Postgresql源码(132)分布式行锁的原理分析
相关
《Postgresql源码(131)行锁的原理分析》
1 分布式行锁
PG中的行锁在上一片中做了分析《Postgresql源码(131)行锁的原理分析》,本篇对分布式PG(PGXL)中的行锁做一些分析。(版本:Postgres-XL 10alpha2)
2 计划生成pgxc_planner
分布式PG中的计划生成有两个入口:
pgxc_plannerresult = pgxc_FQS_planner(query, cursorOptions, boundParams);if (result) return result;result = standard_planner(query, cursorOptions, boundParams);return result;
- pgxc_FQS_planner(Fast Query Shipping planner)尝试确定一个查询是否可以完全在DN上执行,不需要CN节点参与计算。FQS计划比较简单,直接把SQL发到某几个DN上跑。
- standard_planner是标准查询规划器。
查询首先通过pgxc_FQS_planner看是否适合快速分发。如果不适合,会继续走standard_planner。
2.1 pgxc_FQS_planner生成FQS计划
XL默认对行锁的SQL不能走FQS,这里为了简单介绍下FQS用了一个点查的例子。
用例
drop table TBL_33;
create table TBL_33(c3 int);
insert into TBL_33 values(0);
SELECT c3 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c3=0;;
分布式执行计划
explain SELECT c3 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c3=0;QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------Remote Fast Query Execution (cost=0.00..0.00 rows=0 width=0)Node/s: datanode_2-> Seq Scan on tbl_33 (cost=0.00..41.88 rows=13 width=4)Filter: (c3 = 0)
pgxc_FQS_planner
static PlannedStmt *
pgxc_FQS_planner(Query *query, int cursorOptions, ParamListInfo boundParams)
{
- 用规则过滤一些不能FQS的情况:
if (!enable_fast_query_shipping)return NULL;if (cursorOptions & CURSOR_OPT_SCROLL)return NULL;if (query->utilityStmt && IsA(query->utilityStmt, RemoteQuery)){RemoteQuery *stmt = (RemoteQuery *) query->utilityStmt;if (stmt->exec_direct_type != EXEC_DIRECT_NONE)return NULL;}- 遍历查询树,用一些规则排除不能FQS的情况。
- pgxc_shippability_walker函数在遍历的同时,会维护一个bitmap(sc_context.sc_shippability),里面记录了不能ship的各种原因,最后在pgxc_is_query_shippable函数中检测bitmap确认是否能ship。
- exec_nodes中记录的最重要的信息就是需要在哪个节点上执行,由pgxc_FQS_find_datanodes函数计算出来。
- 计算逻辑:

exec_nodes = pgxc_is_query_shippable(query, 0);if (exec_nodes == NULL)return NULL;glob = makeNode(PlannerGlobal);glob->boundParams = boundParams;root = makeNode(PlannerInfo);root->parse = query;root->glob = glob;root->query_level = 1;root->planner_cxt = CurrentMemoryContext;top_plan = (Plan *)pgxc_FQS_create_remote_plan(query, exec_nodes, false);top_plan = set_plan_references(root, top_plan);result = makeNode(PlannedStmt);result->commandType = query->commandType;result->canSetTag = query->canSetTag;result->utilityStmt = query->utilityStmt;if (query->commandType != CMD_SELECT)result->resultRelations = list_make1_int(query->resultRelation);result->planTree = top_plan;result->rtable = query->rtable;result->queryId = query->queryId;result->relationOids = glob->relationOids;result->invalItems = glob->invalItems;return result;
}
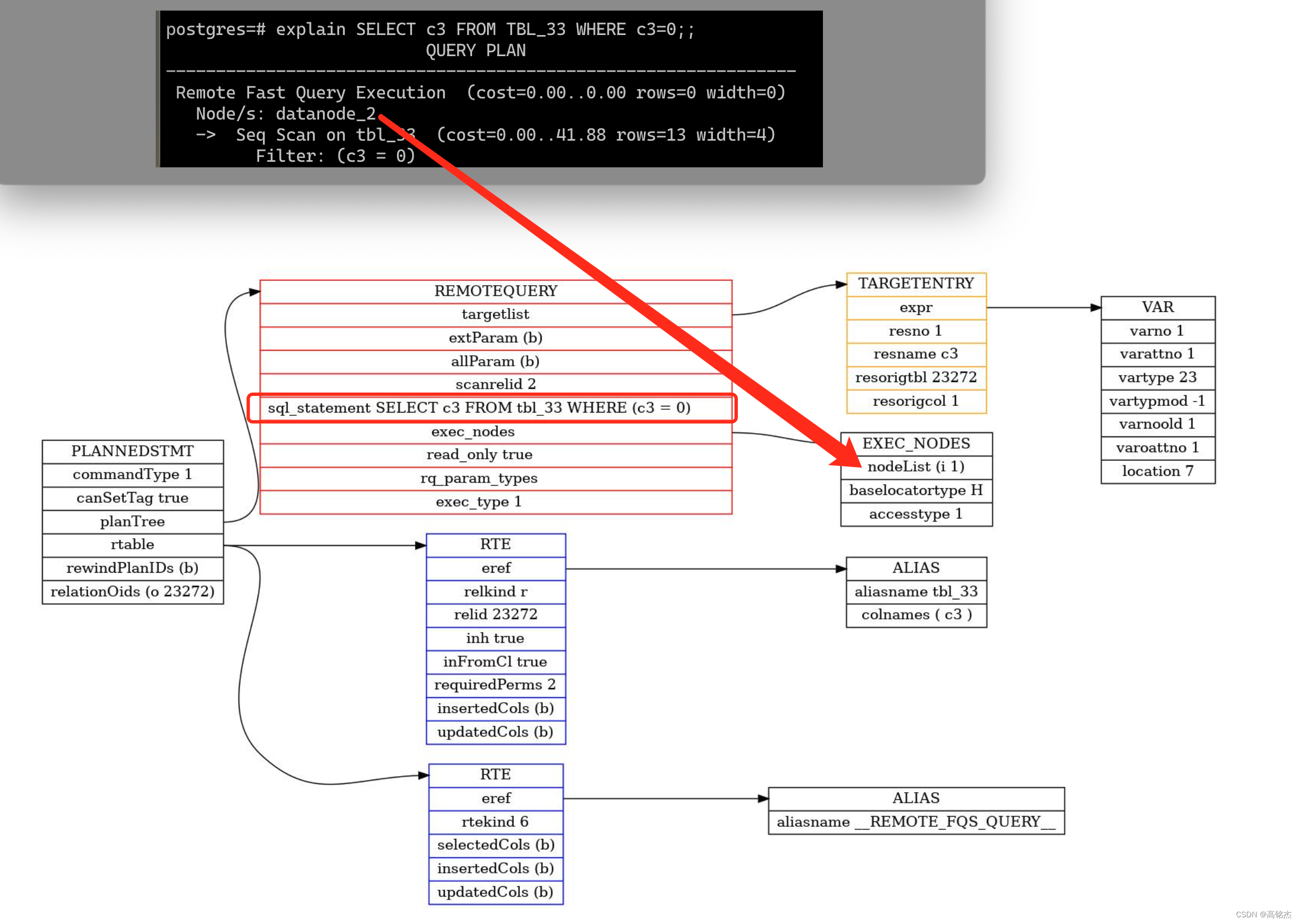
- FQS的计划会比较简单,基本就是把SQL用deparse_query出来,然后拼到计划节点中,找到发到哪些节点执行即可。
2.2 standard_planner生成remote计划
回到行锁用例上:
drop table TBL_33;
create table TBL_33(c33 int);
insert into TBL_33 values(0);SELECT c33 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c33=0 for update;
分布式执行计划
explain SELECT c33 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c33=0 for update;QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Remote Subquery Scan on all (datanode_2) (cost=0.00..42.01 rows=13 width=10)-> LockRows (cost=0.00..42.01 rows=13 width=10)-> Seq Scan on tbl_33 (cost=0.00..41.88 rows=13 width=10)Filter: (c33 = 0)
2.2.1 subquery_planner→grouping_planner生成local计划
subquery_planner生成计划:
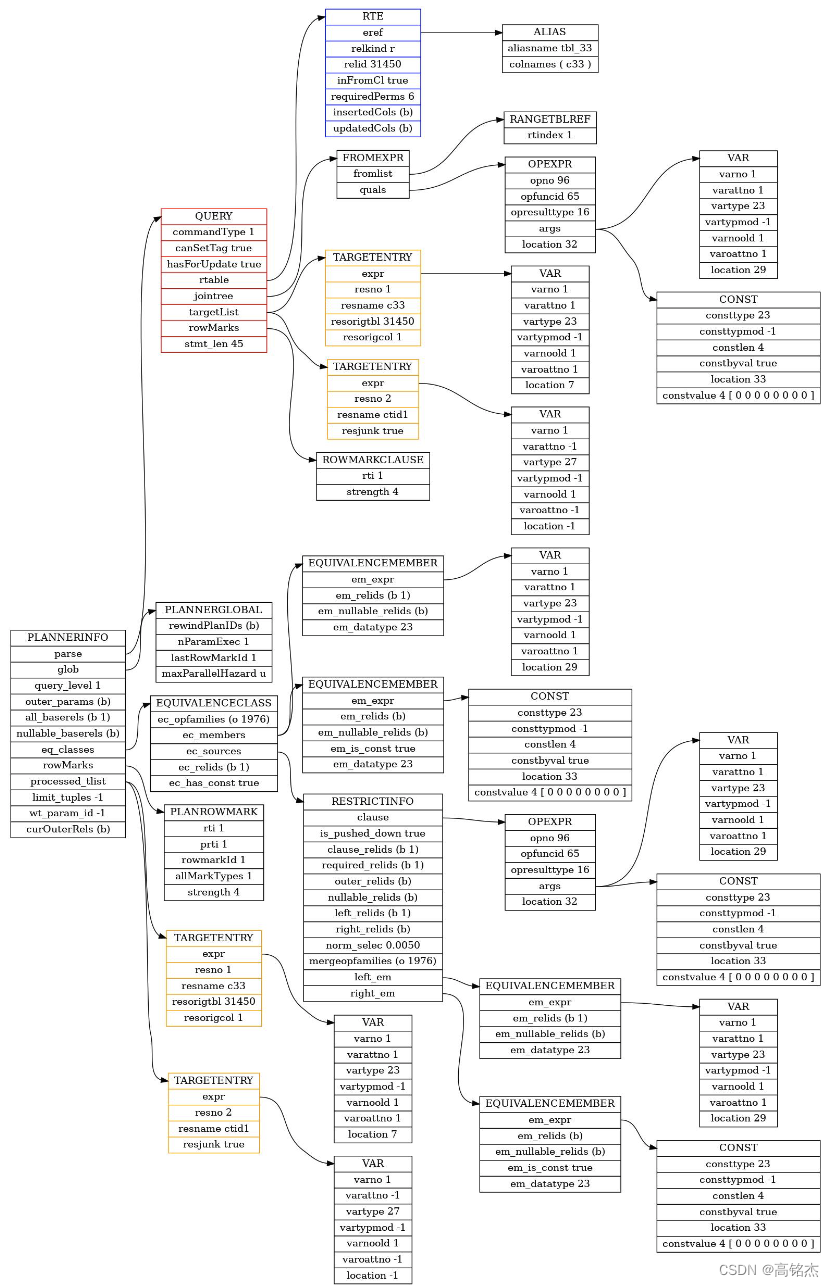
2.2.2 make_remotesubplan为计划添加remote算子
standard_planner → make_remotesubplan
standard_planner...best_path = get_cheapest_fractional_path(final_rel, tuple_fraction);if (!root->distribution)root->distribution = best_path->distribution;top_plan = create_plan(root, best_path);if (root->distribution)top_plan = (Plan *) make_remotesubplan(root, top_plan, NULL, root->distribution, root->sort_pathkeys);
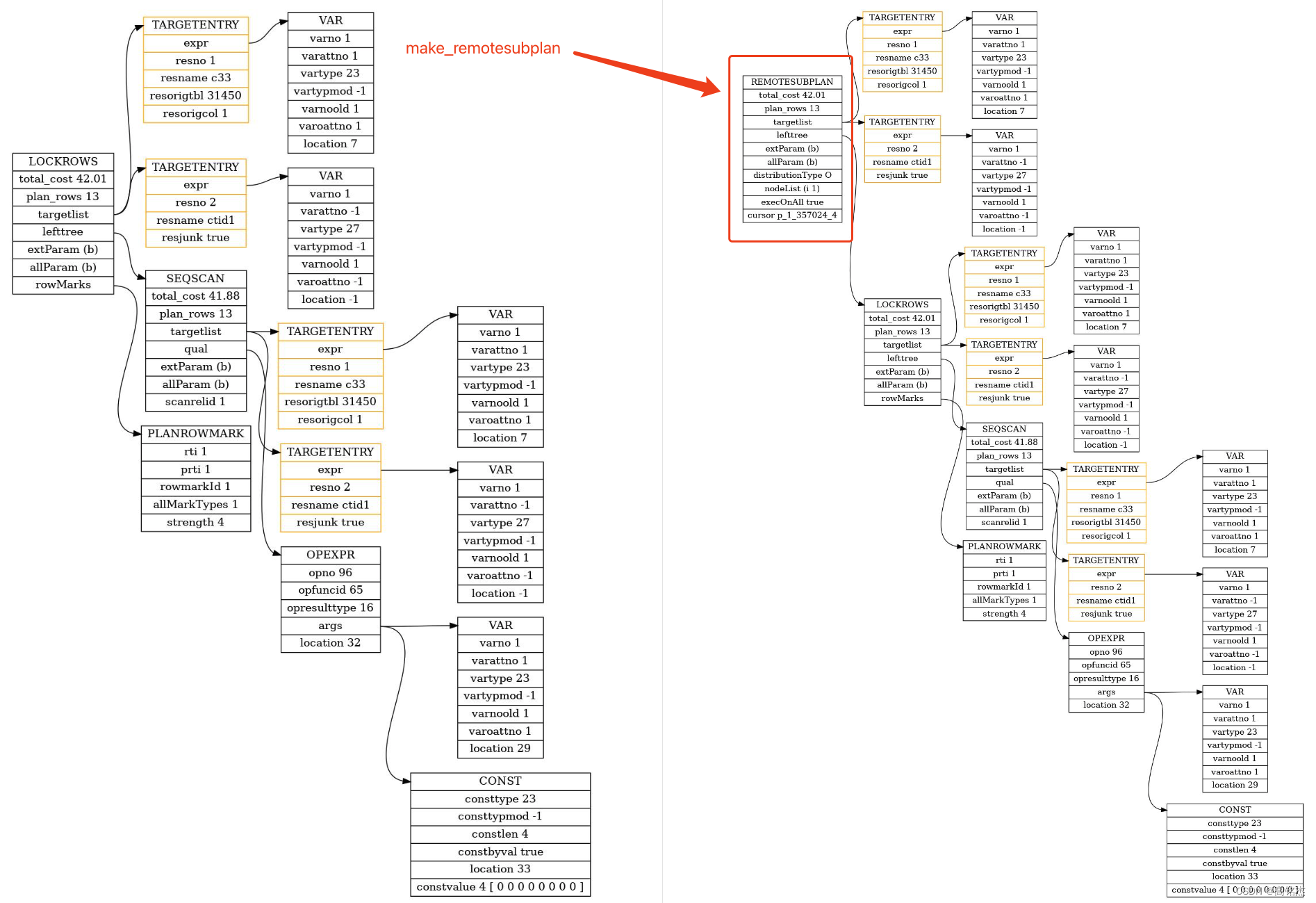
2.2.3 path的distribution信息从哪来?
explain SELECT c33 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c33=0 for update;QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Remote Subquery Scan on all (datanode_2) (cost=0.00..42.01 rows=13 width=10)-> LockRows (cost=0.00..42.01 rows=13 width=10)-> Seq Scan on tbl_33 (cost=0.00..41.88 rows=13 width=10)Filter: (c33 = 0)
SELECT c33 FROM TBL_33 WHERE c33=0 for update;执行时会生成两个算子:
- create_seqscan_path
- create_lockrows_path
create_seqscan_path
Path *
create_seqscan_path(PlannerInfo *root, RelOptInfo *rel,Relids required_outer, int parallel_workers)
{Path *pathnode = makeNode(Path);pathnode->pathtype = T_SeqScan;pathnode->parent = rel;pathnode->pathtarget = rel->reltarget;pathnode->param_info = get_baserel_parampathinfo(root, rel,required_outer);pathnode->parallel_aware = parallel_workers > 0 ? true : false;pathnode->parallel_safe = rel->consider_parallel;pathnode->parallel_workers = parallel_workers;pathnode->pathkeys = NIL; /* seqscan has unordered result */#ifdef XCP
- set_scanpath_distribution会配置pathnode->distribution信息,标记计划需要发到哪个节点执行。
- restrict_distribution会更严格的检查计划发到哪个节点。
set_scanpath_distribution(root, rel, pathnode);if (rel->baserestrictinfo){ListCell *lc;foreach (lc, rel->baserestrictinfo){RestrictInfo *ri = (RestrictInfo *) lfirst(lc);restrict_distribution(root, ri, pathnode);}}
#endifcost_seqscan(pathnode, root, rel, pathnode->param_info);return pathnode;
}- 经过set_scanpath_distribution后
pathnode->distribution->nodes标记了dn0、dn1。p/t pathnode->distribution->nodes->words[0] = 11
- 经过restrict_distribution后
pathnode->distribution->nodesrestrictNodes只标记了datanode1。p/t pathnode->distribution->restrictNodes->words[0] = 10
p *pathnode->distribution
$27 = {type = T_Distribution, distributionType = 72 'H', distributionExpr = 0x135fea8, nodes = 0x1360650, restrictNodes = 0x1360898}
(gdb) p/t pathnode->distribution->nodes->words[0]
$31 = 11
(gdb) p/t pathnode->distribution->restrictNodes->words[0]
$30 = 10
create_lockrows_path
- lockrows节点比较特殊,不需要做什么事情,执行器会在执行阶段特殊处理。
- pathnode→distribution信息集成subplan的即可。
LockRowsPath *
create_lockrows_path(PlannerInfo *root, RelOptInfo *rel,Path *subpath, List *rowMarks, int epqParam)
{LockRowsPath *pathnode = makeNode(LockRowsPath);pathnode->path.pathtype = T_LockRows;...... pathnode->path.distribution = copyObject(subpath->distribution);......return pathnode;
}
