数据结构之栈和队列
1.前言
大家好久不见,这段时间由于忙去了。就没有即使维护我的博客,先给大家赔个不是。
我们还是规矩不乱,先赞后看~
今天讲的内容是数据结构中非常重要的一个部分:栈和队列。它在今后的学习中也会再次出现(c++)话不多说,直接进入正题!
2.栈
2.1栈的概念和结构
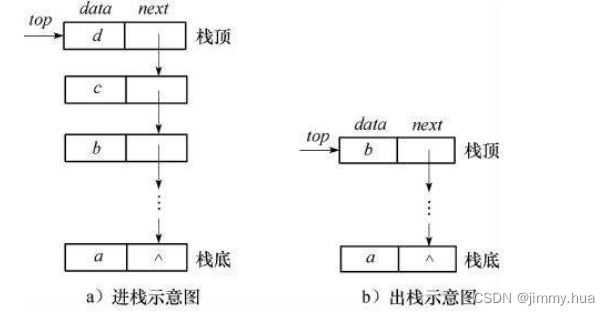
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。


2.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
// 下面是定长的静态栈的结构,实际中一般不实用,所以我们主要实现下面的支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType _a[N];
int _top; // 栈顶
}Stack;
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
接下来是各个函数的实现过程:
#include"stack.h"int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;//?
}void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;//pst->top = -1;//与栈顶元素精准对齐(先++,再放数据);若指向栈顶元素的下一个位置 --- top = 0(不合理)pst->top = 0;//指向栈顶数据的下一个位置pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;//capacity=0 --- 直接赋为4;不是0就二倍STDataType* tmp = realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;//把x放到栈顶pst->top++;
}bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false; }
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(!STEmpty(pst));pst->top--;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = 0;pst->capacity = 0;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(!STEmpty(pst));return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}3.队列
3.1队列的概念和结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。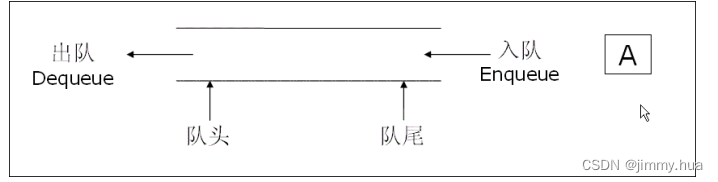
3.2队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。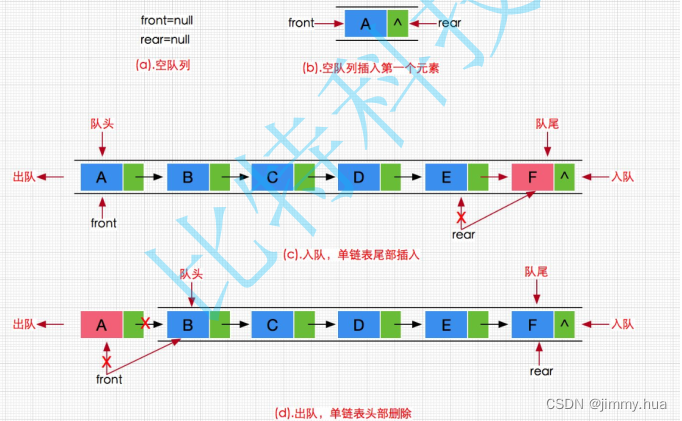
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* _pNext;
QDataType _data;
}QNode;
// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* _front;
QNode* _rear;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);具体函数实现如下:
#include"queue.h"bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;//return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL;
}void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq;QNode* next = NULL;while (cur && next){next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->phead == NULL){assert(pq->ptail == NULL);pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//1个结点//多个节点if (pq->phead->next == NULL){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}else{//头删QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}4.小结
以上就是栈和队列的基础知识点,还需要多刷题来巩固基础知识,各位有什么不懂的尽管在评论区留言,博主一定尽全力来给大家解答,谢谢大家,我们下篇见~
