Golang的context
目录
context的基本使用
为什么需要context
Context interface
标准 error
emptyCtx
cancelCtx
Deadline 方法
Done 方法
Err 方法
Value 方法
context.WithCancel()
newCancelCtx
WithCancel中propagateCancel
cancel
timerCtx
valueCtx
context的基本使用
创建:
context.Background():创建一个空的父类context
context.TODO(): 创建一个未来 可能有内容的父类 context,有扩展性
// 创建一个可以取消的ContextctxCancel, cancelCancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())defer cancelCancel() // 当不再需要时,确保调用cancel来释放资源// 创建一个带有截止时间的Contextdeadline := time.Now().Add(time.Second * 10)ctxDeadline, cancelDeadline := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), deadline)defer cancelDeadline()// 创建一个带有超时时间的Contexttimeout := 10 * time.SecondctxTimeout, cancelTimeout := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), timeout)defer cancelTimeout()
返回值: Context 上下文本体 和 CancelFunc 关闭Context 的函数
类别:
context.WithCancel 创建一个可以取消的Context,当调用 返回值 cancel 时 就可以通知关闭
context.WithDeadline 创建一个带有截止时间的Context,到一个特定时间时便发出通知
context.WithTimeout 创建一个带有超时时间的Context,过了一段时间后就发出通知
防止go协程泄漏使用例子
package mainimport ("context""fmt"
)func main() {//WithCancel(ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc)=(名 Context,处理函数 CancelFunc)ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background()) //context.Background() 处理 Goroutinecontext.TODO()ch := func(ctx context.Context) <-chan int {ch := make(chan int)go func() {for i := 0; ; i++ {select {case <-ctx.Done():returncase ch <- i:}}}()return ch}(ctx)for v := range ch {fmt.Println(v)if v == 5 {cancel()break}}
}
为什么需要context
场景1: 当主协程启动了m个子协程,m个子协程又启动更多的协程,
那监控起来需要很多的channel, 操作非常繁琐。
如果我们使用 context 时,当父类的context关闭,子类也会一起关闭以此类推,类似Qt中的对象树
场景2:任务A 挂在 任务B 下,我们希望 B 有着定时退出的功能,而且当B退出时A也需要退出
使用定时器+channel时,就显的有些繁琐,我们可以直接使用context.WithTimeout 一步到位
Context interface
golang的接口 类似 c++的基类
type Context interface {Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)Done() <-chan struct{}Err() errorValue(key any) any
}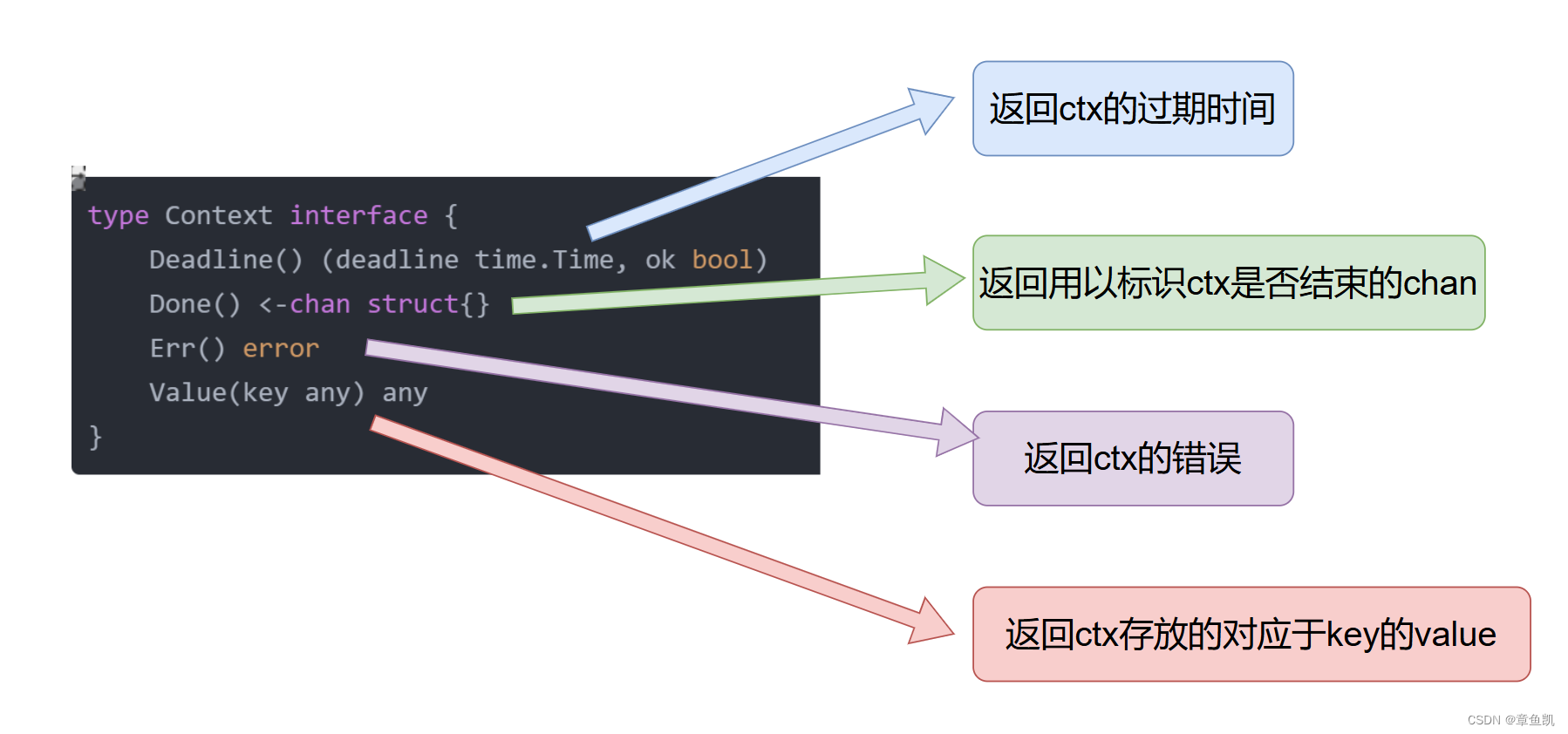
Context 为 interface,定义了四个核心 api:
• Deadline:返回 context 的过期时间;
• Done:返回 context 中的 channel;
• Err:返回错误;
• Value:返回 context 中的对应 key 的值.
标准 error
var Canceled = errors.New("context canceled")var DeadlineExceeded error = deadlineExceededError{}type deadlineExceededError struct{}func (deadlineExceededError) Error() string { return "context deadline exceeded" }
func (deadlineExceededError) Timeout() bool { return true }
func (deadlineExceededError) Temporary() bool { return true• Canceled:context 被 cancel 时会报此错误;
• DeadlineExceeded:context 超时时会报此错误.
emptyCtx
重写了接口 api:
type emptyCtx intfunc (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {return
}func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {return nil
}func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {return nil
}func (*emptyCtx) Value(key any) any {return
}返回的什么东西都为空
• emptyCtx 是一个空的 context,本质上类型为一个整型;
• Deadline 方法会返回一个公元元年时间以及 false 的 flag,标识当前 context 不存在过期时间;
• Done 方法返回一个 nil 值,用户无论往 nil 中写入或者读取数据,均会陷入阻塞;
• Err 方法返回的错误永远为 nil;
• Value 方法返回的 value 同样永远为 nil.
var (background = new(emptyCtx)todo = new(emptyCtx)
)func Background() Context {return background
}func TODO() Context {return todo
}当使用context.Background() & context.TODO() 创建emptyCtx 时返回固定的 emptyCtx
cancelCtx
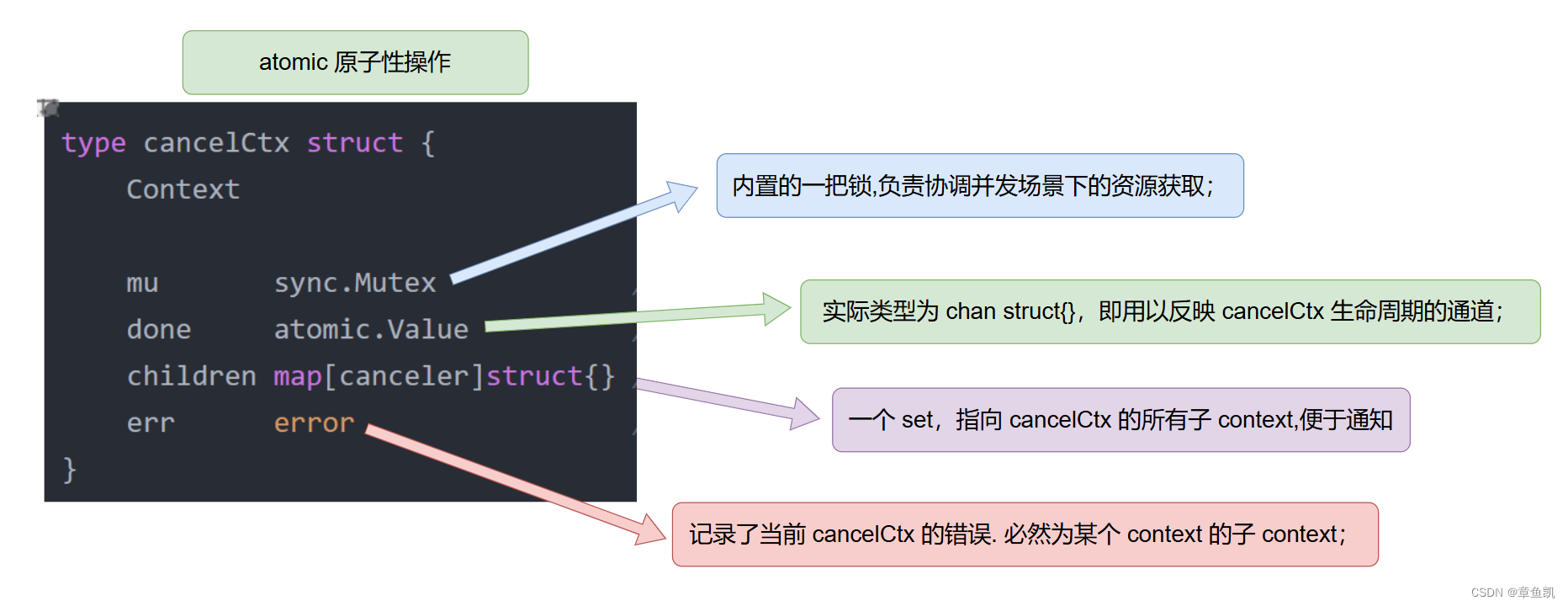
type cancelCtx struct {Contextmu sync.Mutex // protects following fieldsdone atomic.Value // of chan struct{}, created lazily, closed by first cancel callchildren map[canceler]struct{} // set to nil by the first cancel callerr error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
}type canceler interface {cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)Done() <-chan struct{}
}
Deadline 方法
cancelCtx 未实现该方法,仅是 embed 了一个带有 Deadline 方法的 Context interface,因此倘若直接调用会报错.
Done 方法
流程如下:
源码:
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {d := c.done.Load()if d != nil {return d.(chan struct{})}c.mu.Lock()defer c.mu.Unlock()d = c.done.Load()if d == nil {d = make(chan struct{})c.done.Store(d)}return d.(chan struct{})
}
• 基于 atomic 包,读取 cancelCtx 中的 chan;倘若已存在,则直接返回;
• 加锁后,在此检查 chan 是否存在,若存在则返回;(双重检查 double check)
• 初始化 chan 存储到 aotmic.Value 当中,并返回.(懒加载机制 懒汉)
Err 方法
func (c *cancelCtx) Err() error {c.mu.Lock()err := c.errc.mu.Unlock()return err
}
• 加锁;
• 读取 cancelCtx.err;
• 解锁;
• 返回结果;
Value 方法
func (c *cancelCtx) Value(key any) any {if key == &cancelCtxKey {return c}return value(c.Context, key)
}• 倘若 key 特定值 &cancelCtxKey,则返回 cancelCtx 自身的指针;
• 否则遵循 valueCtx 的思路取值返回;
context.WithCancel()
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {if parent == nil {panic("cannot create context from nil parent")}c := newCancelCtx(parent)propagateCancel(parent, &c)return &c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}• 校验父 context 非空;
• 注入父 context 构造好一个新的 cancelCtx;
• 在 propagateCancel 方法内启动一个守护协程,以保证父 context 终止时,该 cancelCtx 也会被终止;
• 将 cancelCtx 返回,连带返回一个用以终止该 cancelCtx 的闭包函数.
newCancelCtx
没用propagateCancel 方法
func newCancelCtx(parent Context) cancelCtx {return cancelCtx{Context: parent}
}• 注入父 context 后,返回一个新的 cancelCtx.
WithCancel中propagateCancel
propagateCancel 传播取消

func propagateCancel(parent Context, child canceler) {done := parent.Done()if done == nil {return // parent is never canceled}select {case <-done:// parent is already canceledchild.cancel(false, parent.Err())returndefault:}if p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent); ok {p.mu.Lock()if p.err != nil {// parent has already been canceledchild.cancel(false, p.err)} else {if p.children == nil {p.children = make(map[canceler]struct{})}p.children[child] = struct{}{}}p.mu.Unlock()} else {atomic.AddInt32(&goroutines, +1)go func() {select {case <-parent.Done():child.cancel(false, parent.Err())case <-child.Done():}}()}
}cancel
// cancel closes c.done, cancels each of c's children, and, if
// removeFromParent is true, removes c from its parent's children.
// cancel sets c.cause to cause if this is the first time c is canceled.
func (c *cancelCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err, cause error) {if err == nil {panic("context: internal error: missing cancel error")}if cause == nil {cause = err}c.mu.Lock()if c.err != nil {c.mu.Unlock()return // already canceled}c.err = errc.cause = caused, _ := c.done.Load().(chan struct{})if d == nil {c.done.Store(closedchan)} else {close(d)}for child := range c.children {// NOTE: acquiring the child's lock while holding parent's lock.child.cancel(false, err, cause)}c.children = nilc.mu.Unlock()if removeFromParent {removeChild(c.Context, c)}
}timerCtx
只介绍类,其他与cancel差不多,加上了过期时刻
type timerCtx struct {cancelCtxtimer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.deadline time.Time
}
valueCtx
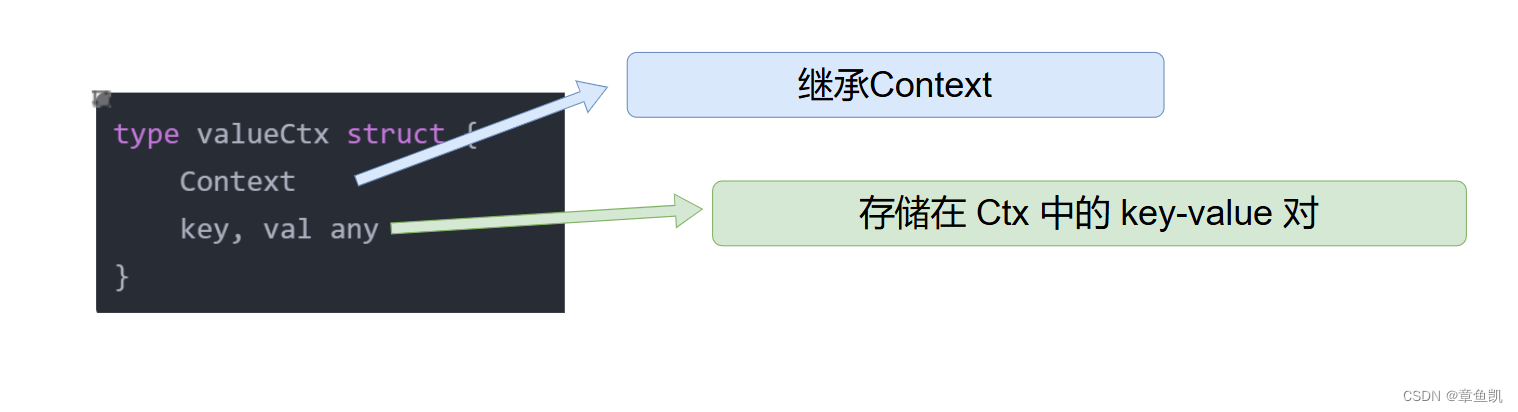
键值对 Ctx
type valueCtx struct {Contextkey, val any
}
参考 : 小徐先生1212 --context 底层实现
