mybatis(5)参数处理+语句查询
参数处理+语句查询
- 1、简单单个参数
- 2、Map参数
- 3、实体类参数
- 4、多参数
- 5、@Param注解
- 6、语句查询
- 6.1 返回一个实体类对象
- 6.2 返回多个实体类对象 List<>
- 6.3 返回一个Map对象
- 6.4 返回多个Map对象 List<Map>
- 6.5 返回一个大Map
- 6.6 结果映射
- 6.6.1 使用resultMap
- 6.6.2 驼峰式映射
1、简单单个参数
简单类型包括:
● byte short int long float double char
● Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Character
● String
● java.util.Date
● java.sql.Date
总而言之就是 mybaits可以自动匹配参数类型,之后通过setXXX来注入。
我们也可以显示标注类型,省去mybatis的类型匹配。
比如 char 类 我们可以通过parameterType 来告诉mybatis 参数类型是什么,其他基本数据类型都一样,不在举例。
<select id="selectbysex" resultType="student" parameterType="java.lang.Character">select *from t_student where sex=#{sex}</select>
2、Map参数
注意的是 我们传的如果是map,则我们#{map的key值},不能是其他的。
<select id="selectBYmap" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{namekey} and age=#{agekey}</select>
@Testpublic void testMap(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();map.put("namekey","cky");map.put("agekey",18);mapper.selectBYmap(map).forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));sqlSession.close();}
3、实体类参数
注意:如果我们传的是实体类,则#{},{}里应该是实体类的属性名,不能是其他。
<select id="selectByclass" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{name} and age=#{age}</select>
@Testpublic void testClass(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);Student student=new Student();student.setAge(18);student.setId(10L);student.setBirth(new Date());student.setHeight(1.65);student.setSex('女');student.setName("c");mapper.selectByclass(student).forEach(stu -> System.out.println(stu));sqlSession.close();}
4、多参数
传入多参数时,其实mybatis底层是帮我们封装成了map集合。
使用arg
List<Student> selectNameandSex2(String name, Character sex);
<select id="selectNameandSex2" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{arg0} and sex=#{arg1}</select>
@Testpublic void testarg(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);mapper.selectNameandSex2("cky",'女').forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));sqlSession.close();}
使用param
<select id="selectNameandSex2" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{param1} and sex=#{param2}</select>
两者联合使用
<select id="selectNameandSex2" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{param1} and sex=#{arg1}</select>
这里例子 就等同于帮我们封装了一个map集合
map(“arg0”,“cky”);map(“arg1”,18);map(“param1”,“cky”);map(“param2”,18);
args从0开始,param参数从1开始。
两个都在map中。
5、@Param注解
如果我们想要使用自己标注的名字,就要使用@Param注解。
List<Student> selectNameandSex(@Param("name1") String name,@Param("sex1") Character sex);
<select id="selectNameandSex" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name=#{name1} and sex=#{sex1}</select>
使用了param注解,底层也是帮我们封装成了map集合,但是是将我们自己定义的名字封装为key,且这里argx不能再用,但是paramx仍可以使用。
就相当于帮我们封装成
map(“param1”,“cky”);map(“param2”,18);map(“name1”,“cky”);map(“sex1”,18);
6、语句查询
6.1 返回一个实体类对象
根据id查找时,我们查找的对象正好有对应的实体类,则我们可以直接返回一个实体类对象
<select id="selectByid" resultType="car">select * from t_car where id=#{id}</select>
@Testpublic void testid1(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);Car car = mapper.selectByid(2);System.out.println(car);sqlSession.close();}
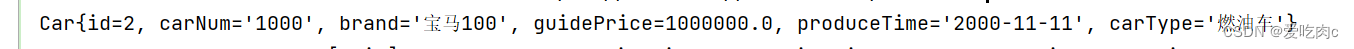
6.2 返回多个实体类对象 List<>
<select id="selectAllCar" resultType="Car">select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car ;</select>
@Testpublic void tesr(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();//getMapper() 参数传入我们要代理的接口类 之后底层 会调用javassist 自动帮助我们生成 实现类 并将实现类返回 我们可以直接调用接口类的方法CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAllCar();cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));sqlSession.close();}

6.3 返回一个Map对象
如果我们返回的对象在我们的项目中没有对应的实体类的话,我们可以使用map
Map<String,Object> selectByID(int id);
<select id="selectByID" resultType="map">select * from t_car where id=#{id}</select>
@Testpublic void test1(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();//getMapper() 参数传入我们要代理的接口类 之后底层 会调用javassist 自动帮助我们生成 实现类 并将实现类返回 我们可以直接调用接口类的方法CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);Map<String, Object> map = mapper.selectByID(2);System.out.println(map);sqlSession.close();}
使用map接收时,其key就是数据库的列名,并不是我们类的列名

6.4 返回多个Map对象 List
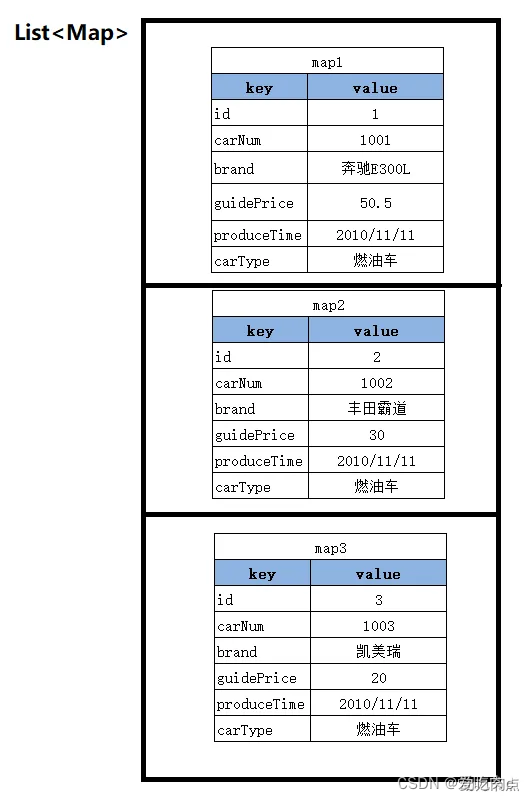
List<Map<String,Object>> selectAllCar();
<select id="selectAllCar" resultType="map">select * from t_car ;</select>
@Testpublic void tesr(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();//getMapper() 参数传入我们要代理的接口类 之后底层 会调用javassist 自动帮助我们生成 实现类 并将实现类返回 我们可以直接调用接口类的方法CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);List<Map<String, Object>> maps = mapper.selectAllCar();maps.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));sqlSession.close();}

6.5 返回一个大Map
如果我们使用List
@MapKey("id")Map<Integer,Map<String,Object>> selectmyMap();
<select id="selectmyMap" resultType="map">select * from t_car</select>
@Testpublic void test2(){SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();//getMapper() 参数传入我们要代理的接口类 之后底层 会调用javassist 自动帮助我们生成 实现类 并将实现类返回 我们可以直接调用接口类的方法CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);Map<Integer, Map<String, Object>> integerMapMap = mapper.selectmyMap();System.out.println(integerMapMap);sqlSession.close();}
结果是一个大的map
{2={car_num=1000, id=2, guide_price=1000000.00, produce_time=2000-11-11, brand=宝马100, car_type=燃油车},
3={car_num=102, id=3, guide_price=40.30, produce_time=2014-10-05, brand=丰田mirai, car_type=氢能源},
4={car_num=102, id=4, guide_price=40.30, produce_time=2014-10-05, brand=丰田mirai, car_type=氢能源},
7={car_num=1002, id=7, guide_price=100.00, produce_time=2023-03-28, brand=五菱11, car_type=电车},
8={car_num=1000, id=8, guide_price=100.00, produce_time=2024-04-09, brand=1, car_type=dianche},
9={car_num=1000, id=9, guide_price=100.00, produce_time=2024-04-09, brand=1, car_type=dianche}}
6.6 结果映射
查询结果的列名和java对象的属性名对应不上怎么办?
● 第一种方式:as 给列起别名
● 第二种方式:使用resultMap进行结果映射
● 第三种方式:是否开启驼峰命名自动映射(配置settings)
不知道为什么 ,我没有起过别名,也没有进行自动映射,但是如果我用一个实体类接收,他自动帮我转成了实体类的属性名。
6.6.1 使用resultMap
<!--resultMap:id:这个结果映射的标识,作为select标签的resultMap属性的值。type:结果集要映射的类。可以使用别名。
-->
<resultMap id="carResultMap" type="car"><!--对象的唯一标识,官方解释是:为了提高mybatis的性能。建议写上。--><id property="id" column="id"/><result property="carNum" column="car_num"/><!--当属性名和数据库列名一致时,可以省略。但建议都写上。--><!--javaType用来指定属性类型。jdbcType用来指定列类型。一般可以省略。--><result property="brand" column="brand" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/><result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price"/><result property="produceTime" column="produce_time"/><result property="carType" column="car_type"/>
</resultMap><!--resultMap属性的值必须和resultMap标签中id属性值一致。-->
<select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap">select * from t_car
</select>
6.6.2 驼峰式映射
是否开启驼峰命名自动映射
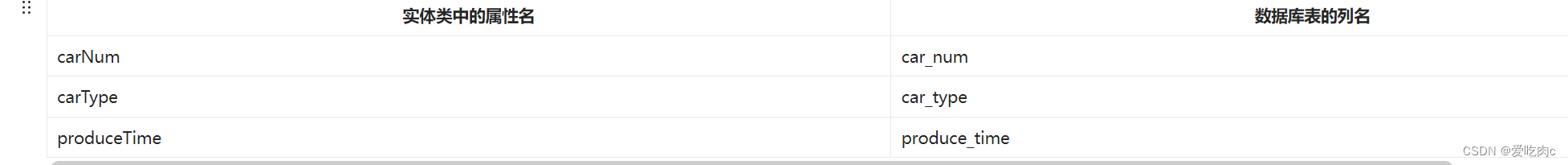
使用这种方式的前提是:属性名遵循Java的命名规范,数据库表的列名遵循SQL的命名规范。
Java命名规范:首字母小写,后面每个单词首字母大写,遵循驼峰命名方式。
SQL命名规范:全部小写,单词之间采用下划线分割。
比如以下的对应关系:
如何启用该功能,在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行配置:
<!--放在properties标签后面-->
<settings><setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
