【自动化运维神器Ansible】Ansible常用模块之group模块详解
目录
1 Ansible简介与group模块概述
2 group模块参数详解
2.1 核心参数
2.2 高级参数
2.3 参数使用示例
3 group模块使用场景与实例
3.1 基础使用场景
3.1.1 场景一:创建基本用户组
3.1.2 场景二:创建带有特定GID的用户组
3.2 高级使用场景
3.2.1 场景一:创建系统组
3.2.2 场景二:删除用户组
3.3 实际综合应用示例
4 group模块工作流程解析
5 group模块与相关模块的协作
6 group模块的幂等性设计
7 group模块在不同操作系统中的差异
7.1 主要差异点
7.2 跨平台兼容的Playbook示例
8 group模块的实践示例
9 group模块的常见问题与解决方案
9.1 常见问题汇总
9.2 调试技巧
10 group模块的高级应用技巧
10.1 动态组管理
10.2 从变量文件加载组配置
10.3 条件化组管理
11 总结
1 Ansible简介与group模块概述
Ansible是一款开源的自动化运维工具,它基于Python开发,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。Ansible通过SSH协议进行通信,不需要在被管理节点上安装客户端,这使得它的部署和使用变得非常简单。
在众多Ansible模块中,group模块是一个基础但非常重要的模块,它专门用于管理Linux系统中的用户组。通过group模块,我们可以:
- 创建新的用户组
- 删除已存在的用户组
- 修改用户组的属性(如GID)
- 管理系统用户组的基本信息
group模块的核心功能可以总结为以下几点:
- 确保系统中存在(或不存在)特定的用户组
- 精确控制用户组的属性配置
- 实现用户组管理的幂等性(即无论执行多少次,结果都一致)
2 group模块参数详解
2.1 核心参数
| 参数名 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| name | 是 | 无 | 要管理的用户组名称 |
| state | 否 | present | 用户组状态:present(存在)或absent(不存在) |
| gid | 否 | 无 | 设置用户组的GID(组ID) |
| system | 否 | no | 是否创建为系统组(yes/no) |
2.2 高级参数
| 参数名 | 说明 |
| local | 是否使用本地命令而非LDAP等(某些系统支持) |
| non_unique | 是否允许非唯一的GID(当GID已存在时) |
2.3 参数使用示例
- name: Ensure developers group existsansible.builtin.group:name: developersgid: 2000state: presentsystem: no3 group模块使用场景与实例
3.1 基础使用场景
3.1.1 场景一:创建基本用户组
- name: Create a basic user groupgroup:name: webadminsstate: present3.1.2 场景二:创建带有特定GID的用户组
- name: Create group with specific GIDgroup:name: dbadminsgid: 2001state: present3.2 高级使用场景
3.2.1 场景一:创建系统组
- name: Create system group for service accountgroup:name: nginxsystem: yesstate: present3.2.2 场景二:删除用户组
- name: Remove temporary groupgroup:name: tempusersstate: absent3.3 实际综合应用示例
- name: Configure server groupshosts: alltasks:- name: Create admin groupgroup:name: wheelgid: 10state: present- name: Create docker groupgroup:name: dockergid: 994state: present- name: Create application groupgroup:name: appusergid: 2000state: present- name: Remove old temporary groupgroup:name: oldtempstate: absent4 group模块工作流程解析
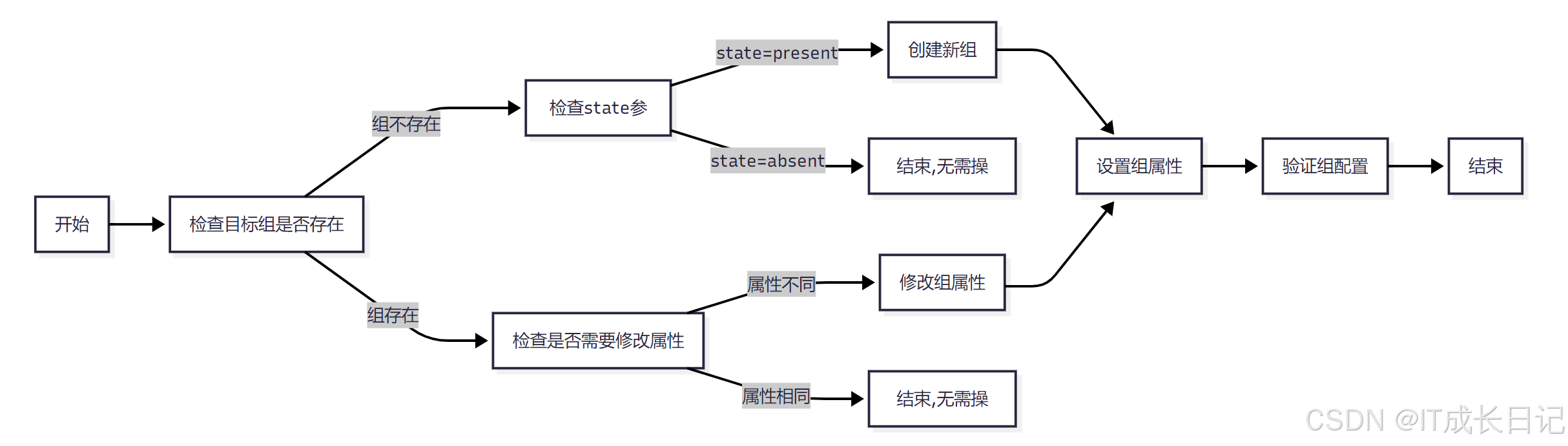
- Ansible首先检查目标组是否已经存在
- 如果组不存在:
- 当state=present时,创建新组并设置指定属性
- 当state=absent时,不做任何操作
- 如果组已存在:
- 检查现有属性是否符合要求,不符合则修改
- 属性一致则不做任何操作
- 最后验证组配置是否正确
5 group模块与相关模块的协作
- 在实际的自动化运维中,group模块通常不会单独使用,而是与其他模块协同工作,特别是user模块

- 协作示例代码:
- name: Set up application user and grouphosts: app_serverstasks:- name: Ensure application group existsgroup:name: myappgid: 2000state: present- name: Ensure application user existsuser:name: myappuid: 2000group: myappgroups: wheelappend: yesshell: /sbin/nologinsystem: yes- name: Set application directory permissionsfile:path: /opt/myappowner: myappgroup: myappmode: '0750'state: directory6 group模块的幂等性设计
Ansible的一个核心理念就是"幂等性",group模块完美体现了这一设计理念。幂等性意味着无论执行多少次,结果都保持一致。这对于自动化运维非常重要,因为它可以避免意外更改和重复操作带来的问题。
group模块的幂等性体现在:
- 如果组已经存在且属性一致,不会执行任何操作
- 如果组不存在但应该存在,会创建组并设置正确属性
- 如果组存在但属性不一致,会修正属性
- 如果组存在但应该不存在,会删除组
- 幂等性测试示例:
- name: Test idempotence of group modulehosts: localhosttasks:- name: Ensure test group exists (first run)group:name: testgroupgid: 3000state: presentregister: result- name: Show result of first rundebug:var: result- name: Ensure test group exists (second run)group:name: testgroupgid: 3000state: presentregister: result- name: Show result of second rundebug:var: result7 group模块在不同操作系统中的差异
7.1 主要差异点
| 特性 | RedHat/CentOS | Debian/Ubuntu | SUSE |
| 系统组GID范围 | 小于1000 | 小于100 | 小于1000 |
| 默认用户组 | 创建用户时新建同名组 | 默认使用users组 | 类似RedHat |
| 特殊组 | wheel(admin) | sudo(admin) | wheel |
7.2 跨平台兼容的Playbook示例
- name: Create admin group compatible across distributionsgroup:name: "{{ 'wheel' if ansible_os_family == 'RedHat' else 'sudo' }}"gid: 10state: present8 group模块的实践示例
- 明确指定GID:避免依赖系统自动分配的GID,特别是在多服务器环境中
- name: Good practice - specify GIDgroup:name: deploygid: 2001- 使用有意义的组名:组名应清晰表达其用途
# 好例子
- name: Create database admin groupgroup:name: db_admins# 坏例子
- name: Create groupgroup:name: grp1- 系统组标记:对于服务账户使用的组,标记为系统组
- name: Create system group for servicegroup:name: nginxsystem: yes- 与user模块配合时的注意事项:
- name: Proper way to work with user modulegroup:name: developers# 注意顺序,先创建组user:name: johngroups: developersappend: yes # 重要:保留用户原有组- 文档化GID分配:维护一个GID分配表,避免冲突
GID分配表:
1000-1999 - 系统服务组
2000-2999 - 应用程序组
3000-3999 - 功能组
4000-4999 - 项目组9 group模块的常见问题与解决方案
9.1 常见问题汇总
| 问题现象 | 可能原因 | 解决方案 |
| 组创建失败,提示GID已存在 | 指定的GID已被其他组使用 | 使用non_unique: yes或更换GID |
| 组属性未按预期修改 | 模块参数拼写错误 | 检查参数名,如gid不是group_id |
| 组删除后用户出现问题 | 有用户以此组为主组 | 先修改这些用户的主组再删除组 |
| 组存在但模块报告changed | 组的其他属性不一致 | 检查system等属性是否一致 |
9.2 调试技巧
- 技巧一:使用verbose模式获取详细信息
ansible-playbook playbook.yml -vvv- 技巧二:注册变量检查结果
- name: Create group and check resultgroup:name: testgroupgid: 5000register: group_result- name: Debug group resultdebug:var: group_result- 技巧三:使用check模式预演
ansible-playbook playbook.yml --check10 group模块的高级应用技巧
10.1 动态组管理
- name: Create groups from listgroup:name: "{{ item.name }}"gid: "{{ item.gid }}"state: presentloop:- { name: 'web', gid: 2001 }- { name: 'db', gid: 2002 }- { name: 'app', gid: 2003 }10.2 从变量文件加载组配置
- groups_vars.yml:
required_groups:- name: developersgid: 2001system: no- name: deploygid: 2002system: yes- name: Create all required groupsgroup:name: "{{ item.name }}"gid: "{{ item.gid }}"system: "{{ item.system | default(no) }}"state: presentloop: "{{ required_groups }}"10.3 条件化组管理
- name: Create group only on productiongroup:name: prod_accessstate: presentwhen: inventory_hostname in groups['production']11 总结
Ansible的group模块虽然看起来简单,但在自动化运维中扮演着基础而重要的角色。通过本文我们学习了解了:
- group模块提供了完整的用户组管理功能,包括创建、修改和删除
- 模块设计遵循幂等性原则,确保操作安全可靠
- 通过与其他模块(如user、file)的配合,可以实现复杂的权限管理方案
- 在不同环境中使用时需要注意操作系统差异
- 遵循最佳实践可以构建健壮的自动化运维方案
掌握group模块的使用,是Ansible自动化运维的基础技能之一。
