C++之运算符重载
1、运算符重载

//Complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_class Complex
{
public:Complex(int real_, int imag_);Complex();~Complex();Complex& Add(const Complex& other); void Display() const;Complex operator+(const Complex& other);private:int real_;int imag_;
};
#endif // _COMPLEX_H_// Complex.cpp
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Complex::Complex(int real, int imag) : real_(real), imag_(imag)
{}Complex::Complex()
{}Complex::~Complex()
{}Complex& Complex::Add(const Complex& other)
{real_ += other.real_;imag_ += other.imag_;return *this; // 因为是引用,所以返回的时候不会调用拷贝构造函数
}void Complex::Display() const
{cout << real_ << "+" << imag_ << endl;
}Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& other)
{int r = real_ + other.real_;int i = imag_ + other.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}// main.cpp
#include "Complex.h"int main(void)
{Complex c1(3, 5);Complex c2(4, 6);//c1.Add(c2); // 但是这样就修改到了c1对象,我们希望是Complex c3 = c1 + c2;这个时候我们就需要运算符的重载//c1.Display();Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // 这边其实就是函数调用,相当于c1.operator(c2);// Complex c3 = c1.operator(c2);c1.Display();c2.Display();c3.Display();return 0;
}其实运算符的重载,在这边也就是成员函数的重载。

2、非成员函数重载(友元的方式重载)

在vs2008中友元函数的运算符重载能和成员函数的运算符重载共存,有些编译器不行。如果共存,那么优先调用成员函数的运算符重载。
//Complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_class Complex
{
public:Complex(int real_, int imag_);Complex();~Complex();Complex& Add(const Complex& other); void Display() const;Complex operator+(const Complex& other);friend Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);private:int real_;int imag_;
};
#endif // _COMPLEX_H_// Complex.cpp
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Complex::Complex(int real, int imag) : real_(real), imag_(imag)
{}Complex::Complex()
{}Complex::~Complex()
{}Complex& Complex::Add(const Complex& other)
{real_ += other.real_;imag_ += other.imag_;return *this; // 因为是引用,所以返回的时候不会调用拷贝构造函数
}void Complex::Display() const
{cout << real_ << "+" << imag_ << endl;
}Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& other)
{int r = real_ + other.real_;int i = imag_ + other.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}Complex operator+(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
{int r = c1.real_ + c2.real_;int i = c1.imag_ + c2.imag_;return Complex(r, i);
}// main.cpp
#include "Complex.h"int main(void)
{Complex c1(3, 5);Complex c2(4, 6);//c1.Add(c2); // 但是这样就修改到了c1对象,我们希望是Complex c3 = c1 + c2;这个时候我们就需要运算符的重载//c1.Display();Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // 这边其实就是函数调用,相当于c1.operator(c2);// Complex c3 = c1.operator(c2);c1.Display();c2.Display();c3.Display();return 0;
}3、运算符重载的规则
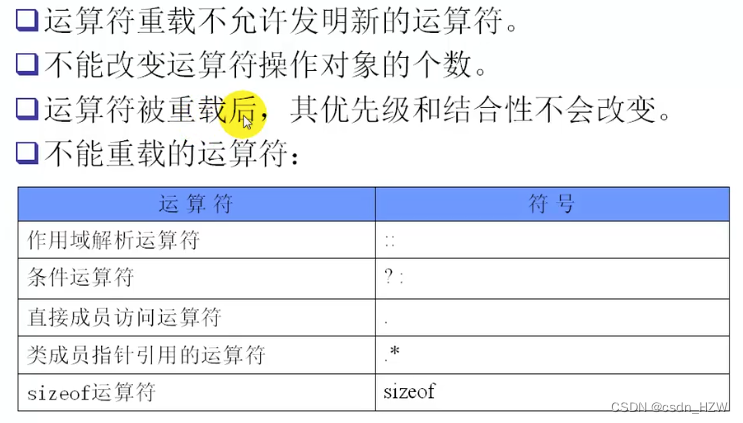
不能重载的运算符:因为如果开放了这些运算符的重载,那么语法就会变得混乱不可控制。

4、++运算符重载

推荐用成员函数进行重载,因为友元重载是全局的。
// Integer.h
#ifndef _INTEGER_H
#define _INTEGER_Hclass Integer
{
public:Integer (int n);~Integer();void Display();Integer& operator++(); // 前置++成员函数重载//friend Integer& operator++(Integer &i); // 前置++友元重载// 友元不能共存// 后置中的参数int i没什么用,只是为了区分是否是前置还是后置Integer operator++(int i); // 后置++成员函数重载//friend Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int i); // 前置++友元重载
private:int n_;
};#endif //_INTEGER_H// Integer.cpp
#include "Integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;Integer::Integer(int n) : n_(n)
{}Integer::~Integer()
{}void Integer::Display()
{cout << "n_ = " << n_ << endl;
}//Integer& Integer::operator++()
//{
// cout << "Integer& Integer::operator++()" << endl;
// ++n_;
// return *this;
//}Integer& operator++(Integer &i)
{cout << "Integer& operator++(Integer &i)" << endl;++i.n_;return i; // 因为返回的是引用不是对象,所以不会调用拷贝构造函数
}//Integer Integer::operator++(int i)
//{
// cout << "Integer& Integer::operator++(int i)" << endl;
// //n++,
// Integer tmp(n_);
// n_++;
// return tmp;
//}Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int j)
{cout << "Integer& operator++(Integer &i, int i)" << endl;//n++,Integer tmp(i.n_);i.n_++;return tmp;
}
// main.cpp
#include "Integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{Integer n(10);n.Display();Integer n2 = ++n;n.Display();n2.Display();Integer n3 = n++;n.Display();n3.Display();return 0;
}5、=赋值运算符重载
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abc");String s2(s1);String s3;s3 = s1;s3.Display();s3 = "xxxx"; // 如果没有去重载String& operator=(const char* str);那么先调用转换构造函数String(const char* str)将字符串构造成一个对象,然后再调用String& operator=(const String& other);重载等号运算符进行赋值。s3.Display();return 0;
}其实主要是内存释放的问题,因为如果直接=,就是浅拷贝,如果有用malloc的话,释放的时候,一块内存会被释放两次。还有就是写法中调用的问题,s1("abc")调用构造函数;s1(s2)调用拷贝构造,当在构造函数中有开辟空间,则在拷贝构造里面也要开辟空间,避免重复释放。
6、!运算符重载
当字符串是空的,那就是假的,当字符串不为空,那就是真。
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];menset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abc");String s2(s1);String s3;s3 = s1;s3.Display();s3 = "xxxx"; // 如果没有去重载String& operator=(const char* str);那么先调用转换构造函数String(const char* str)将字符串构造成一个对象,然后再调用String& operator=(const String& other);重载等号运算符进行赋值。s3.Display();String s4;bool notEmpty;notEmpty = !s4;cout << notEmpty << endl;s4 = "aaaa";notEmpty = !s4;cout << notEmpty << endl;return 0;
}7、[]运算符重载
//String.h
#ifndef _STRING_H
#define _STRING_Hclass String
{
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;void Display() const;~String(void);private:char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //_STRING_H// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];menset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}// main.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(void)
{String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcreturn 0;
}8、+运算符重载
最好写成友元的方式去重载。
9、+=运算符的重载
// String.h
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H
class String {
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;//+运算符重载(最好用友元的方式来重载)friend String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2);//+=运算符重载String& operator+=(const String& other);void Display() const;~String(void);private:static char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //STRING_H
// String.cpp
#include "String.h"
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{int len = strlen(s1.str_) + strlen(s2.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, s1.str_);strcat(newStr, s2.str_);String tmp(newStr);delete newStr;return tmp;
}String& String::operator+=(const String& other)
{int len = strlen(str_) + strlen(other.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str_);strcat(newStr, other.str_);delete[] str_;str_ = newStr;return *this;
}// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");//s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcString s3 = "xxx";String s4 = "yyy";String s5 = s3 + s4;s5.Display();s3 += s4;s3.Display();return 0;
}
10、<<和>>运算符重载

//String.h
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class String {
public:String(const char* str = "");String(const String& other); // 拷贝构造// 当你使用obj1 = obj2的时候,也是浅拷贝,即obj1.str_ = obj2.str_,所以要重载等号运算符,在里面进行深拷贝String& operator=(const String& other);String& operator=(const char* str);bool operator!() const;char& operator[](unsigned int index);const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;//+运算符重载(最好用友元的方式来重载)friend String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2);//+=运算符重载String& operator+=(const String& other);// << 运算符重载friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str);// >> 运算符重载friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, String& str);void Display() const;~String(void);private:static char* AllocAndCopy(const char* str);char* str_;
};#endif //STRING_H
//String.cpp
include "String.h"
#include "String.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;String::String(const char* str)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);
}String::String(const String& other)
{str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);
}String& String::operator=(const String& other)
{if (this == &other)return *this;delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(other.str_);return *this;
}char* String::AllocAndCopy(const char* str)
{int len= strlen(str)+ 1;char* newStr= new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str);return newStr;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* str)
{delete[] str_;str_ = AllocAndCopy(str);return *this;
}bool String::operator!() const
{return strlen(str_) != 0;
}char& String::operator[](unsigned int index)
{return str_[index];// 因为这里面的代码和const的代码一样,所以最好合并成同一份代码// 做法是,non const 版本调用const版本return const_cast<char&>(static_cast<const String&>(*this)[index]);
}const char& String::operator[](unsigned int index) const
{return str_[index];
}void String::Display() const
{cout << str_ << endl;
}String::~String()
{delete[] str_;
}String operator+(const String& s1, const String& s2)
{int len = strlen(s1.str_) + strlen(s2.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, s1.str_);strcat(newStr, s2.str_);String tmp(newStr);delete newStr;return tmp;
}String& String::operator+=(const String& other)
{int len = strlen(str_) + strlen(other.str_);char* newStr = new char[len];memset(newStr, 0, len);strcpy(newStr, str_);strcat(newStr, other.str_);delete[] str_;str_ = newStr;return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str)
{os << str.str_;return os;
}istream& operator>>(istream& is, String& str)
{char tmp[1024];cin >> tmp;str = tmp;return is;
}
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {String s1("abcdefg");char ch = s1[2];cout << ch << endl; // 输出c//为什么[]的返回值是字符串的引用?因为一个函数,如果返回值是引用的话,就可以出现在表达式的左边,这样就能重新赋值。s1[2] = 'A';s1.Display(); // 输出abAdefgconst String s2("xyzabc");//s2[2] = 'M'; // 这边会调用char& operator[](unsigned int index) const这个重载。因为是const对象,所以希望这个操作是不允许的;解决方案:前面加上const,变成const char& operator[](unsigned int index) const;这样的话,这句在编译的时候就会报错ch = s2[2]; // 希望这个操作是允许的s2.Display(); // 输出xyMabcString s3 = "xxx";String s4 = "yyy";String s5 = s3 + s4;s5.Display();s3 += s4;s3.Display();cout << s3 << endl;String s7;cin >> s7;cout << s7 << endl;return 0;
}
11、类型转换运算符的重载

12、指针运算符->
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class DBHelper
{
public:DBHelper(){cout << "DB..." << endl;}~DBHelper(){cout << "~DB..." << endl;}void Open(){cout << "Open..." << endl;}void Close(){cout << "Close..." << endl;}void Query(){cout << "Query..." << endl;}
};class DB
{
public:DB(){db_ = new DBHelper();}~DB(){delete db_;}DBHelper* operator->(){return db_;}private:DBHelper* db_;
};
int main() {// ->指针运算符(一个指针A包装了另一个指针B,利用了A生命周期结束的时候的确定性析构,在析构中销毁B)// 相当于智能指针DB db;db->Open();db->Query();db->Close();return 0;
}
13、operator new、operator delete的重载
new有三种用法
new operator:不能被重载
operator new
placement new

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//类中operator new、operator delete的重载
class Test
{
public:Test(int n):n_(n){cout << "Test(int n):n_(n)" << endl;}Test(const Test& other){cout << "Test(const Test& other)" << endl;}~Test(){cout << "~Test()" << endl;}// 重载operator newvoid* operator new(size_t size){cout << "void* operator new(size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;}// 重载operator deletevoid operator delete (void* p){cout << "void operator delete (void* p)" << endl;free(p);}// 这两个可以共存,看你是调用哪个void operator delete (void* p, size_t size){cout << "void operator delete (void* p, size_t size)" << endl;free(p);}// 不同参数的newvoid* operator new(size_t size, const char* file, long line){cout << "void* operator new(size_t size, const char* file, long line)" << endl;cout << file << ":" << line << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;}// 重载operator deletevoid operator delete (void* p, const char* file, long line){cout << "void operator delete (void* p, const char* file, long line)" << endl;cout << file << ":" << line << endl;free(p);}// 重载placement newvoid* operator new(size_t size, void* p){cout << "placement new" << endl;return p;}void operator delete(void*, void*){cout << "placement delete" << endl;}int n_;
};// 全局operator new、operator delete的重载
// 重载operator new
void* operator new(size_t size)
{cout << "global void* operator new(size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;
}// 重载operator delete
void operator delete (void* p)
{cout << "global void operator delete (void* p)" << endl;free(p);
}// 重载operator new
void* operator new[](size_t size)
{cout << "global void* operator new[](size_t size)" << endl;void* p = malloc(size);return p;
}// 重载operator delete
void operator delete[](void* p)
{cout << "global void operator delete[] (void* p)" << endl;free(p);
}int main() {Test* p1 = new Test(100); // 这边是调用 new operator这个函数;这个函数相当于调用operator new 然后调用构造函数,两个函数的结合delete p1;char* str = new char;delete str;char* str2 = new char[100];delete []str2;char chunk[10];Test* p2 = new (chunk) Test(200); // 调用placement new,不分配内存,是在chunk这段内存上构造对象的;然后调用operator new 然后调用构造函数cout << p2->n_ << endl;p2->~Test(); // 显示调用析构函数,这边不能用delete,因为是在chunk上面的内存//Test* p3 = (Test*)chunk; // 强制转化Test* p3 = reinterpret_cast<Test*>(chunk);cout << p3->n_ << endl;Test* p4 = new(__FILE__, __LINE__) Test(300);delete p4;return 0;
}