Golang每日一练(leetDay0047)

目录
138. 复制带随机指针的链表 Copy List with Random-pointer 🌟🌟
139. 单词拆分 Word Break 🌟🌟
140. 单词拆分 II Word Break II 🌟🌟🌟
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
138. 复制带随机指针的链表 Copy List with Random-pointer
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val,random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
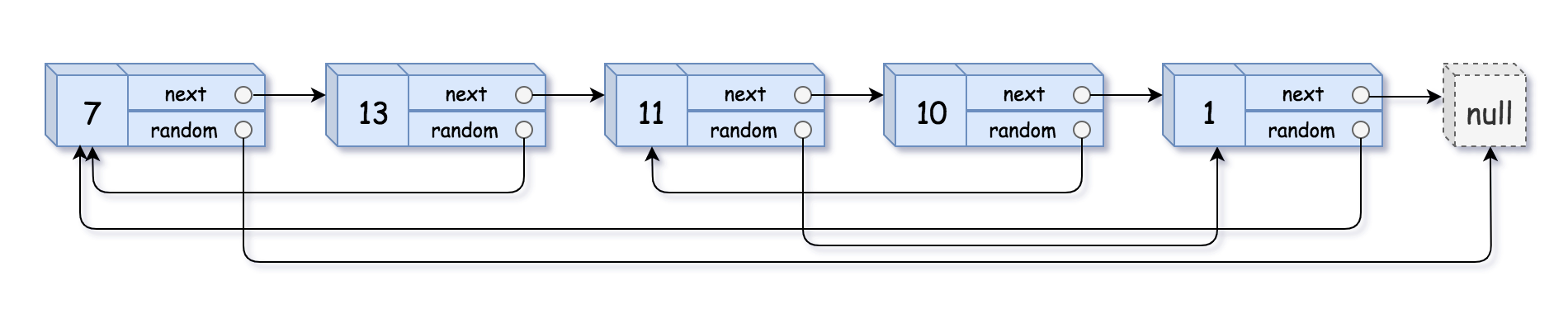
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
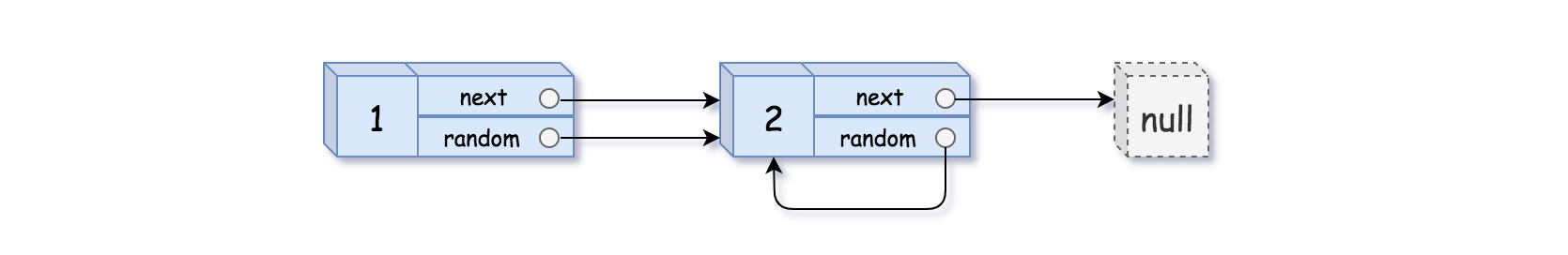
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
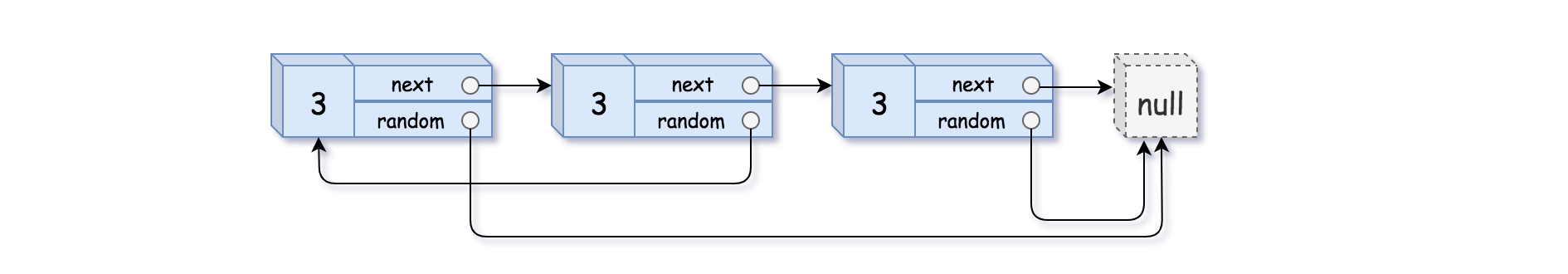
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
代码1: 直接在节点结构里增加Index属性
package mainimport "fmt"const null = -1 << 31type Node struct {Val intNext *NodeRandom *NodeIndex int
}func createNode(val int) *Node {return &Node{Val: val,Next: nil,Random: nil,}
}func buildRandomList(nums [][]int) *Node {if len(nums) == 0 {return nil}nodes := make([]*Node, len(nums))for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {nodes[i] = &Node{Val: nums[i][0], Index: i}}for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {if nums[i][1] != null {nodes[i].Random = nodes[nums[i][1]]}if i < len(nums)-1 {nodes[i].Next = nodes[i+1]}}return nodes[0]
}func traverseList(head *Node) {if head == nil {return}visited := make(map[*Node]bool)cur := headfmt.Print("[")for cur != nil {fmt.Print("[")fmt.Printf("%d,", cur.Val)if cur.Random != nil {fmt.Printf("%d", cur.Random.Index)} else {fmt.Print("null")}fmt.Print("]")visited[cur] = trueif cur.Next != nil && !visited[cur.Next] {fmt.Print(",")cur = cur.Next} else {break}}fmt.Println("]")
}func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {if head == nil {return nil}cur := headfor cur != nil {copy := &Node{cur.Val, cur.Next, nil, cur.Index}cur.Next = copycur = copy.Next}cur = headfor cur != nil {if cur.Random != nil {cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next}cur = cur.Next.Next}newHead := head.Nextcur = headfor cur != nil {copy := cur.Nextcur.Next = copy.Nextif copy.Next != nil {copy.Next = copy.Next.Next}cur = cur.Next}return newHead
}func copyRandomList2(head *Node) *Node {if head == nil {return nil}m := make(map[*Node]*Node)cur := headfor cur != nil {m[cur] = &Node{cur.Val, nil, nil, cur.Index}cur = cur.Next}cur = headfor cur != nil {m[cur].Next = m[cur.Next]m[cur].Random = m[cur.Random]cur = cur.Next}return m[head]
}func main() {nodes := [][]int{{7, null}, {13, 0}, {11, 4}, {10, 2}, {1, 0}}head := buildRandomList(nodes)traverseList(head)head = copyRandomList(head)traverseList(head)nodes = [][]int{{1, 1}, {2, 1}}head = buildRandomList(nodes)traverseList(head)head = copyRandomList(head)traverseList(head)nodes = [][]int{{3, null}, {3, 0}, {3, null}}head = buildRandomList(nodes)traverseList(head)head = copyRandomList(head)traverseList(head)
}
代码2: 增加getIndex()函数获取Index索引号
func getIndex(node *Node, head *Node) int
package mainimport ("fmt""strings"
)const null = -1 << 31type Node struct {Val intNext *NodeRandom *Node
}func createNode(val int) *Node {return &Node{Val: val,Next: nil,Random: nil,}
}func buildRandomList(nums [][]int) *Node {if len(nums) == 0 {return nil}nodes := make([]*Node, len(nums))for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {nodes[i] = &Node{Val: nums[i][0]}}for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {if nums[i][1] != null {nodes[i].Random = nodes[nums[i][1]]}if i < len(nums)-1 {nodes[i].Next = nodes[i+1]}}return nodes[0]
}func traverseList(head *Node) [][]int {if head == nil {return nil}visited := make(map[*Node]bool)cur := headres := make([][]int, 0)for cur != nil {visited[cur] = truerandomIndex := nullif cur.Random != nil {randomIndex = getIndex(cur.Random, head)}res = append(res, []int{cur.Val, randomIndex})if cur.Next != nil && !visited[cur.Next] {cur = cur.Next} else {break}}return res
}func getIndex(node *Node, head *Node) int {index := 0cur := headfor cur != node {index++cur = cur.Next}return index
}func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {if head == nil {return nil}cur := headfor cur != nil {copy := &Node{cur.Val, cur.Next, nil}cur.Next = copycur = copy.Next}cur = headfor cur != nil {if cur.Random != nil {cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next}cur = cur.Next.Next}newHead := head.Nextcur = headfor cur != nil {copy := cur.Nextcur.Next = copy.Nextif copy.Next != nil {copy.Next = copy.Next.Next}cur = cur.Next}return newHead
}func copyRandomList2(head *Node) *Node {if head == nil {return nil}m := make(map[*Node]*Node)cur := headfor cur != nil {m[cur] = &Node{cur.Val, nil, nil}cur = cur.Next}cur = headfor cur != nil {m[cur].Next = m[cur.Next]m[cur].Random = m[cur.Random]cur = cur.Next}return m[head]
}func Array2DToString(array [][]int) string {if len(array) == 0 {return "[]"}arr2str := func(arr []int) string {res := "["for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {if arr[i] == null {res += "null"} else {res += fmt.Sprint(arr[i])}if i != len(arr)-1 {res += ","}}return res + "]"}res := make([]string, len(array))for i, arr := range array {res[i] = arr2str(arr)}return strings.Join(strings.Fields(fmt.Sprint(res)), ",")
}func main() {nodes := [][]int{{7, null}, {13, 0}, {11, 4}, {10, 2}, {1, 0}}head := buildRandomList(nodes)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))head = copyRandomList(head)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))nodes = [][]int{{1, 1}, {2, 1}}head = buildRandomList(nodes)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))head = copyRandomList(head)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))nodes = [][]int{{3, null}, {3, 0}, {3, null}}head = buildRandomList(nodes)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))head = copyRandomList(head)fmt.Println(Array2DToString(traverseList(head)))
}
输出:
[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
[[1,1],[2,1]]
[[1,1],[2,1]]
[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
139. 单词拆分 Word Break
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符串列表 wordDict 作为字典。请你判断是否可以利用字典中出现的单词拼接出 s 。
注意:不要求字典中出现的单词全部都使用,并且字典中的单词可以重复使用。
示例 1:
输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为 "leetcode" 可以由 "leet" 和 "code" 拼接成。
示例 2:
输入: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为 "applepenapple" 可以由 "apple" "pen" "apple" 拼接成。注意,你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"] 输出: false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 3001 <= wordDict.length <= 10001 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20s和wordDict[i]仅有小写英文字母组成wordDict中的所有字符串 互不相同
代码1: 暴力枚举
package mainimport ("fmt"
)func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) bool {return helper(s, wordDict)
}func helper(s string, wordDict []string) bool {if s == "" {return true}for i := 1; i <= len(s); i++ {if contains(wordDict, s[:i]) && helper(s[i:], wordDict) {return true}}return false
}func contains(wordDict []string, s string) bool {for _, word := range wordDict {if word == s {return true}}return false
}func main() {s := "leetcode"wordDict := []string{"leet", "code"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "applepenapple"wordDict = []string{"apple", "pen"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "catsandog"wordDict = []string{"cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))
}
代码2: 记忆化搜索
package mainimport ("fmt"
)func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) bool {memo := make([]int, len(s))for i := range memo {memo[i] = -1}return helper(s, wordDict, memo)
}func helper(s string, wordDict []string, memo []int) bool {if s == "" {return true}if memo[len(s)-1] != -1 {return memo[len(s)-1] == 1}for i := 1; i <= len(s); i++ {if contains(wordDict, s[:i]) && helper(s[i:], wordDict, memo) {memo[len(s)-1] = 1return true}}memo[len(s)-1] = 0return false
}func contains(wordDict []string, s string) bool {for _, word := range wordDict {if word == s {return true}}return false
}func main() {s := "leetcode"wordDict := []string{"leet", "code"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "applepenapple"wordDict = []string{"apple", "pen"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "catsandog"wordDict = []string{"cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))
}
代码3: 动态规划
package mainimport ("fmt"
)func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) bool {n := len(s)dp := make([]bool, n+1)dp[0] = truefor i := 1; i <= n; i++ {for j := 0; j < i; j++ {if dp[j] && contains(wordDict, s[j:i]) {dp[i] = truebreak}}}return dp[n]
}func contains(wordDict []string, s string) bool {for _, word := range wordDict {if word == s {return true}}return false
}func main() {s := "leetcode"wordDict := []string{"leet", "code"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "applepenapple"wordDict = []string{"apple", "pen"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))s = "catsandog"wordDict = []string{"cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"}fmt.Println(wordBreak(s, wordDict))
}
输出:
true
true
false
140. 单词拆分 II Word Break II
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串字典 wordDict ,在字符串 s 中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。以任意顺序 返回所有这些可能的句子。
注意:词典中的同一个单词可能在分段中被重复使用多次。
示例 1:
输入:s = "catsanddog", wordDict = ["cat","cats","and","sand","dog"] 输出:["cats and dog","cat sand dog"]
示例 2:
输入:s = "pineapplepenapple", wordDict = ["apple","pen","applepen","pine","pineapple"] 输出:["pine apple pen apple","pineapple pen apple","pine applepen apple"] 解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入:s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats","dog","sand","and","cat"] 输出:[]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 201 <= wordDict.length <= 10001 <= wordDict[i].length <= 10s和wordDict[i]仅有小写英文字母组成wordDict中所有字符串都 不同
代码1: 回溯法
package mainimport ("fmt""strings"
)func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) []string {// 构建字典dict := make(map[string]bool)for _, word := range wordDict {dict[word] = true}// 回溯函数var res []stringvar backtrack func(start int, path []string)backtrack = func(start int, path []string) {if start == len(s) {res = append(res, strings.Join(path, " "))return}for i := start + 1; i <= len(s); i++ {if dict[s[start:i]] {path = append(path, s[start:i])backtrack(i, path)path = path[:len(path)-1]}}}backtrack(0, []string{})return res
}func ArrayToString(arr []string) string {res := "[\""for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {res += arr[i]if i != len(arr)-1 {res += "\",\""}}res += "\"]"if res == "[\"\"]" {res = "[]"}return res
}func main() {s := "catsanddog"wordDict := []string{"cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))s = "pineapplepenapple"wordDict = []string{"apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))s = "catsandog"wordDict = []string{"cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))
}
代码2: 动态规划 + 回溯法
package mainimport ("fmt""strings"
)func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) []string {// 构建字典dict := make(map[string]bool)for _, word := range wordDict {dict[word] = true}// 动态规划n := len(s)dp := make([]bool, n+1)dp[0] = truefor i := 1; i <= n; i++ {for j := 0; j < i; j++ {if dp[j] && dict[s[j:i]] {dp[i] = truebreak}}}if !dp[n] {return []string{}}// 回溯函数var res []stringvar backtrack func(start int, path []string)backtrack = func(start int, path []string) {if start == len(s) {res = append(res, strings.Join(path, " "))return}for i := start + 1; i <= len(s); i++ {if dict[s[start:i]] {path = append(path, s[start:i])backtrack(i, path)path = path[:len(path)-1]}}}backtrack(0, []string{})return res
}func ArrayToString(arr []string) string {res := "[\""for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {res += arr[i]if i != len(arr)-1 {res += "\",\""}}res += "\"]"if res == "[\"\"]" {res = "[]"}return res
}func main() {s := "catsanddog"wordDict := []string{"cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))s = "pineapplepenapple"wordDict = []string{"apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))s = "catsandog"wordDict = []string{"cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"}fmt.Println(ArrayToString(wordBreak(s, wordDict)))
}
代码3: 动态规划 + 记忆化搜索
func wordBreak(s string, wordDict []string) []string {// 构建字典dict := make(map[string]bool)for _, word := range wordDict {dict[word] = true}// 动态规划n := len(s)dp := make([]bool, n+1)dp[0] = truefor i := 1; i <= n; i++ {for j := 0; j < i; j++ {if dp[j] && dict[s[j:i]] {dp[i] = truebreak}}}if !dp[n] {return []string{}}// 记忆化搜索memo := make(map[int][][]string)var dfs func(start int) [][]stringdfs = func(start int) [][]string {if _, ok := memo[start]; ok {return memo[start]}var res [][]stringif start == len(s) {res = append(res, []string{})return res}for i := start + 1; i <= len(s); i++ {if dict[s[start:i]] {subRes := dfs(i)for _, subPath := range subRes {newPath := append([]string{s[start:i]}, subPath...)res = append(res, newPath)}}}memo[start] = resreturn res}return format(dfs(0))
}
// 格式化结果集
func format(paths [][]string) []string {var res []stringfor _, path := range paths {res = append(res, strings.Join(path, " "))}return res
}输出:
["cat sand dog","cats and dog"]
["pine apple pen apple","pine applepen apple","pineapple pen apple"]
[]
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
🌟 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
 | Golang每日一练 专栏 |
 | Python每日一练 专栏 |
 | C/C++每日一练 专栏 |
 | Java每日一练 专栏 |
