【神经网络】生成对抗网络GAN
生成对抗网络GAN
欢迎访问Blog总目录!
文章目录
- 生成对抗网络GAN
- 1.学习链接
- 2.GAN结构
- 2.1.生成模型Generator
- 2.2.判别模型Discrimintor
- 2.3.伪代码
- 3.优缺点
- 3.1.优势
- 3.2.缺点
- 4.pytorch GAN
- 4.1.API
- 4.2.GAN的搭建
- 4.2.1.结果
- 4.2.2.代码
- 4.3.示意图:star:
1.学习链接
Generative Adversarial Networks
生成对抗网络(GAN) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
深度学习----GAN(生成对抗神经网络)原理解析_gan神经网络-CSDN博客
图解 生成对抗网络GAN 原理 超详解_生成对抗网络gan图解-CSDN博客
2.GAN结构
GAN包含两个模型:
- 生成模型(Generator):接收随机噪声,生成看起来真实的、与原始数据相似的实例。
- 判别模型(Discrimintor):判断Generator生成的实例是真实的还是人为伪造的。(真实实例来源于数据集,伪造实例来源于生成模型)
最终得到效果极好的生成模型,其生成的实例真假难辨。
GAN的灵感来源于 “零和博弈” (完全竞争博弈),GAN就是通过生成网络G(Generator)和判别网络D(Discriminator)不断博弈,进而使G学习到数据的分布,即达到纳什均衡。
【纳什均衡】博弈中这样的局面,对于每个参与者来说,只要其他人不改变策略,他就无法改善自己的状况。对于GAN,即生成模型 G 恢复了训练数据的分布(造出了和真实数据一模一样的样本),判别模型D判别不出来结果(乱猜),准确率为 50%(收敛)。这样双方网络利益均最大化,不再改变自己的策略(不再更新自己的权重)。

2.1.生成模型Generator
- 输入: 数据集的某些向量信息,此处使用满足常见分布(高斯分布、均值分布等)的随机向量。
- 输出: 符合像素大小的图片。
- 结构: 全连接神经网络或者反卷积网络。

2.2.判别模型Discrimintor
- 输入: 伪造图片和数据集图片
- 输出: 图片的真伪标签
- 结构: 判别器模型(全连接网络、卷积网络等)

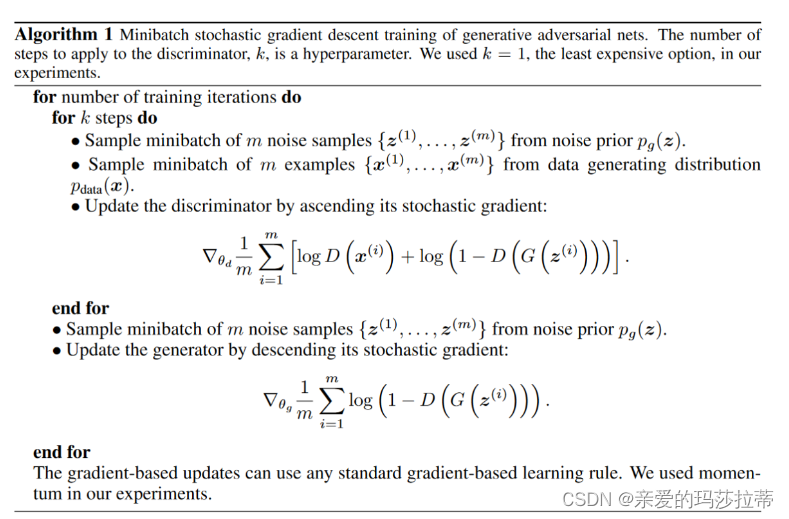
2.3.伪代码
3.优缺点
3.1.优势
- GAN采用的是一种无监督的学习方式训练,可以被广泛用在无监督学习和半监督学习领域
- 模型只用到了反向传播,而不需要马尔科夫链
3.2.缺点
- 难以学习离散数据,如文本
4.pytorch GAN
4.1.API
生成对抗网络 - PyTorch官方教程中文版 (panchuang.net)
4.2.GAN的搭建
绘制在upper_bound和lower_bound之间的一元二次方程画
4.2.1.结果

4.2.2.代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plttorch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
np.random.seed(1)# Hyper Parameters
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR_G = 0.0001 # learning rate for generator
LR_D = 0.0001 # learning rate for discriminator
N_IDEAS = 5 # 噪声点个数
ART_COMPONENTS = 15 # 15个Y轴数据点
PAINT_POINTS = np.vstack([np.linspace(-1, 1, ART_COMPONENTS) for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE)])# show our beautiful painting range
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
# plt.legend(loc='upper right')
# plt.show()def artist_works(): # painting from the famous artist (real target)a = np.random.uniform(1, 2, size=BATCH_SIZE)[:, np.newaxis]paintings = a * np.power(PAINT_POINTS, 2) + (a-1)paintings = torch.from_numpy(paintings).float()return paintingsG = nn.Sequential( # Generatornn.Linear(N_IDEAS, 128), # random ideas (could from normal distribution)nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(128, ART_COMPONENTS), # making a painting from these random ideas
)D = nn.Sequential( # Discriminatornn.Linear(ART_COMPONENTS, 128), # receive art work either from the famous artist or a newbie like Gnn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(128, 1),nn.Sigmoid(), # tell the probability that the art work is made by artist
)opt_D = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=LR_D)
opt_G = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=LR_G)plt.ion() # something about continuous plottingfor step in range(10000):artist_paintings = artist_works() # real painting from artistG_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, N_IDEAS, requires_grad=True) # random ideas\nG_paintings = G(G_noise) # fake painting from G (random ideas)prob_artist0 = D(artist_paintings) # 判断真画prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings) # 判断假画# D增加真画概率,减少伪画概率; 梯度下降法为减小误差,所以添加-号# D_loss越小,prob_artist0越大,prob_artist1越小D_loss = - torch.mean(torch.log(prob_artist0) + torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))opt_D.zero_grad()D_loss.backward(retain_graph=True) # reusing computational graphopt_D.step()# 重新采样G_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, N_IDEAS, requires_grad=True) # random ideas\nG_paintings = G(G_noise) # fake painting from G (random ideas)prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings) # 判断假画# G_loss越小,prob_artist1越大G_loss = torch.mean(torch.log(1. - prob_artist1))opt_G.zero_grad()G_loss.backward()opt_G.step()if step % 50 == 0: # plottingplt.cla()plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], G_paintings.data.numpy()[0], c='#4AD631', lw=3, label='Generated painting', )plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')# D 的判断准确度=50%最优plt.text(-.5, 2.3, 'D accuracy=%.2f (0.5 for D to converge)' % prob_artist0.data.numpy().mean(),fontdict={'size': 13})plt.text(-.5, 2, 'D score= %.2f (-1.38 for G to converge)' % -D_loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 13})plt.ylim((0, 3));plt.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10);plt.draw();plt.pause(0.01)plt.ioff()
plt.show()
4.3.示意图⭐️

