Spring Boot教程之二十一:文件处理
Spring Boot – 文件处理
Spring Boot 是一种流行的、基于 Spring 的开源框架,用于开发强大的 Web 应用程序和微服务。由于它建立在 Spring 框架之上,因此它不仅具有 Spring 的所有功能,而且还包括某些特殊功能,例如自动配置、健康检查等。这使开发人员能够更轻松地以最少的配置设置基于 Spring 的应用程序,从而促进快速应用程序开发。
Spring Boot 文件处理是指使用 RESTful Web 服务下载和上传文件。本文将逐步介绍如何使用 Spring Boot 实现可用于上传和下载文件的 RESTful Web 服务。
Spring Boot 中文件处理的初始设置
需要使用 Spring Initializer 创建具有Spring Web依赖项的 Spring Boot 项目,
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency>
现在让我们开始开发 Spring Boot App。它将为以下对象提供 RESTful Web 服务:
- 上传文件
- 下载文件
- 获取已上传文件名列表
应用程序的实施
步骤 1:设置Application.Properties文件,其中包含分部分文件上传所需的配置。
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=10MB
这些配置可以解释如下:
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled -> 确定是否必须启用 multipart
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file -> 指定允许上传的文件的最大大小。
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size -> 指定允许的 multipart/form-data 请求的最大大小。
步骤 2:创建一个 RestController FileController,处理以下 REST API:
1. 上传API
用法:可用于上传文件。它使用多部分请求。URL
:/upload
HttpMethod:POST
实施细节:
为了开发此 API,我们使用 MultipartFile 作为请求参数。上传的文件以表单数据的形式发送,然后在 Rest 控制器中作为 Multipart 文件检索。因此,MultipartFile只不过是在多部分请求中收到的上传文件的一种表示。
2. 获取文件 API
用法:可用于获取已上传的文件名列表。URL
:/getFIles
HttpMethod:GET
实施细节:
它可以简单地通过使用java.io.File的list()方法来实现,该方法返回一个字符串数组,该数组命名由给定的抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录。
3. 下载API
它可用于下载先前上传的文件。URL
:/download/{filename}
HttpMethod:POST
实施细节:
要实现此 API,我们首先检查所请求下载的文件是否存在于上传的文件夹中。如果文件存在,我们使用InputStreamResource下载该文件。还需要将响应标头中的 Content-Disposition 设置为附件,并将MediaType设置为application/octet-stream。
Content -Disposition响应头作为附件,表示要下载内容。contentType设置为 application/octet-stream ,这样当尝试下载缺少扩展名或格式未知的文件时,系统会将其识别为八位字节流文件。FileController 的实现如下所示:
- Java
| // Java Program to Create Rest Controller // that Defines various API for file handling package com.SpringBootFileHandling.controller;
// Importing required classes import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.util.Arrays;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamResource; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
// Annotation @RestController public class FileController {
// Uploading a file @RequestMapping(value = "/upload", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file){
// Setting up the path of the file String filePath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/Uploads" + File.separator + file.getOriginalFilename(); String fileUploadStatus;
// Try block to check exceptions try {
// Creating an object of FileOutputStream class FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fout.write(file.getBytes());
// Closing the connection fout.close(); fileUploadStatus = "File Uploaded Successfully";
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); fileUploadStatus = "Error in uploading file: " + e; } return fileUploadStatus; }
// Getting list of filenames that have been uploaded @RequestMapping(value = "/getFiles", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String[] getFiles() { String folderPath = System.getProperty("user.dir") +"/Uploads";
// Creating a new File instance File directory= new File(folderPath);
// list() method returns an array of strings // naming the files and directories // in the directory denoted by this abstract pathname String[] filenames = directory.list();
// returning the list of filenames return filenames;
}
// Downloading a file @RequestMapping(value = "/download/{path:.+}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public ResponseEntity downloadFile(@PathVariable("path") String filename) throws FileNotFoundException {
// Checking whether the file requested for download exists or not String fileUploadpath = System.getProperty("user.dir") +"/Uploads"; String[] filenames = this.getFiles(); boolean contains = Arrays.asList(filenames).contains(filename); if(!contains) { return new ResponseEntity("FIle Not Found",HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); }
// Setting up the filepath String filePath = fileUploadpath+File.separator+filename;
// Creating new file instance File file= new File(filePath);
// Creating a new InputStreamResource object InputStreamResource resource = new InputStreamResource(new FileInputStream(file));
// Creating a new instance of HttpHeaders Object HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
// Setting up values for contentType and headerValue String contentType = "application/octet-stream"; String headerValue = "attachment; filename=\"" + resource.getFilename() + "\"";
return ResponseEntity.ok() .contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType(contentType)) .header(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION, headerValue) .body(resource);
} } |
步骤3:运行Spring Boot应用程序并使用postman测试API,如下所示。
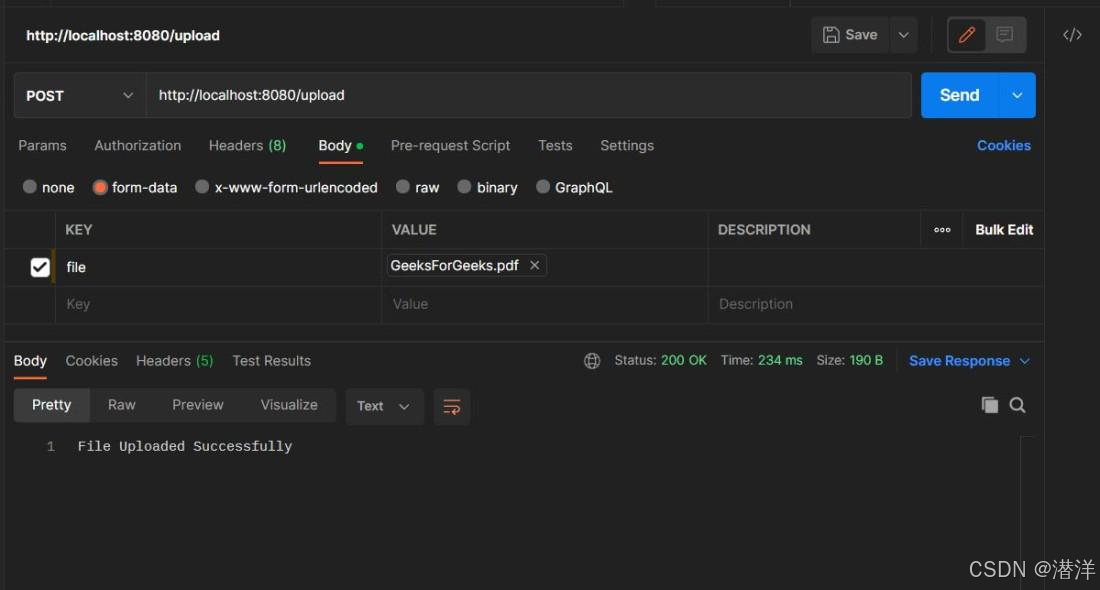
1. 上传API
为了上传文件,我们需要在 Postman 中点击http://localhost:8080/upload,并使用如下所示的表单数据:
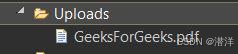
文件上传成功后,我们可以在Uploads文件夹中看到该文件,如下所示:
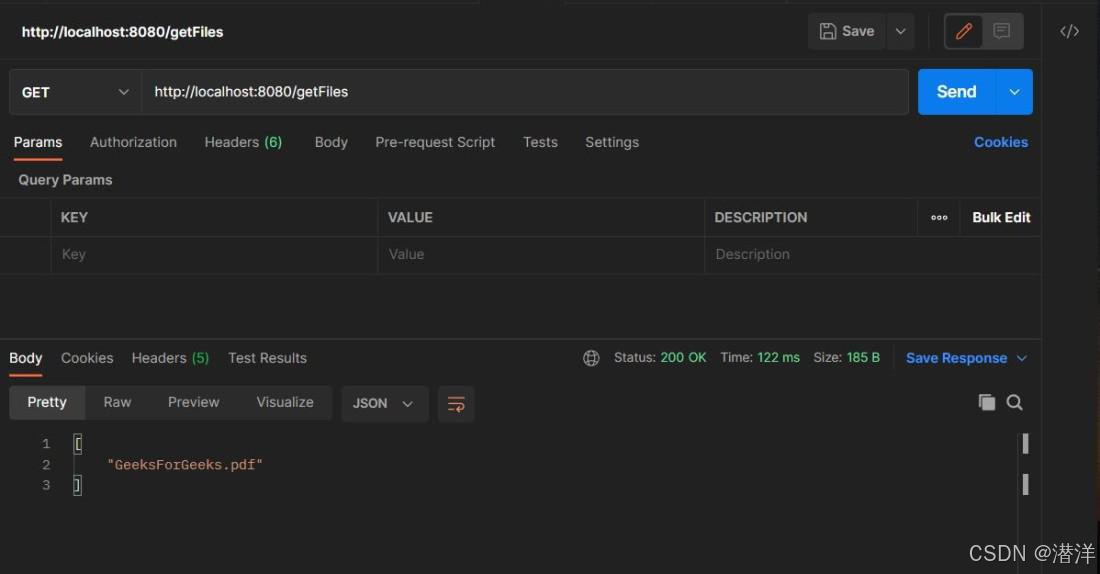
2. 获取文件 API
我们需要在 postman 中点击http://localhost:8080/getFiles来获取已上传的文件名列表。
3. 下载API
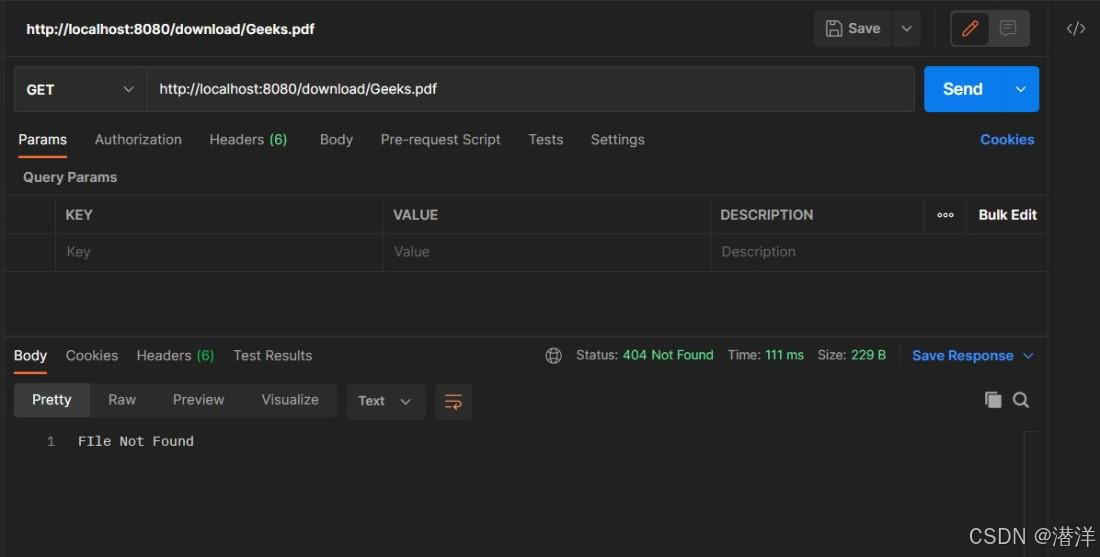
为了下载文件,我们需要在 postman 中点击http://localhost:8080/download/{filename},如下所示。
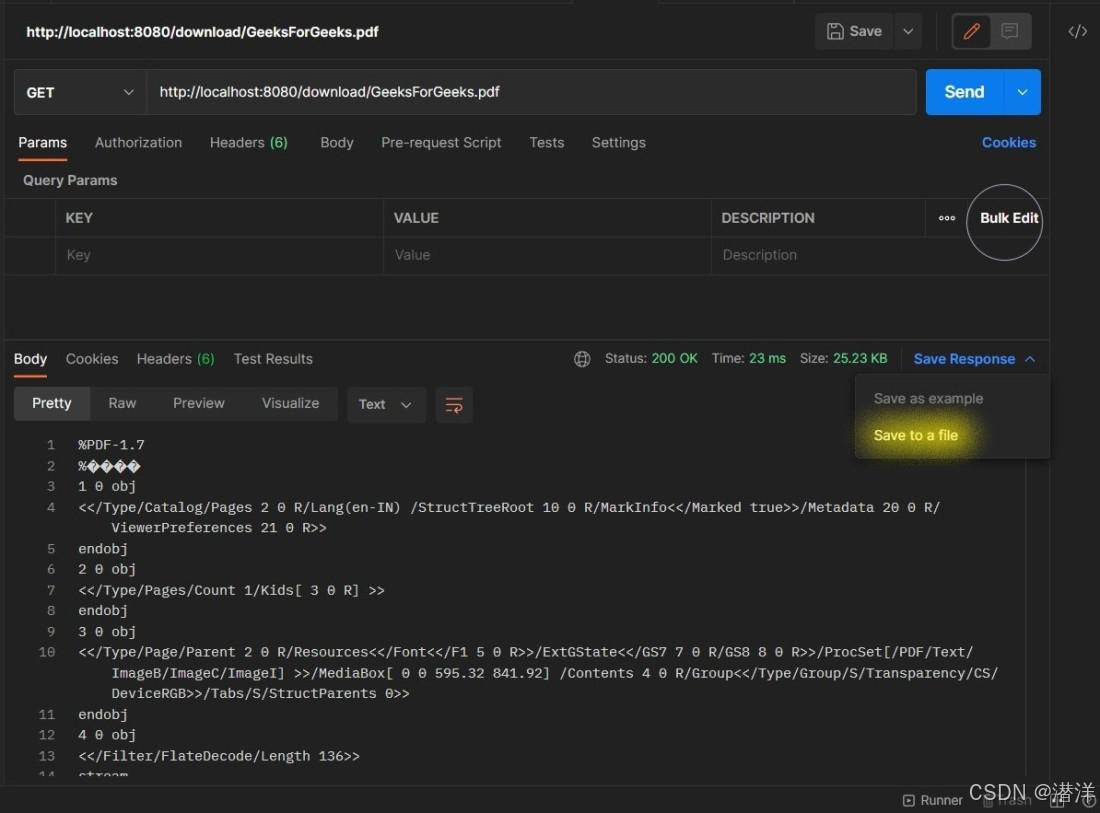
可以通过单击“保存响应”->“保存到文件”将 Postman 中收到的响应下载为文件。也可以在浏览器中点击下载 URL 以直接下载文件。如果我们尝试下载不存在的文件,则会在响应中收到“文件未找到”以及HttpStatus为NOT_FOUND。