cur->val); // 中if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {result.push_back(path);return;}if (cur->left) traversal(cur->left, path + "->", result); // 左if (cur->right) traversal(cur->right, path + "->", result); // 右}public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> result;string path;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, path, result);return result;}
};
在哪儿回溯的?
如上代码貌似没有看到回溯的逻辑,其实不然,回溯就隐藏在traversal(cur->left, path + "->", result);中的 path + "->"。 每次函数调用完,path并没有加上"->",这就是回溯了。
使用如下代码可以更好的体会到回溯
if (cur->left) {path += "->";traversal(cur->left, path, result); // 左path.pop_back(); // 回溯 '>'path.pop_back(); // 回溯 '-'
}
if (cur->right) {path += "->";traversal(cur->right, path, result); // 右path.pop_back(); // 回溯 '>' path.pop_back(); // 回溯 '-'
}
