【Spring】我抄袭了Spring,手写一套MySpring框架。。。
这篇博客实现了一个简单版本的Spring,主要包括Spring的Ioc和Aop功能
文章目录
- 这篇博客实现了一个简单版本的Spring,主要包括Spring的Ioc和Aop功能
- 🚀@ComponentScan注解
- ✈️@Component注解
- 🚁在spring中ioc容器的类是ApplicationContext
- 🚂测试类
- 🚊MySpringConfig类,统一的配置类
- 🚞OrderService类,一个普通的bean
- 🚲来测试一下功能
- 🚡@Scope注解
- 🚟BeanDefinition 类
- 🚠要实现我们的@scope注解,我们需要改造一下我们的代码
- 🚜然后我们从beanDefinitionMap中实例化bean
- 🚙我们来看一下效果
- 🚘@Autowired注解
- 🚗UserService类,orderservice注入该类
- 🚗要使@Autowired注解生效,将bean实例化到一级缓存中方法需要改造一下
- 🚕BeanPostProcessor接口
- 🚖添加自己的BeanPostProcessor
- 🚛Aop
🚀@ComponentScan注解
ComponentScan做的事情就是告诉Spring从哪里找到bean
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {String[] value() default {};}✈️@Component注解
@Component是spring中的一个注解,它的作用就是实现bean的注入
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {String value() default "";}🚁在spring中ioc容器的类是ApplicationContext
所以我们需要创建一个ApplicationContext,有参构造传入config的class
public class ApplicationContext {public ApplicationContext(Class configClass) {}}存放bean的map
public class ApplicationContext {private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);public ApplicationContext(Class configClass) {}}拿到ComponentScan的值
public class ApplicationContext {private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);public ApplicationContext(Class configClass) {//查看是否有ComponentScan注解if (configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)) {ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);String[] paths = componentScanAnnotation.value();}}
}拿到该路径下所有的class文件
public class ApplicationContext {private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);public ApplicationContext(Class configClass) {//查看是否有ComponentScan注解if (configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)) {ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);String[] paths = componentScanAnnotation.value();for (String path : paths) {//拿到包路径ClassLoader classLoader = ApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path.replace(".", "/"));//拿到该路径下所有的class文件File file = new File(resource.getFile());if (file.isDirectory()) {File[] files = file.listFiles();for (File f : files) {}}}}}
}注册有Component注解的bean
public class ApplicationContext {private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);public ApplicationContext(Class configClass) {//查看是否有ComponentScan注解if (configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)) {ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);String[] paths = componentScanAnnotation.value();for (String path : paths) {//拿到包路径ClassLoader classLoader = ApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path.replace(".", "/"));//拿到该路径下所有的class文件File file = new File(resource.getFile());if (file.isDirectory()) {File[] files = file.listFiles();for (File f : files) {try {String filePath = f.getPath();//拿到com.masiyi.service.MySpringConfigString sub = filePath.substring(filePath.indexOf("com"), filePath.indexOf(".class"));String classes = sub.replace("\\", ".");Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(classes);//注册有Component注解的beanif (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {Object bean = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();Component component = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);String beanName = component.value();if ("".equals(beanName) || beanName == null) {singletonObjects.put(f.getName().split("\\.")[0], bean);} else {singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);}}} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InvocationTargetException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}}
}
🚂测试类
现在我们最基础的spring的ioc已经基本实现了,我们新建一个测试类来测试
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ApplicationContext(MySpringConfig.class);}
}
🚊MySpringConfig类,统一的配置类
@ComponentScan("com.masiyi.service")
public class MySpringConfig {}🚞OrderService类,一个普通的bean
@Component
public class OrderService {
}🚲来测试一下功能
拿到包路径
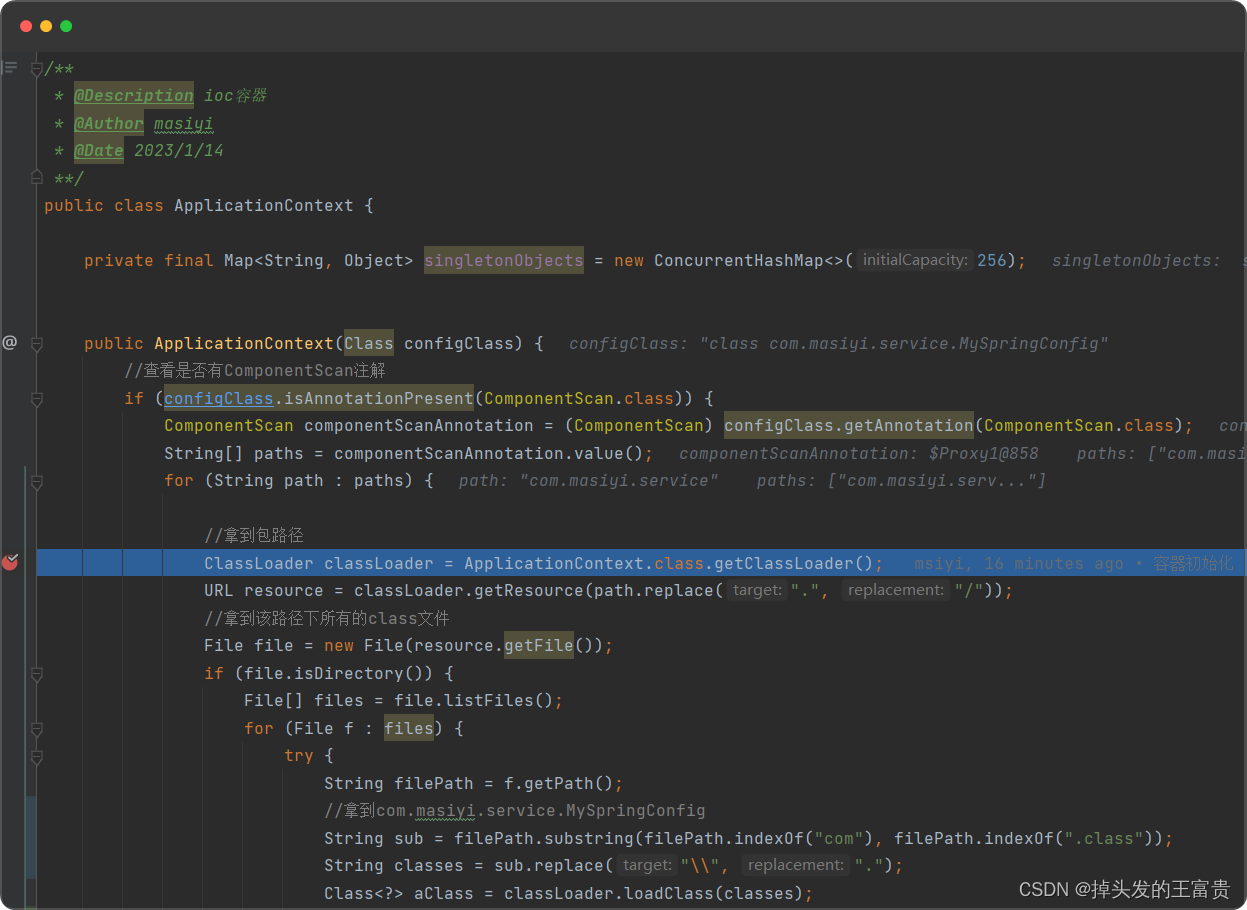
拿到该路径下所有的class文件
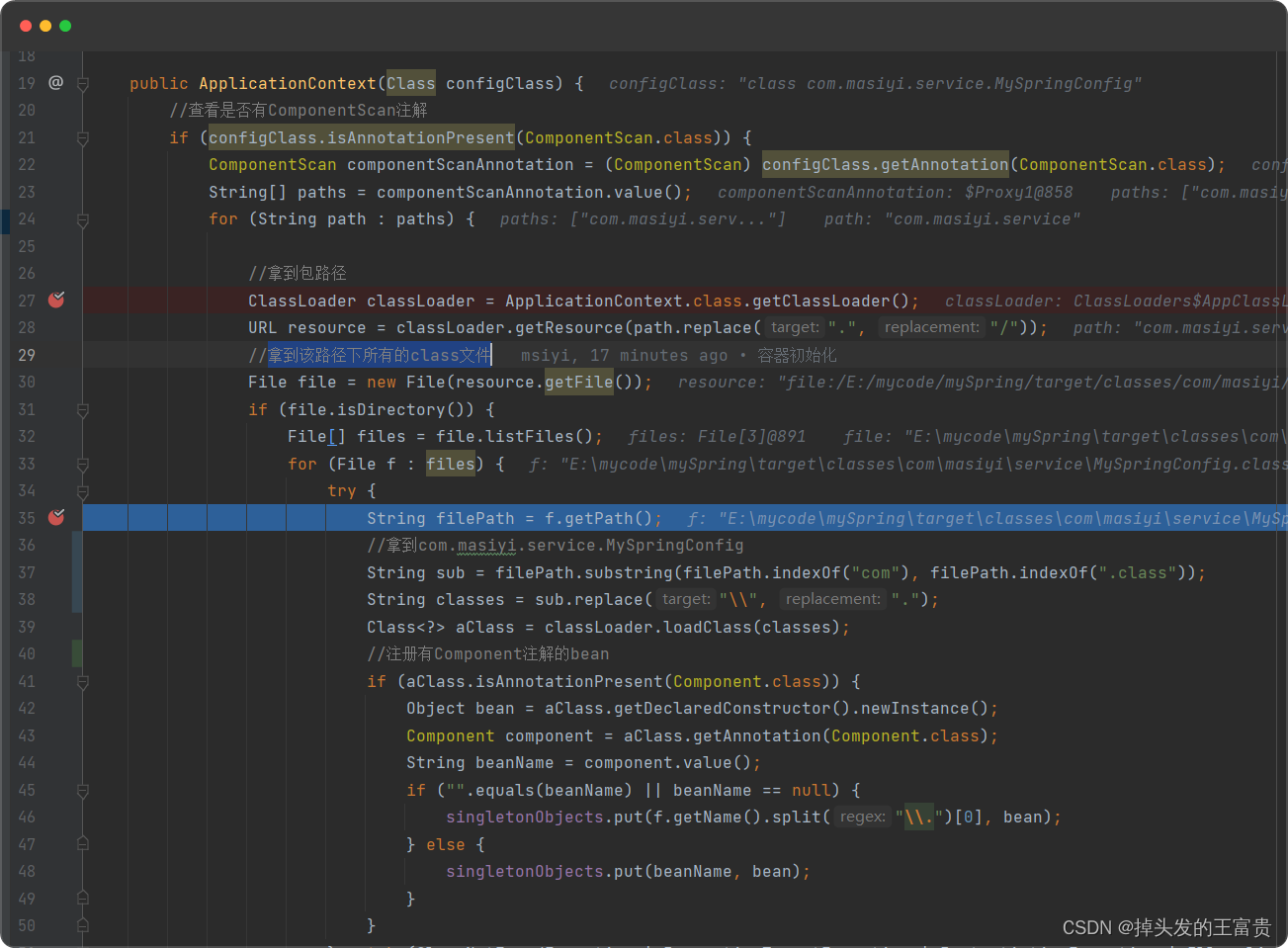
注册有Component注解的bean
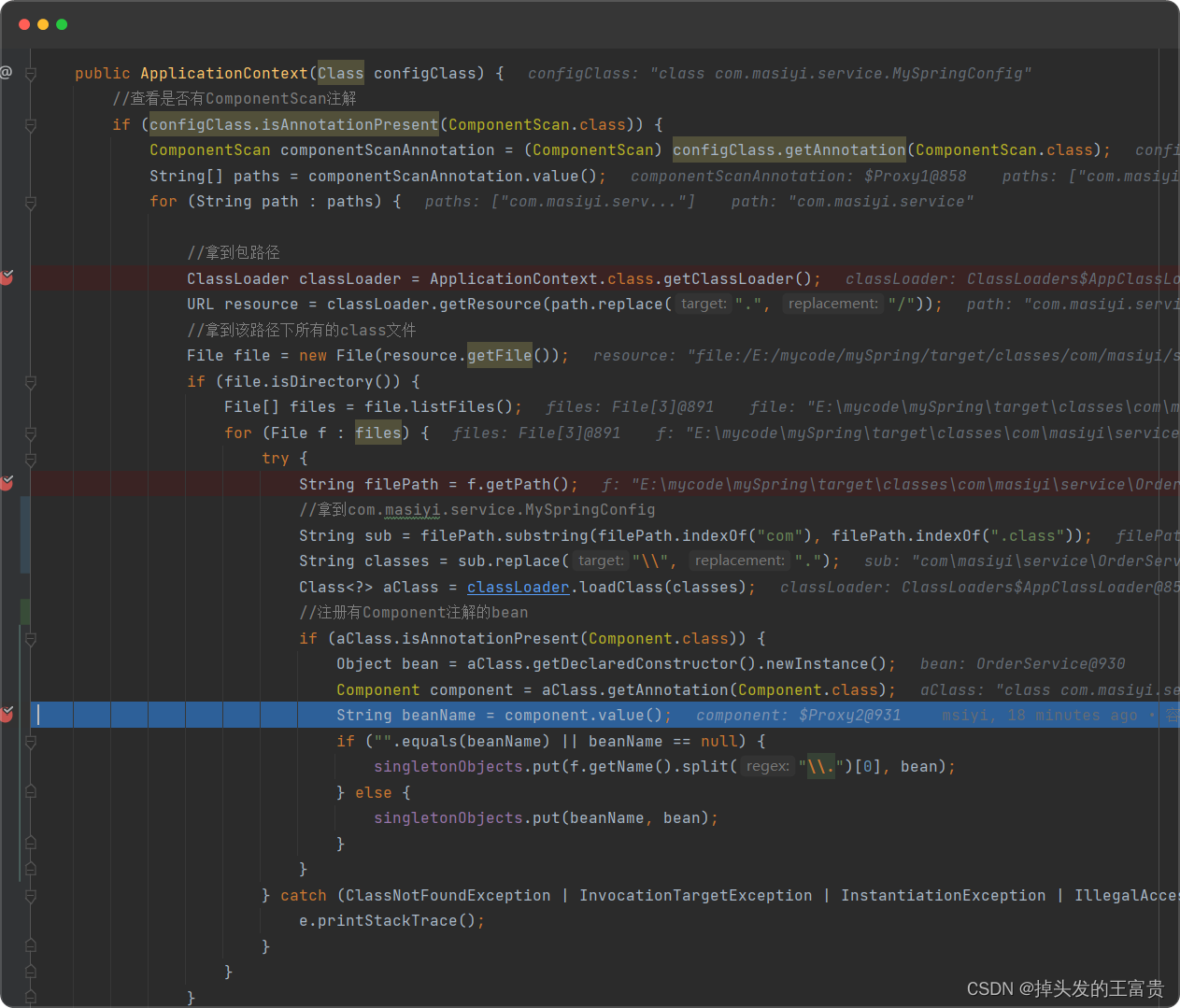
注册进ioc
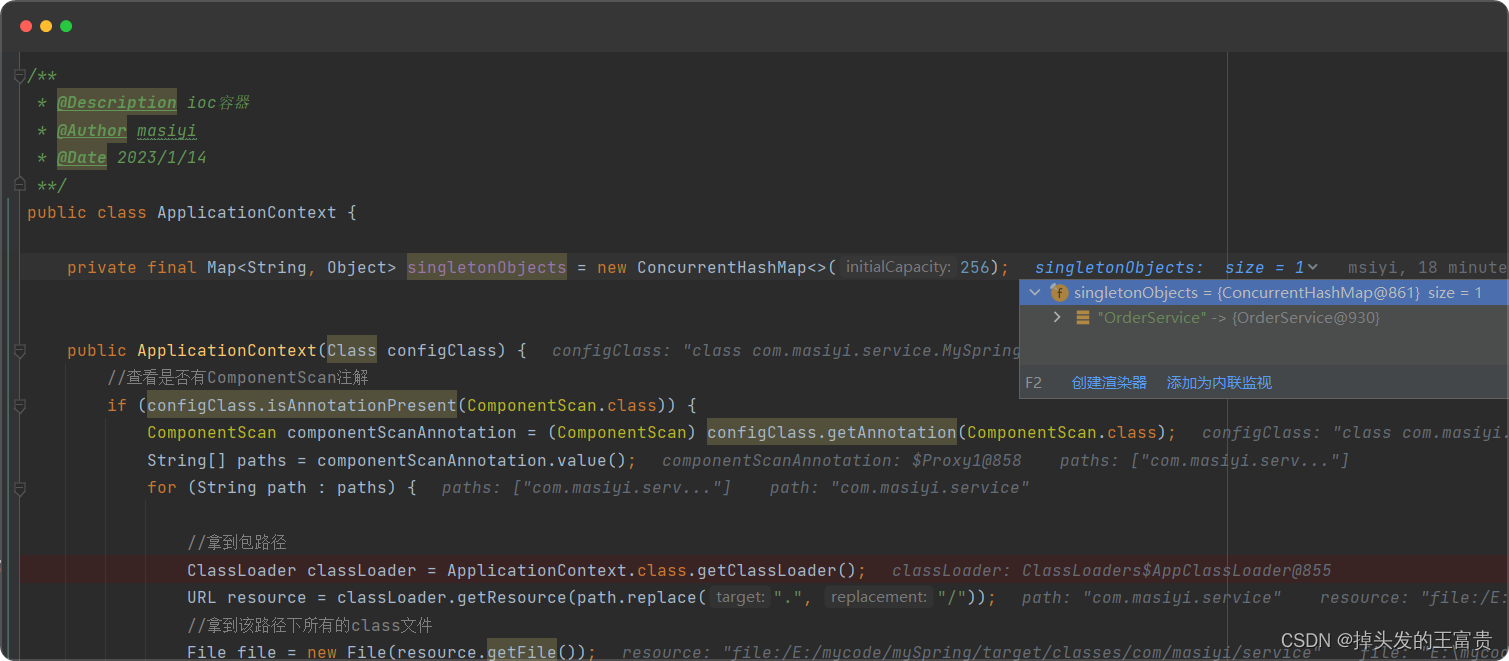
getBean方法
public Object getBean(String beanName) {return this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);}
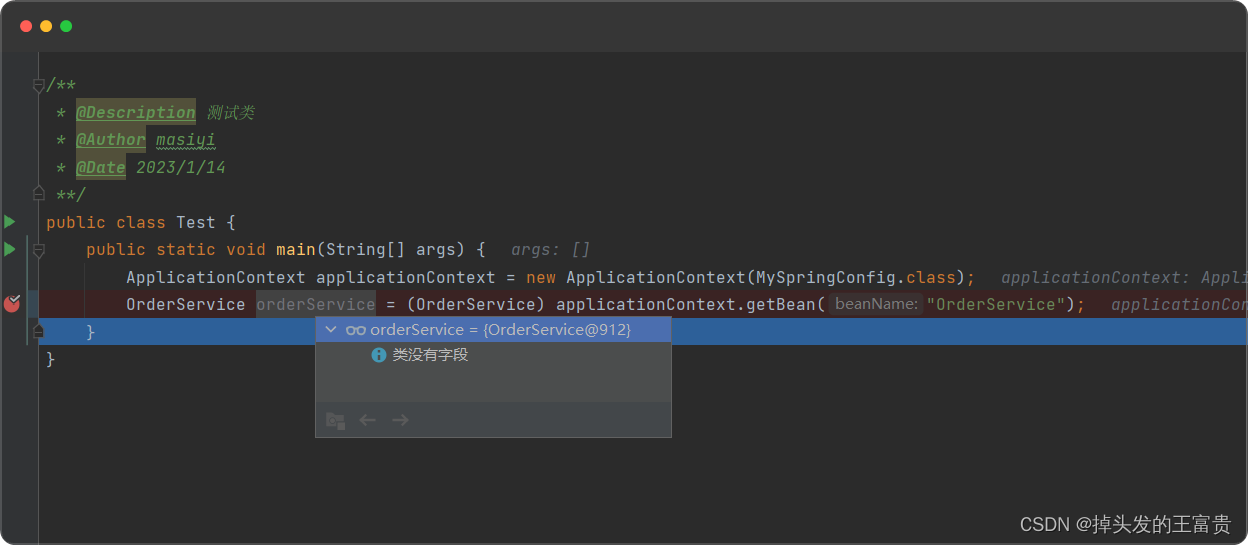
🚡@Scope注解
@Scope注解是 Spring IOC 容器中的一个作用域
🚟BeanDefinition 类
BeanDefinition 是定义 Bean 的配置元信息接口,可以理解为创建bean过程中的一个中间类,扩展bean,存储更多的信息
public class BeanDefinition {private String scope;private Class aClass;public String getScope() {return scope;}public void setScope(String scope) {this.scope = scope;}public Class getaClass() {return aClass;}public void setaClass(Class aClass) {this.aClass = aClass;}
}🚠要实现我们的@scope注解,我们需要改造一下我们的代码
把createBean方法抽离出来
private void createBean(String beanName,Class<?> aClass){//注册有Component注解的beanif (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {Component component = aClass.getAnnotation(Component.class);BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {Scope scope = aClass.getAnnotation(Scope.class);beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());} else {beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");}beanDefinition.setaClass(aClass);String value = component.value();if ("".equals(value)) {beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);} else {beanDefinitionMap.put(value, beanDefinition);}}}
扫描ComponentScan注解的方法体改一下
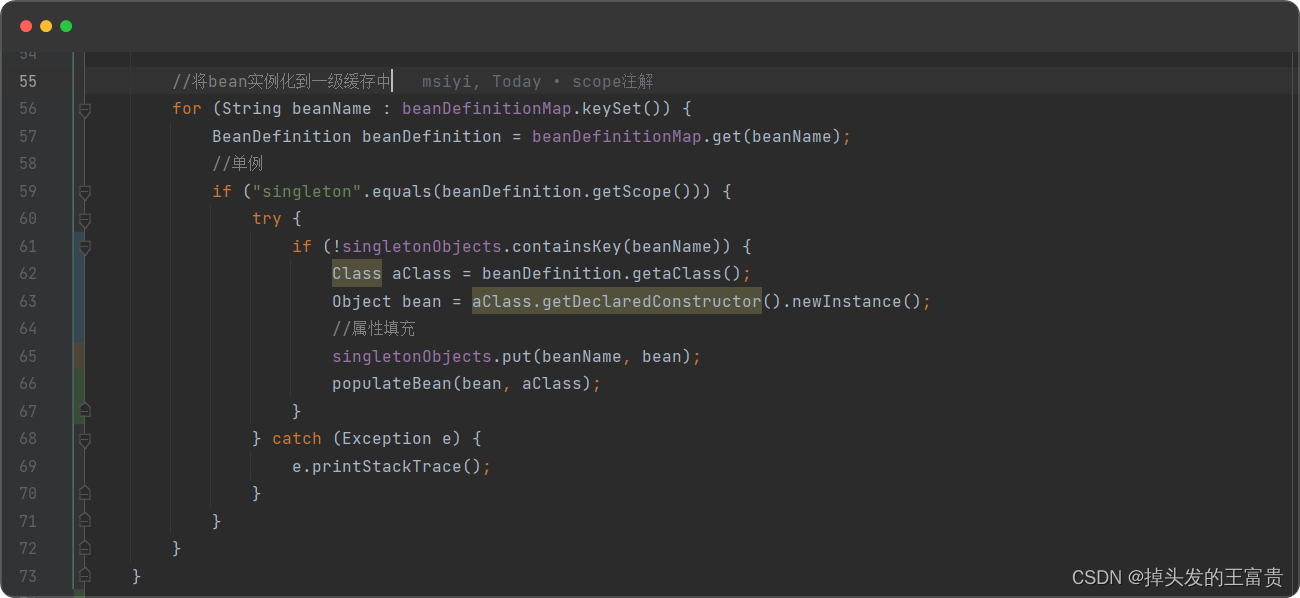
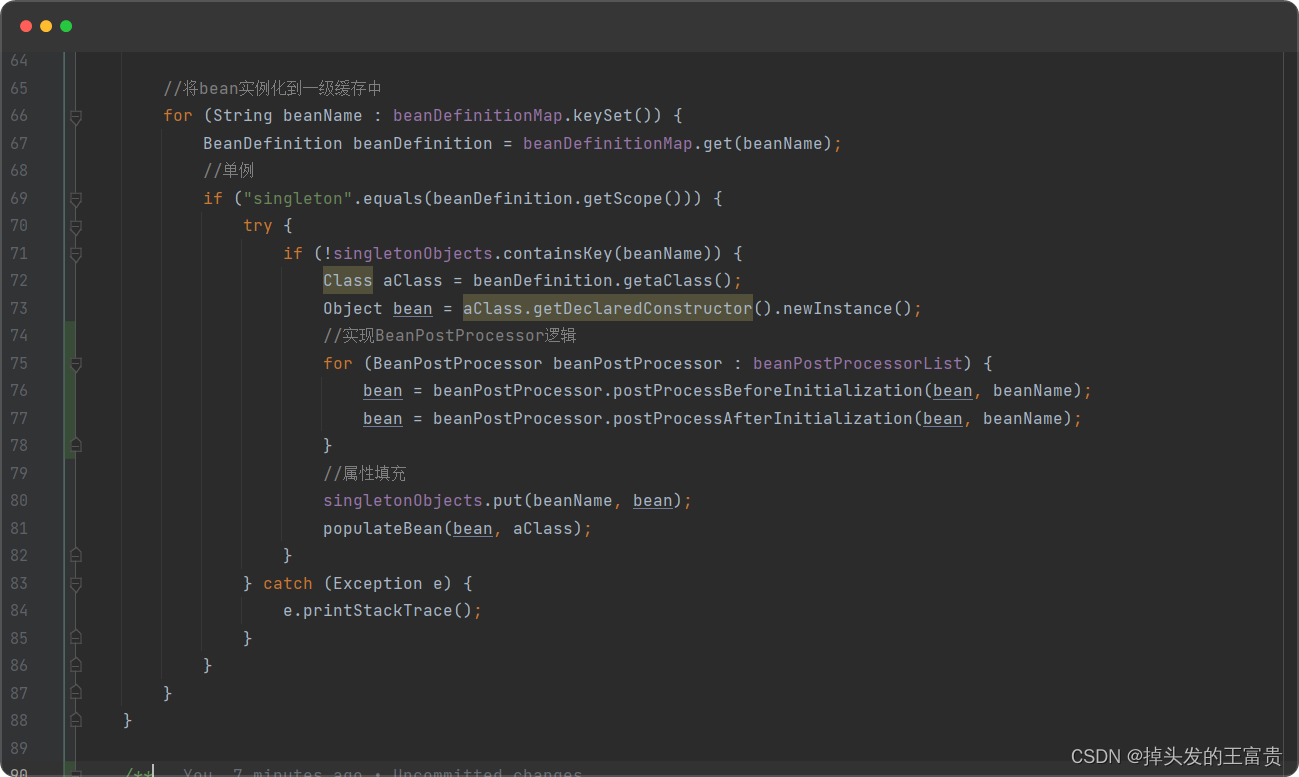
🚜然后我们从beanDefinitionMap中实例化bean
//将bean实例化到一级缓存中for (String beanName : beanDefinitionMap.keySet()) {BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);//单例if ("singleton".equals(beanDefinition.getScope())) {try {Object bean = beanDefinition.getaClass().getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
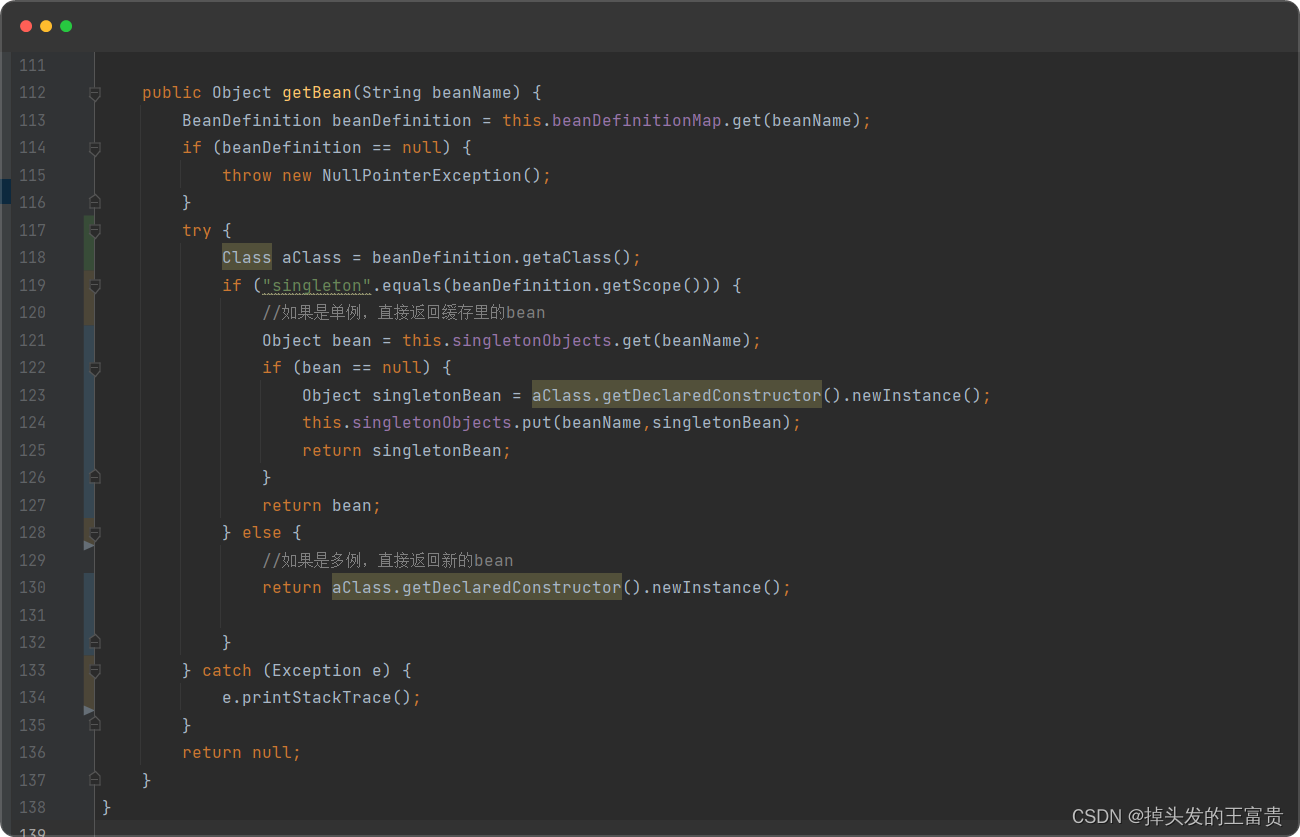
getBean方法也需要改造
public Object getBean(String beanName) {BeanDefinition beanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);if (beanDefinition == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}if ("singleton".equals(beanDefinition.getScope())) {//如果是单例,直接返回缓存里的beanreturn this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);} else {try {//如果是多例,直接返回新的beanreturn beanDefinition.getaClass().getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}return null;}
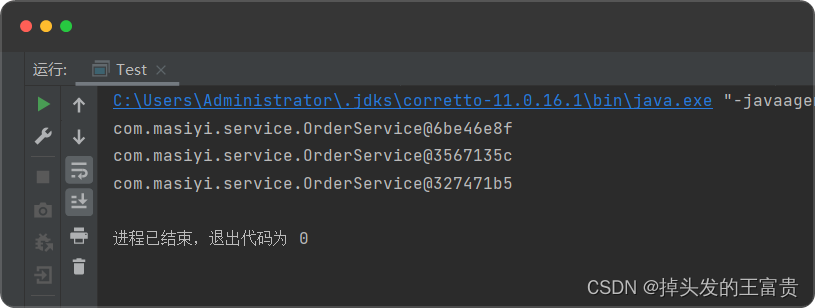
🚙我们来看一下效果
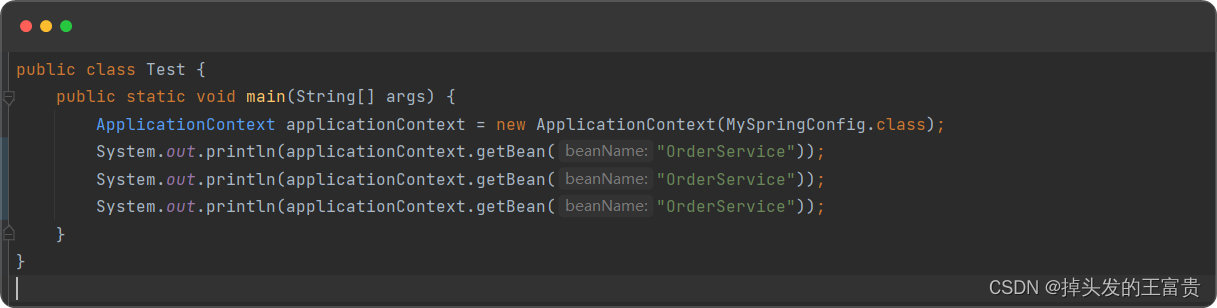
这是没有加scope注解
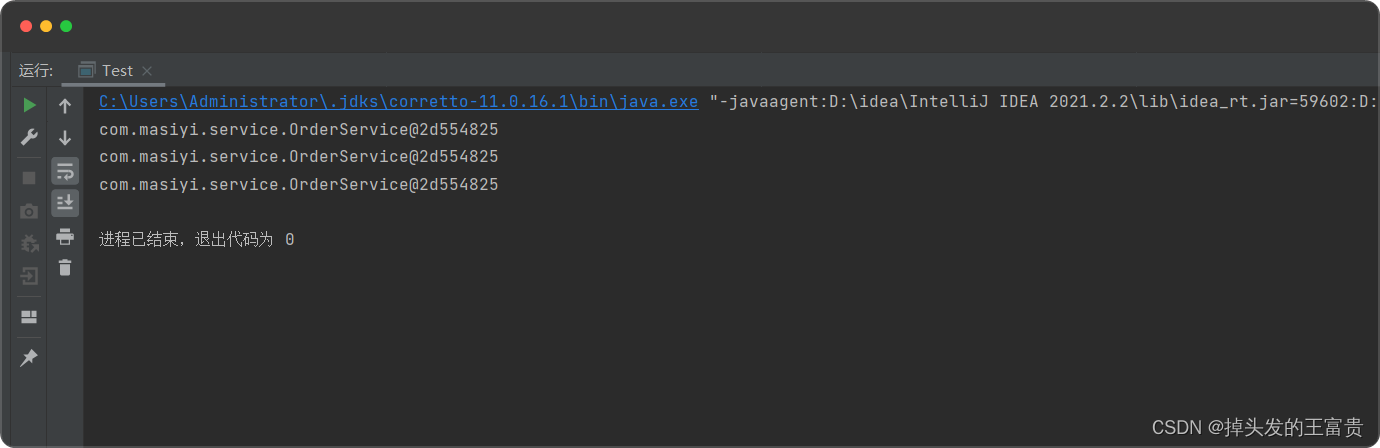
返回的bean都是一个对象
我们给bean加上scope注解
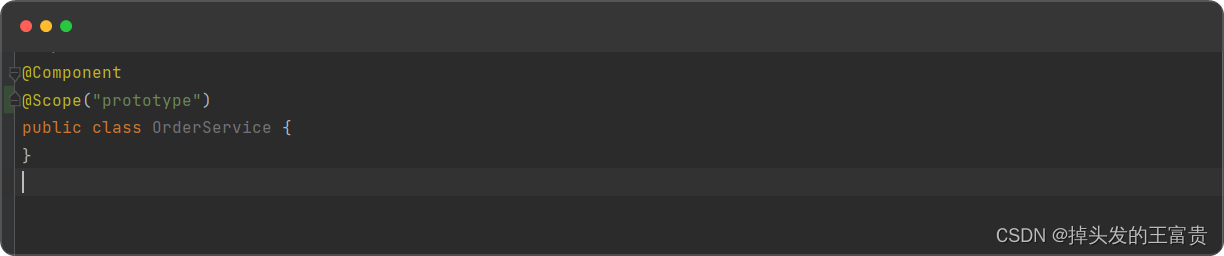
返回来的bean每个都不一样
🚘@Autowired注解
spring中实现依赖注入的注解
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {}🚗UserService类,orderservice注入该类
@Component("userService")
public class UserService {
}@Component
public class OrderService {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;public UserService getUserService() {return userService;}
}🚗要使@Autowired注解生效,将bean实例化到一级缓存中方法需要改造一下
新增populateBean方法,用来初始bean
private void populateBean(Object bean, Class aClass) {Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {declaredField.setAccessible(true);try {declaredField.set(bean, getBean(declaredField.getName()));} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}getBean方法也需要改造一下
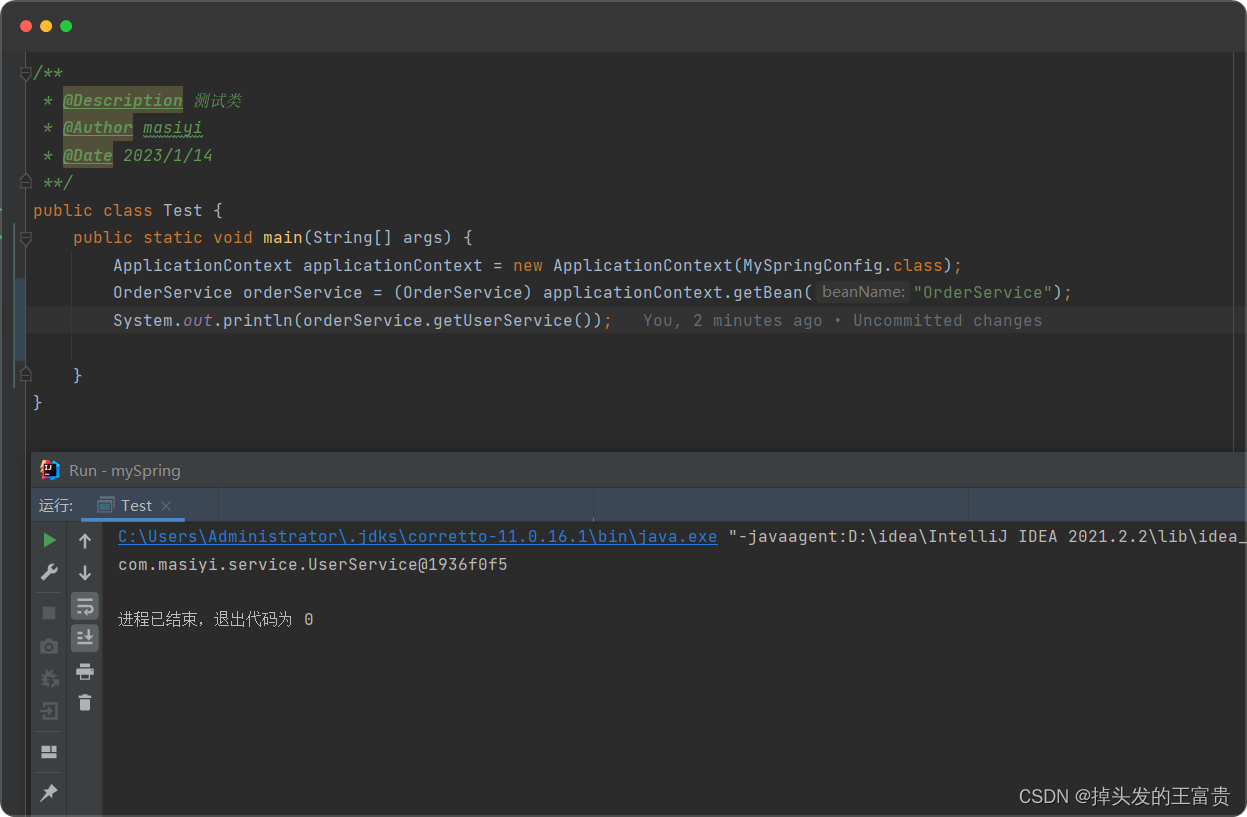
这样我们的orderservice里面的userservice就有值了
🚕BeanPostProcessor接口
该接口在显示调用初始化方法的前后添加我们自己的逻辑
public interface BeanPostProcessor {/*** 之前* @param bean* @param beanName* @return*/default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {return bean;}/*** 之后* @param bean* @param beanName* @return*/default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {return bean;}
}我们创建存储BeanPostProcessor的list

在扫描的时候添加BeanPostProcessor
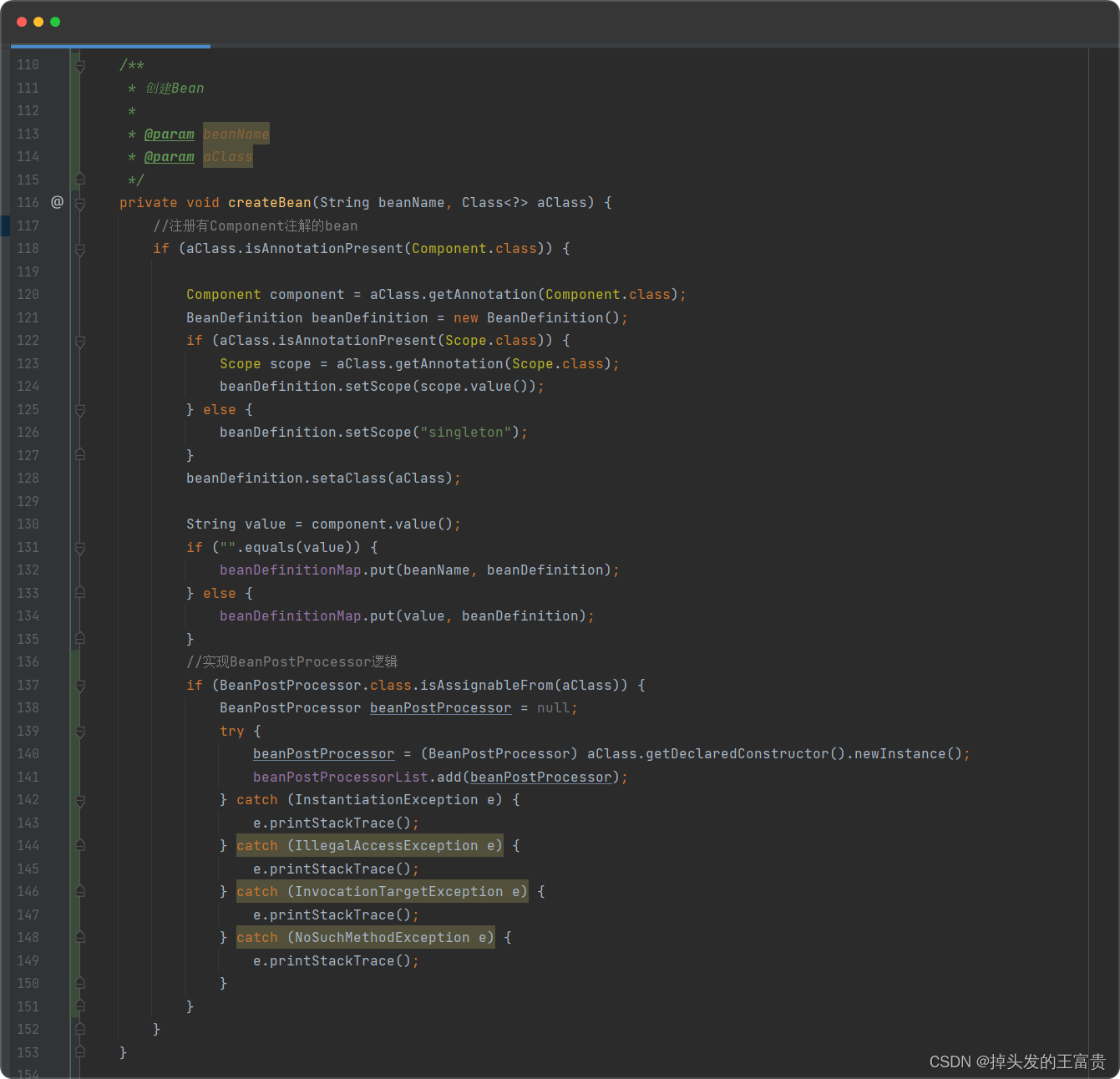
🚖添加自己的BeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class OrderPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {/*** 之前** @param bean* @param beanName* @return*/@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {System.out.println(beanName+"执行前");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);}/*** 之后** @param bean* @param beanName* @return*/@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {System.out.println(beanName+"执行后");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);}
}实例化的时候执行BeanPostProcessor逻辑
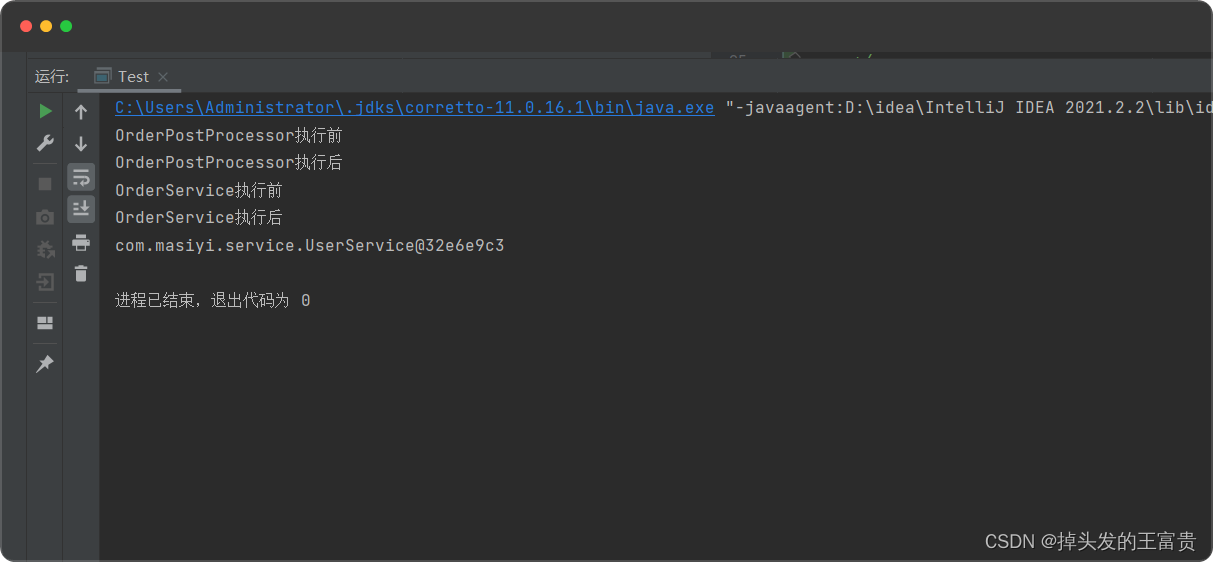
运行结果
🚛Aop
jdk的动态代理是基于接口生成的代理对象
public interface OrderInterface {void test();
}
在OrderPostProcessor类中加以改造
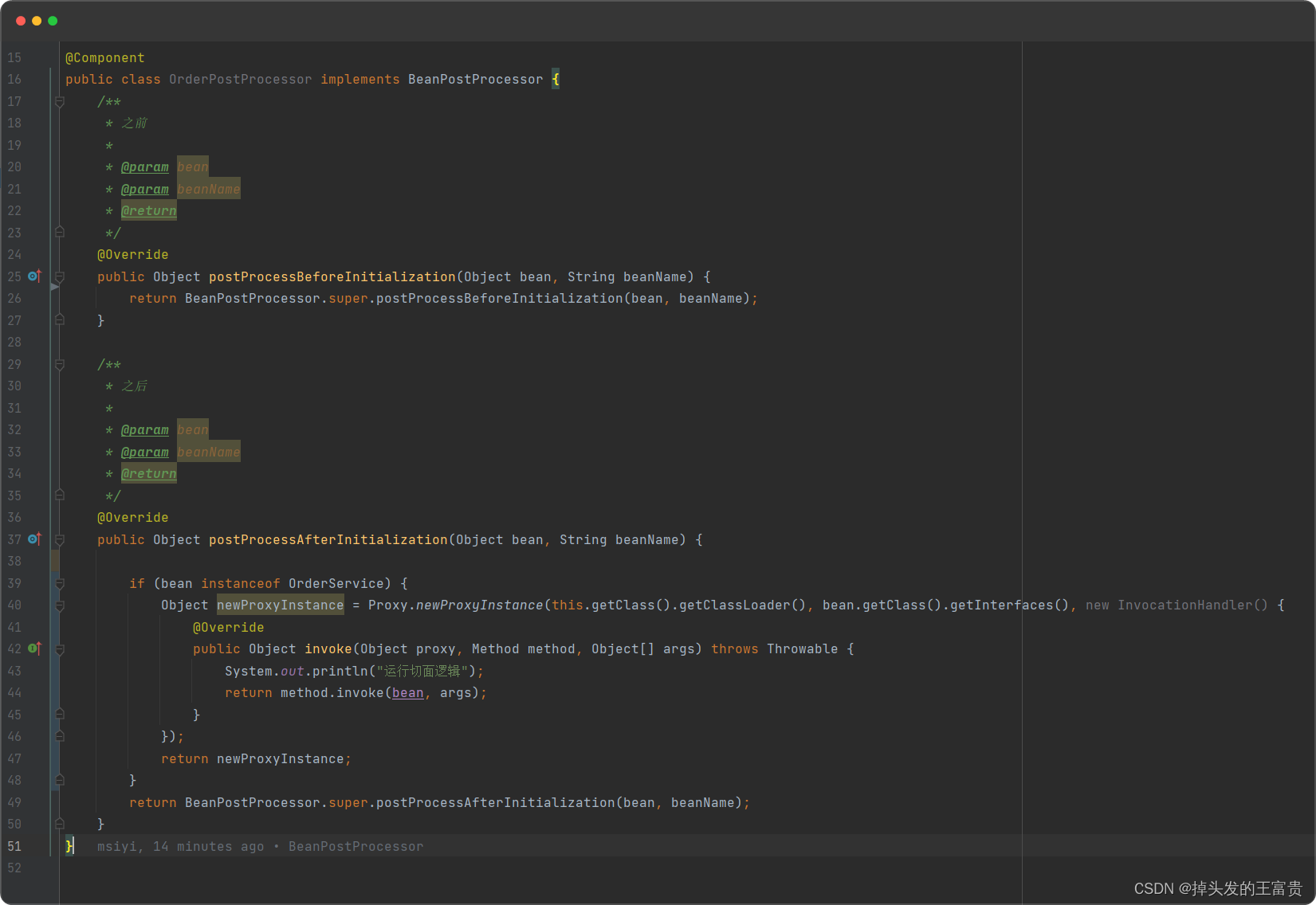
这样我们就可以动态代理切入我们的orderservice类
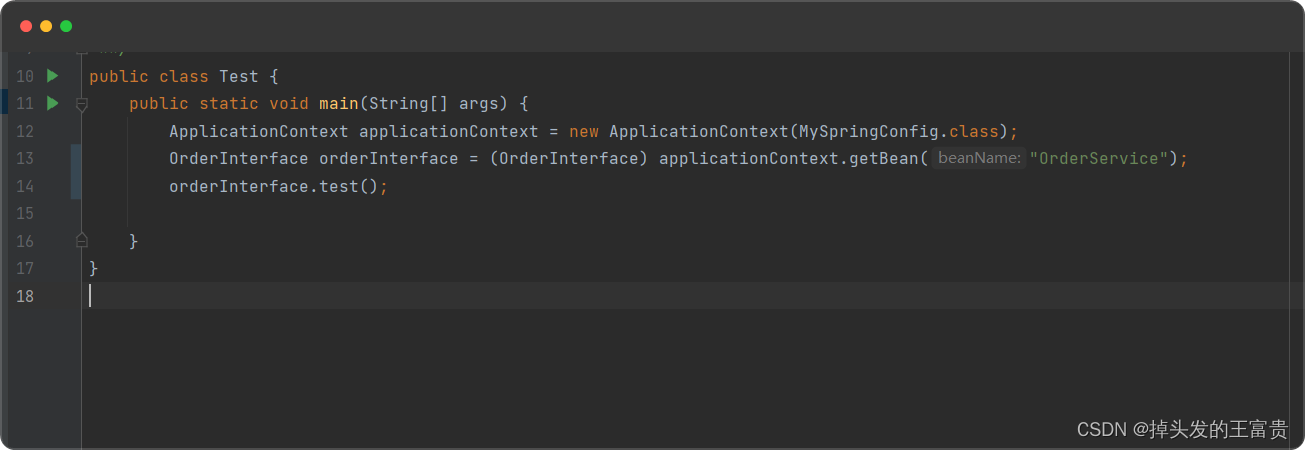
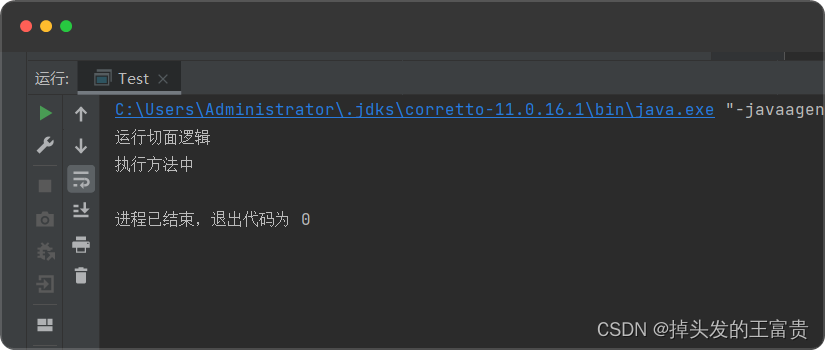
以上就是全部内容
实现了以下
- 🚀@ComponentScan注解
- ✈️@Component注解
- 🚁ApplicationContext类
- 🚡@Scope注解
- 🚟BeanDefinition 类
- 🚘@Autowired注解
- 🚕BeanPostProcessor接口
- 🚛Aop
内容,完成了一个超级简单且基础的spring源码
项目源码
博客码了两天,创作不易,多多点赞

