递归(3)----力扣40组合数2,力扣473火柴拼正方形
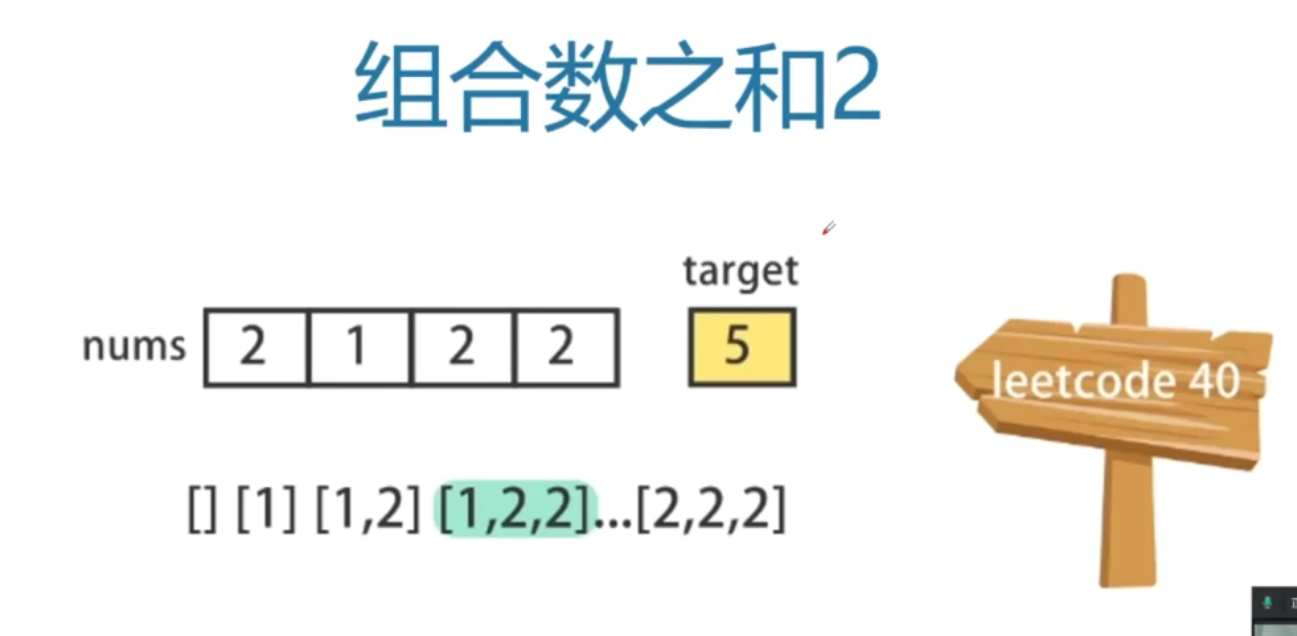
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 输出: [ [1,1,6], [1,2,5], [1,7], [2,6] ]示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, 输出: [ [1,2,2], [5] ]

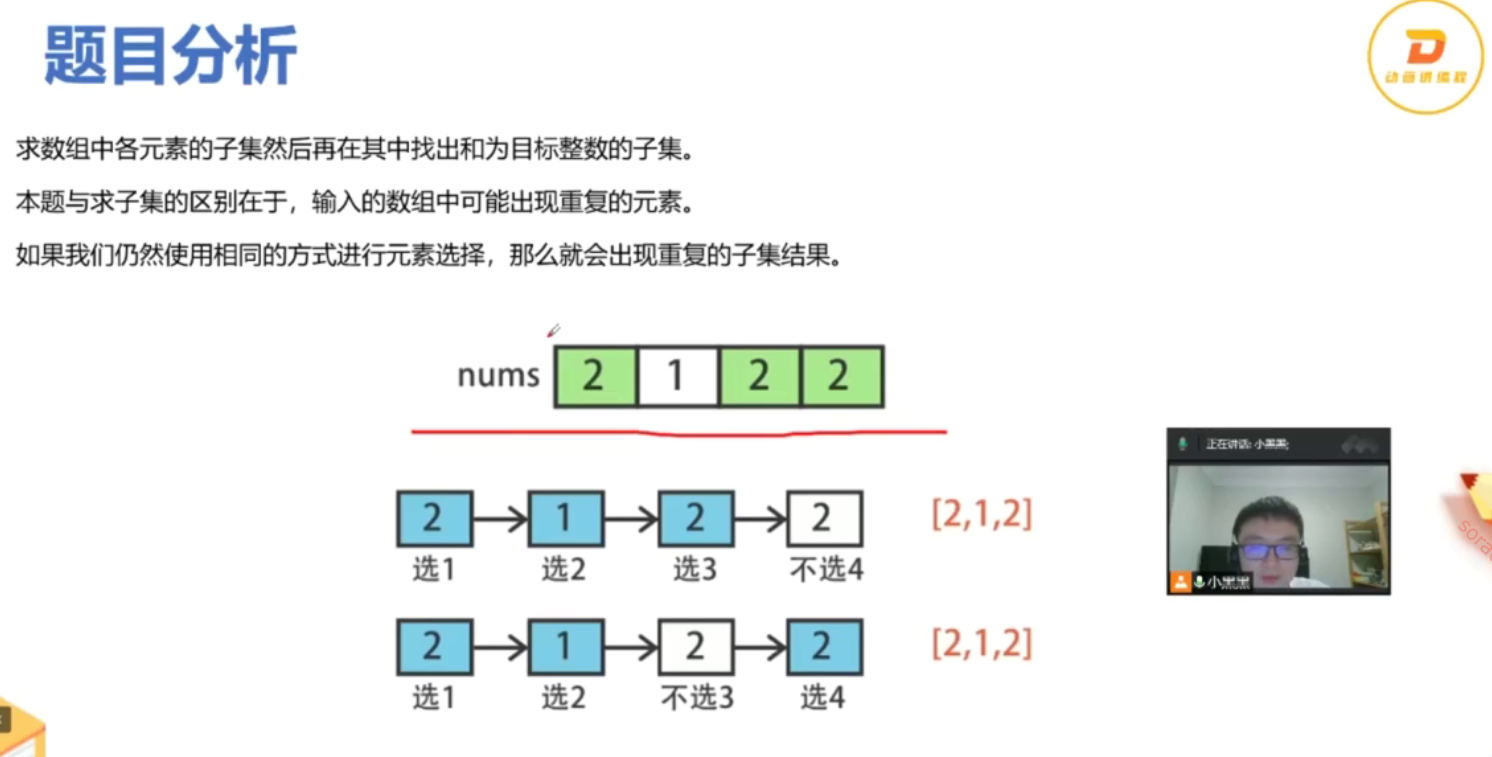
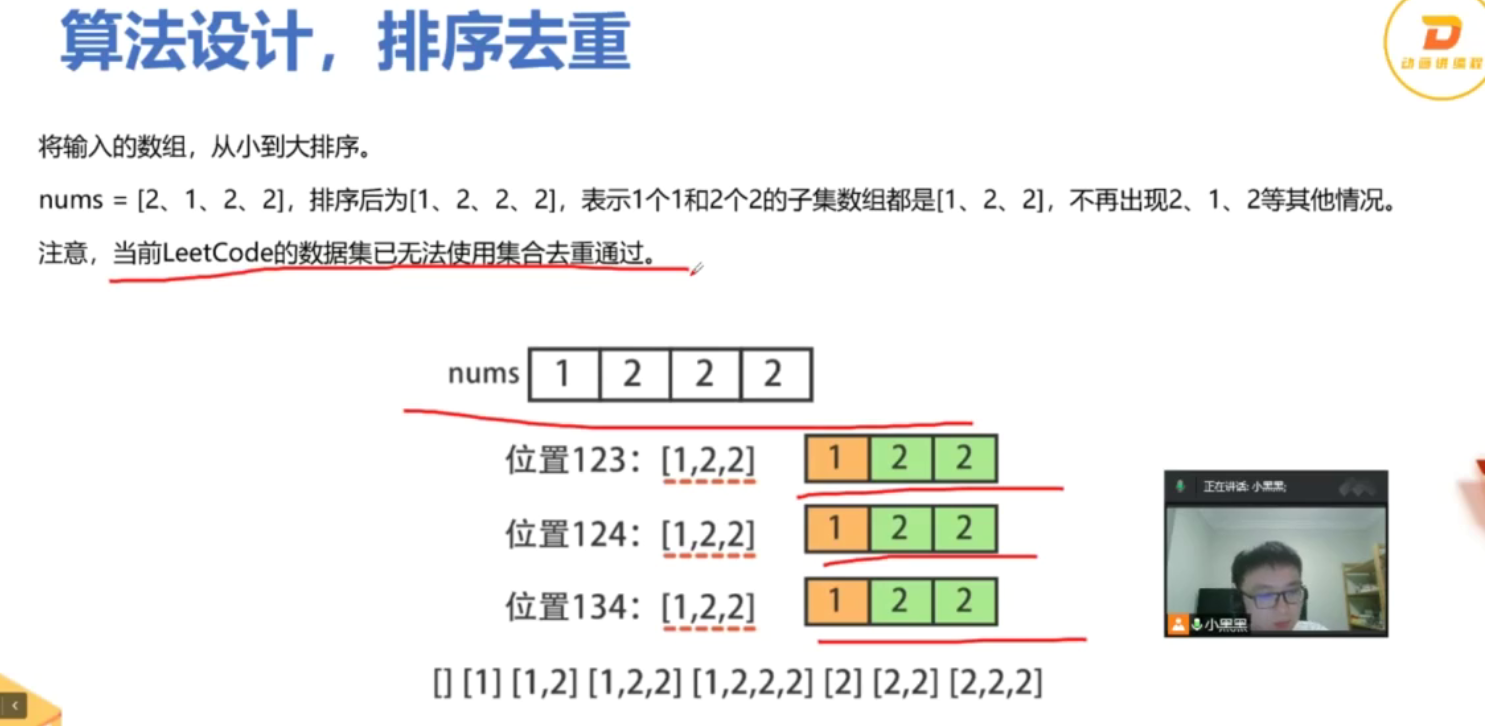
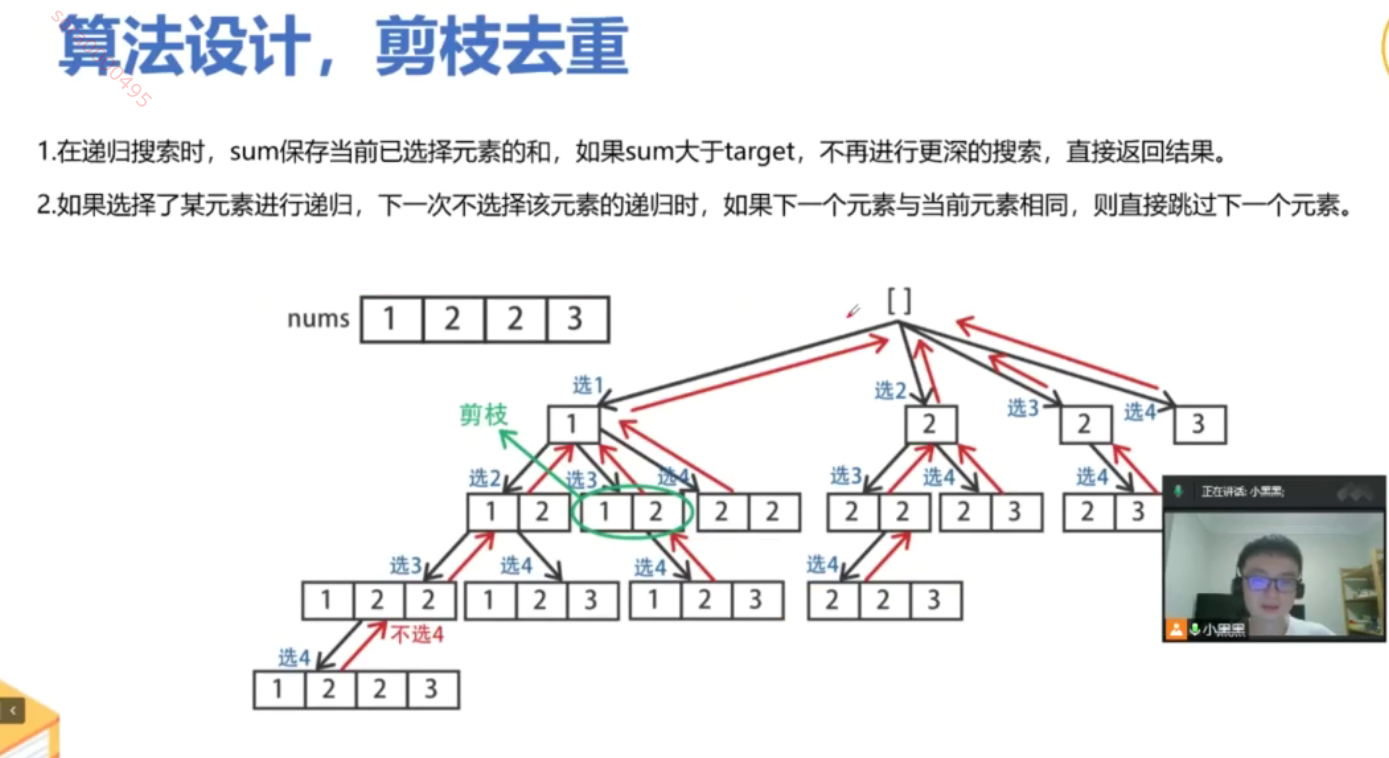
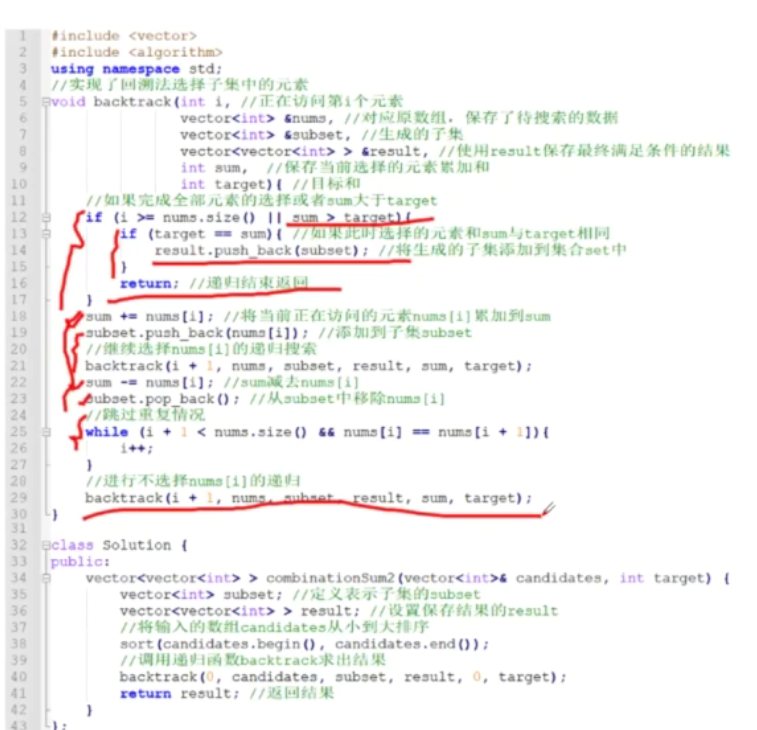
from typing import Listclass Solution:def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:def backtrack(start: int, target: int, current: List[int]):if target == 0:result.append(current[:])returnfor i in range(start, len(candidates)):# 剪枝:如果当前数字大于目标值,后面的数字更大,直接跳出if candidates[i] > target:break# 跳过重复数字,确保不会生成重复组合if i > start and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]:continue# 选择当前数字current.append(candidates[i])# 递归寻找剩余目标值的组合,注意是i+1因为每个数字只能用一次backtrack(i + 1, target - candidates[i], current)# 回溯,移除当前数字current.pop()# 先排序,便于处理重复元素candidates.sort()result = []backtrack(0, target, [])return resultif __name__ == '__main__':s = Solution()print(s.combinationSum2([10,1,2,7,6,1,5], 8))print(s.combinationSum2([2,5,2,1,2], 5))
例子 假设我们有一个候选数字列表 candidates = [1, 2, 3],我们想要找到所有组合,使得它们的和等于 target = 4。 递归过程 初始调用: backtrack(0, 4, []):从索引 0 开始,目标值为 4,当前组合为空。 2. 第一层递归: 选择 candidates[0] = 1: current = [1],目标变为 4 - 1 = 3,调用 backtrack(1, 3, [1])。 选择 candidates[1] = 2: current = [2],目标变为 4 - 2 = 2,调用 backtrack(2, 2, [2])。 选择 candidates[2] = 3: current = [3],目标变为 4 - 3 = 1,调用 backtrack(3, 1, [3])。 3. 第二层递归: 对于 current = [1],目标为 3: 选择 candidates[1] = 2: current = [1, 2],目标变为 3 - 2 = 1,调用 backtrack(2, 1, [1, 2])。 选择 candidates[2] = 3: current = [1, 3],目标变为 3 - 3 = 0,找到一个有效组合 [1, 3],返回。 4. 继续探索: 对于 current = [2],目标为 2: 选择 candidates[2] = 3,目标变为 2 - 3 = -1,无效,返回。 对于 current = [1, 2],目标为 1: 选择 candidates[2] = 3,目标变为 1 - 3 = -2,无效,返回。 5. 最终结果: 通过递归的方式,我们会找到所有有效的组合,最终结果为 [[1, 3], [2, 2]]。 总结 这个例子展示了如何通过递归探索所有可能的组合,直到找到所有和为目标值的组合。每次选择一个数字并递归调用,直到满足条件或超出目标值。
你将得到一个整数数组 matchsticks ,其中 matchsticks[i] 是第 i 个火柴棒的长度。你要用 所有的火柴棍 拼成一个正方形。你 不能折断 任何一根火柴棒,但你可以把它们连在一起,而且每根火柴棒必须 使用一次 。
如果你能使这个正方形,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
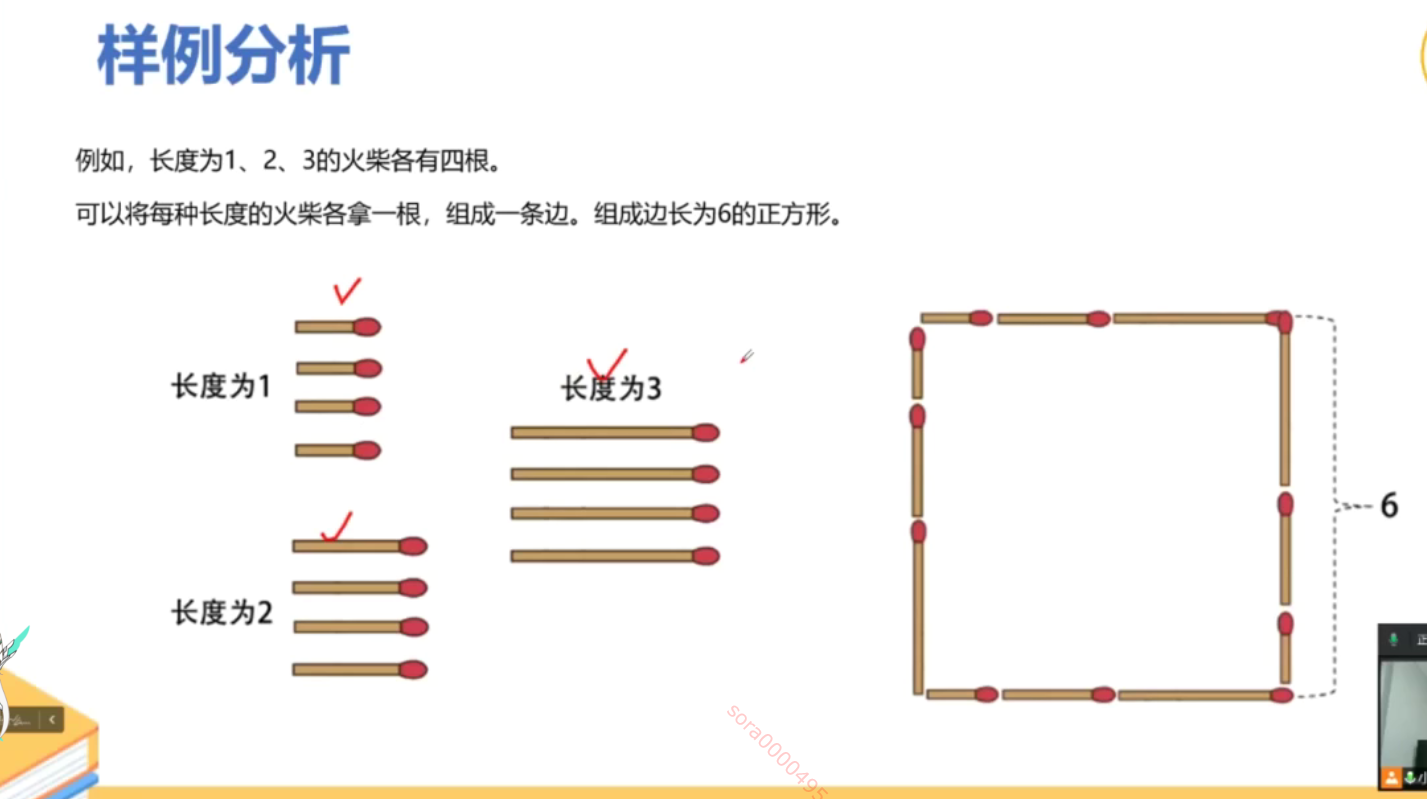
输入: matchsticks = [1,1,2,2,2] 输出: true 解释: 能拼成一个边长为2的正方形,每边两根火柴。
示例 2:
输入: matchsticks = [3,3,3,3,4] 输出: false 解释: 不能用所有火柴拼成一个正方形。

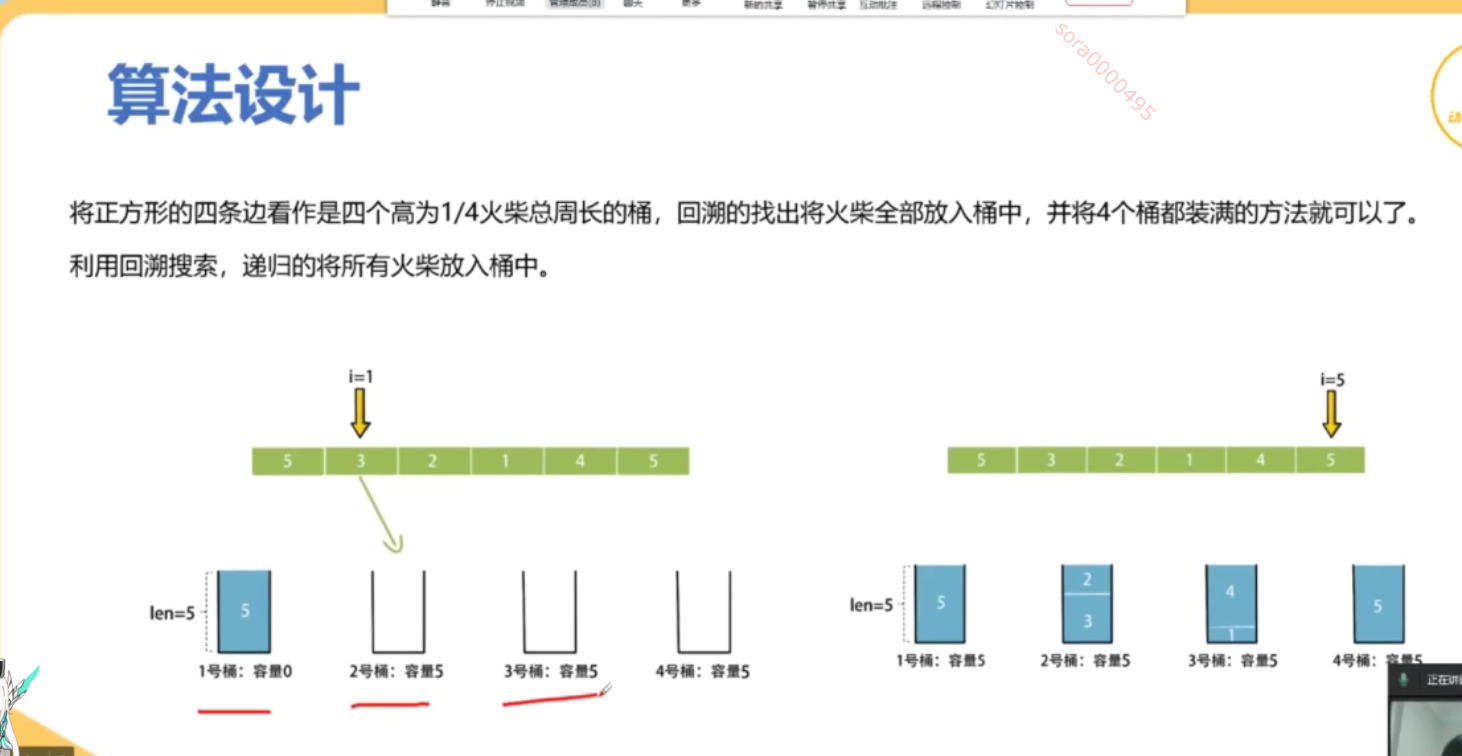

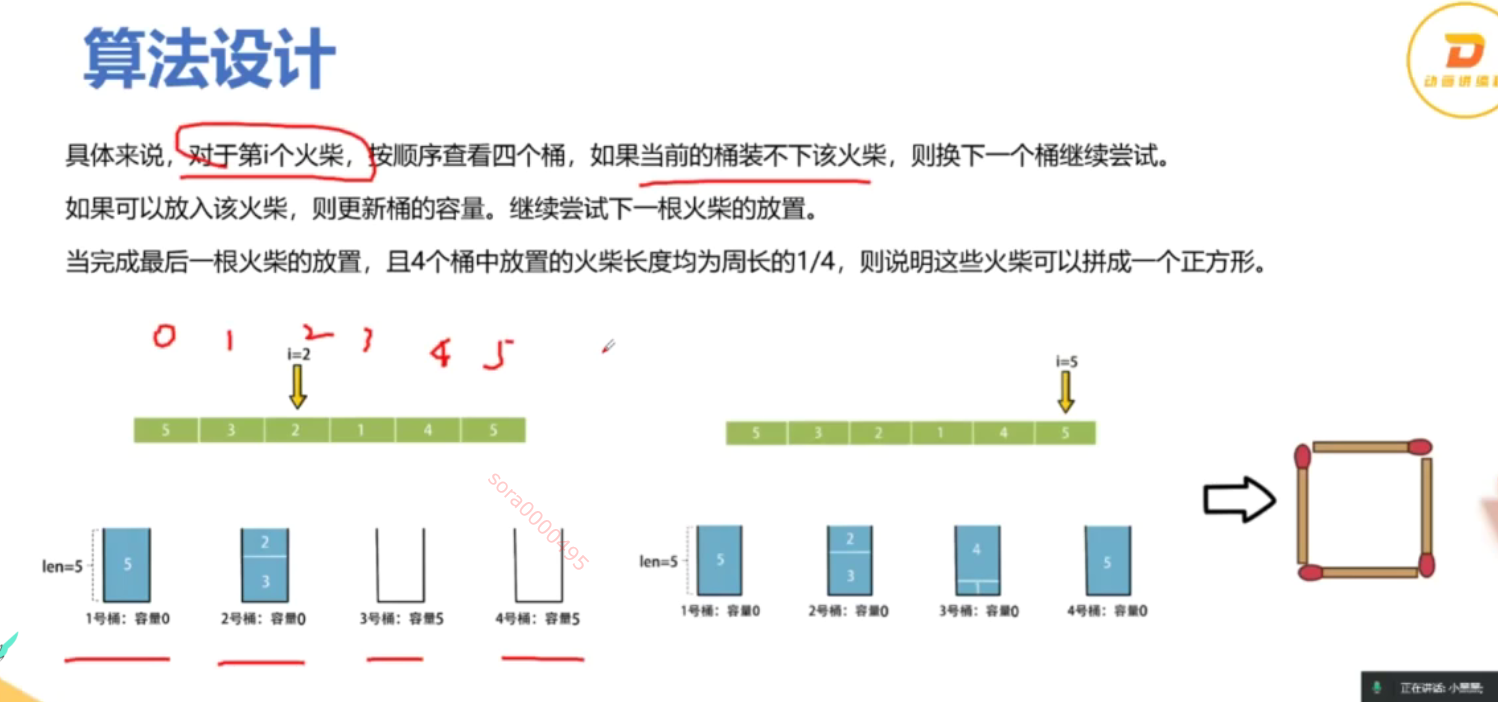

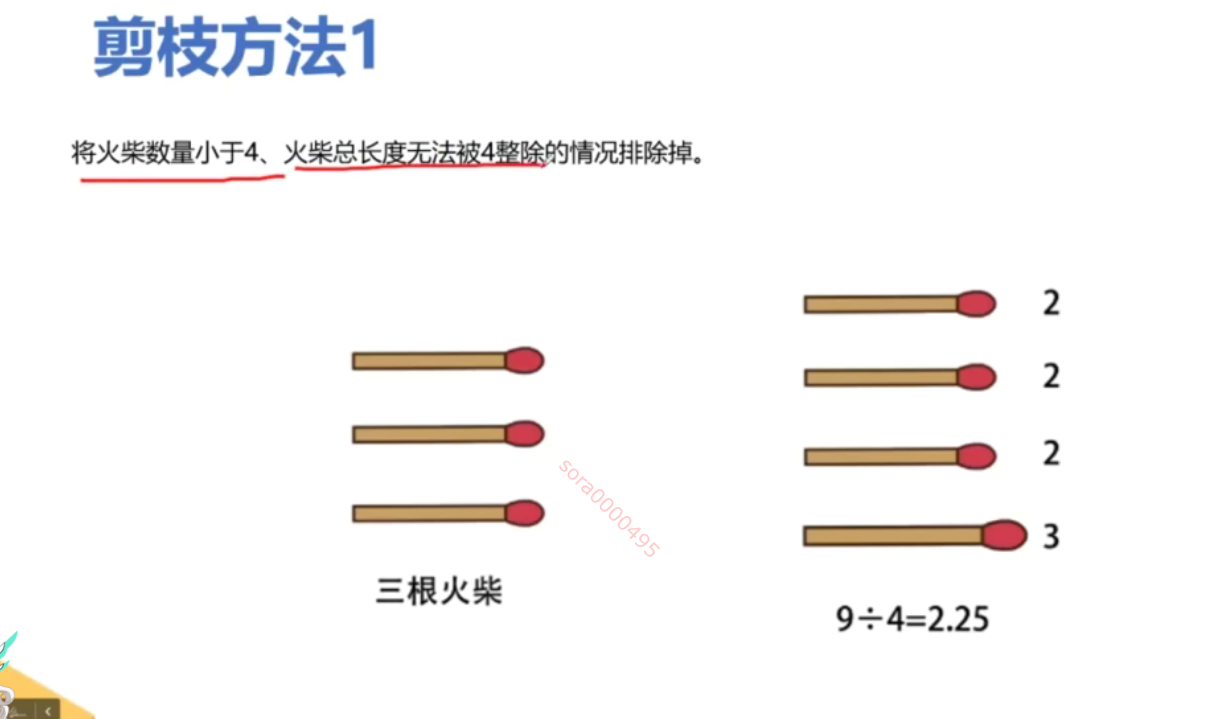
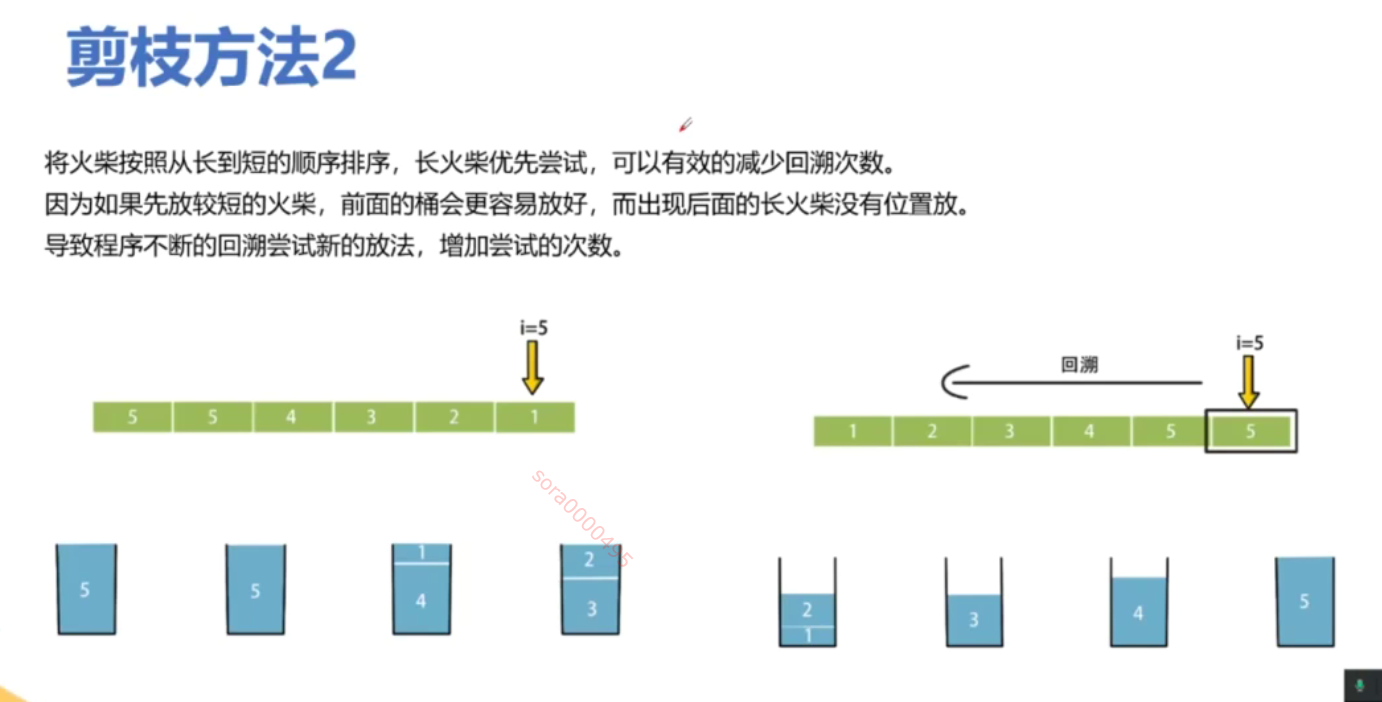
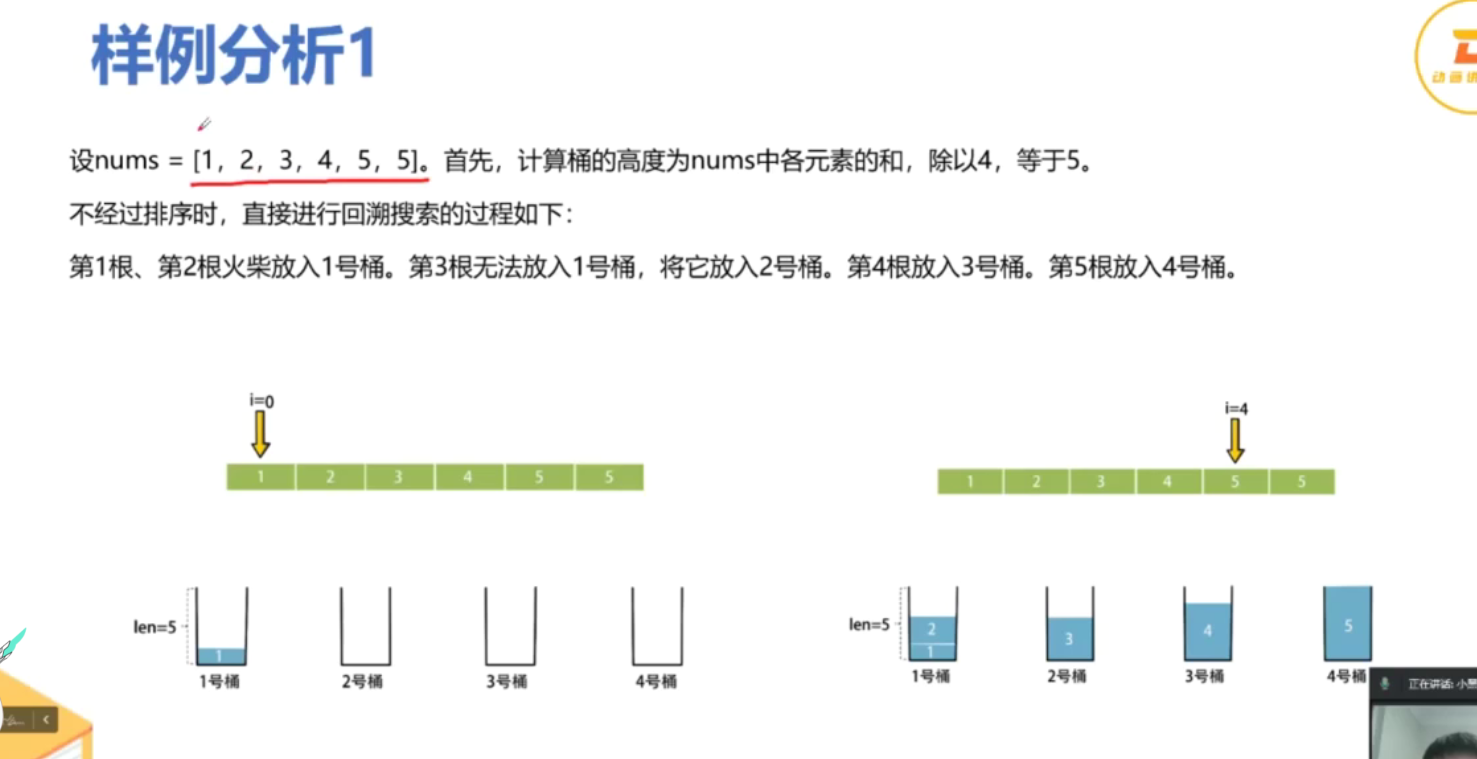
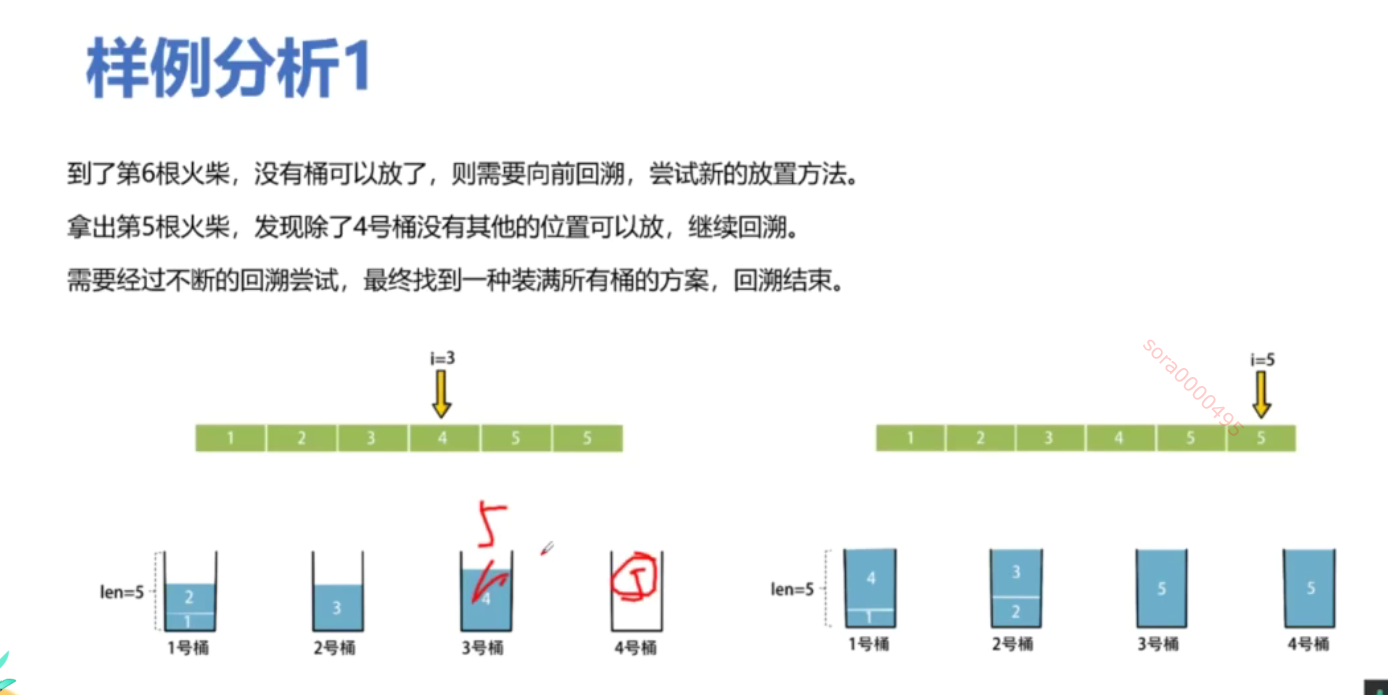
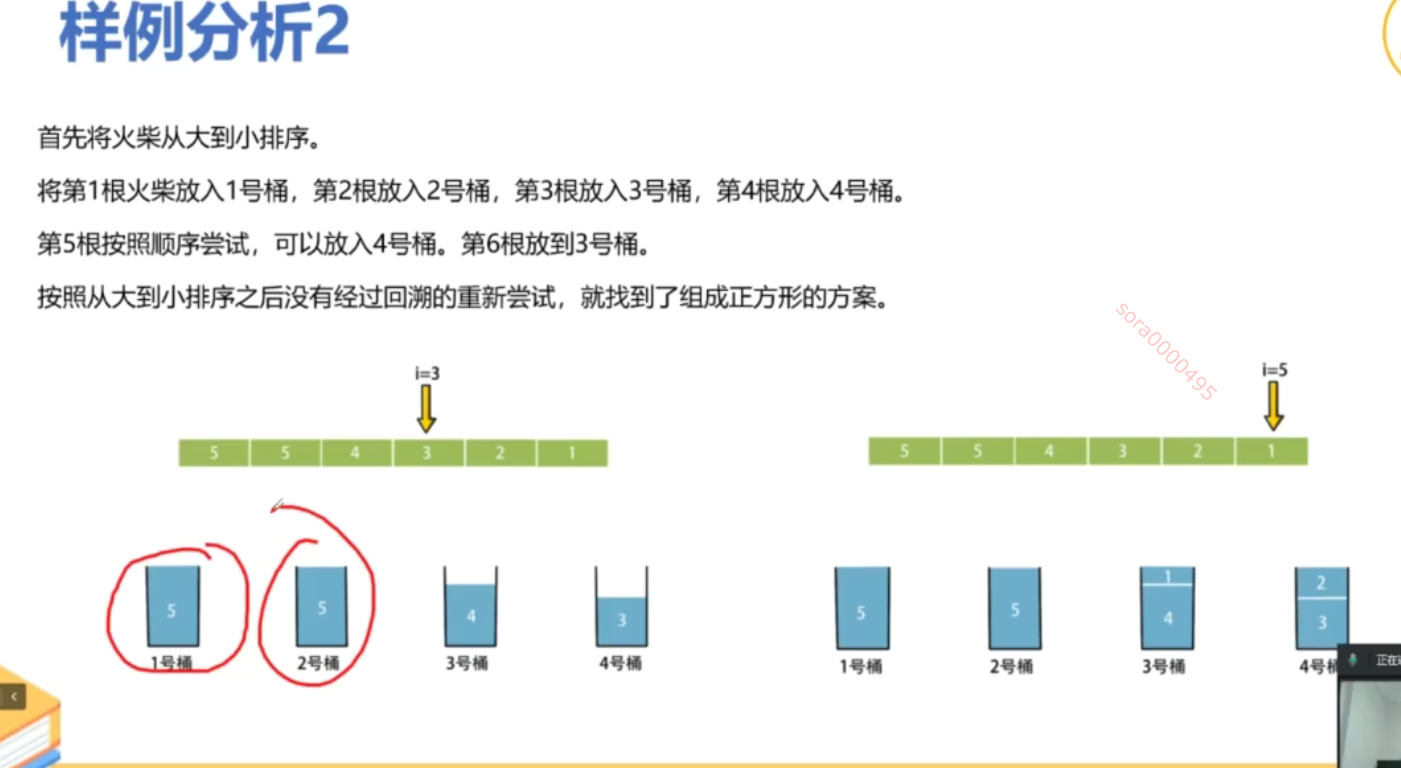

from typing import List # 导入 List 类型class Solution:def makesquare(self, matchsticks: List[int]) -> bool:total_length = sum(matchsticks) # 计算所有火柴棒的总长度# 如果总长度不能被4整除,无法形成正方形if total_length % 4 != 0:return False # 返回 Falseside_length = total_length // 4 # 计算每个边的目标长度matchsticks.sort(reverse=True) # 从大到小排序,优化回溯过程sides = [0] * 4 # 初始化四个边的当前长度为0def backtrack(index: int) -> bool:if index == len(matchsticks): # 如果所有火柴棒都已使用# 检查四个边是否相等return all(side == side_length for side in sides) # 返回是否每个边都等于目标边长for i in range(4): # 遍历四个边if sides[i] + matchsticks[index] <= side_length: # 如果当前边加上火柴棒不超过目标边长sides[i] += matchsticks[index] # 选择当前火柴棒,加入到当前边if backtrack(index + 1): # 递归处理下一个火柴棒return True # 如果成功,返回 Truesides[i] -= matchsticks[index] # 回溯,撤销选择return False # 如果无法拼成正方形,返回 Falsereturn backtrack(0) # 从第一个火柴棒开始回溯if __name__ == '__main__':s = Solution() # 创建 Solution 类的实例print(s.makesquare([1, 1, 2, 2, 2])) # 输出: True,能拼成正方形print(s.makesquare([3, 3, 3, 3, 4])) # 输出: False,不能拼成正方形
