【Java】Thread详解
🍒前言
本文将从以下几方面来展开对Thread的介绍。
1.线程创建 2.线程中断 3.线程等待 4.线程休眠
在前面的文章中,已经总结了关于Thread的一些理解。
在阅读本文之前,最好对其有一些基础的了解。
文章链接: 【JavaSE】进程是什么?
文章链接: 【JavaSE】初识线程,线程与进程的区别
文章链接: 【JavaSE】Thread类中run和start的区别
文章目录
- 🍒前言
- 🍇线程的创建
- 🍐1.继承 Thread 类
- 🍐2.实现Runnable接口
- 🍐3.匿名内部类
- 🍐4.匿名内部类创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
- 🍐5.lambda 表达式创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
- 🍎线程中断
- 🥝1.自己设定条件
- **缺点**
- 🥝2.使用interrupt和isInterrupted方法
- 🍆线程等待
- ✍线程休眠
🍇线程的创建
🍐1.继承 Thread 类
class MyThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("hello thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
public class demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new MyThread();t.start();while (true){System.out.println("hello main");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
🍐2.实现Runnable接口
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("hello thread2");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(new MyRunnable());t.start();while (true){System.out.println("hello main2");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
🍐3.匿名内部类
public class demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){System.out.println("hello thread3");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}};t.start();while (true){System.out.println(" hello main");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
🍐4.匿名内部类创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
public class demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread((Runnable) () ->{while (true){System.out.println("hello thread4");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t.start();while (true){System.out.println(" hello main4");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}
🍐5.lambda 表达式创建 Runnable ⼦类对象
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(()->{while (true){System.out.println("hello thred5");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t.start();while (true){System.out.println(" hello main5");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
🍎线程中断
终止线程,在Java中所有的终止程序都只是“提醒,建议”。真正的是否结束都是由线程本体 自己决定的。
在系统原生的线程中,是有办法让别的线程强制终止的,但这种设定不太好,所以Java没有采纳
主要原因还是线程之间的调度是随机的。
🥝1.自己设定条件
之所以可以结束,是因为thread线程外面写了isRunning这样的条件,所以才能控制
如果thread代码不这样写,那么thread都会继续执行,不会在意外面的条件
最终决定权还是在thread手中。
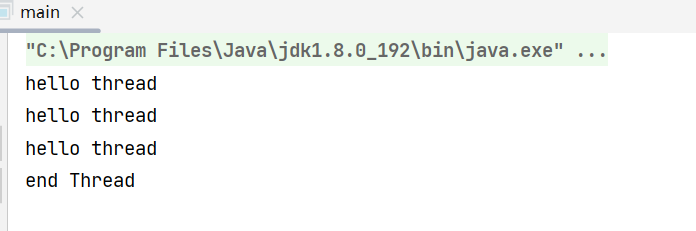
private static boolean isRunning = true;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(()->{while (isRunning){//自己书写条件控制线程的结束System.out.println("hello thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});thread.start();try {Thread.sleep(3000);//三秒之后 } catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}isRunning = false;//三秒之后设置 条件 终止线程System.out.println("end Thread");}
运行结果如下
缺点

🥝2.使用interrupt和isInterrupted方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(()->{// t.isInterrupted();while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){System.out.println("hello thead");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t.start();Thread.sleep(3000);t.interrupt();}

运行程序
发现3s之后,线程确实是结束了。但是是以抛出异常中断的情况结束,
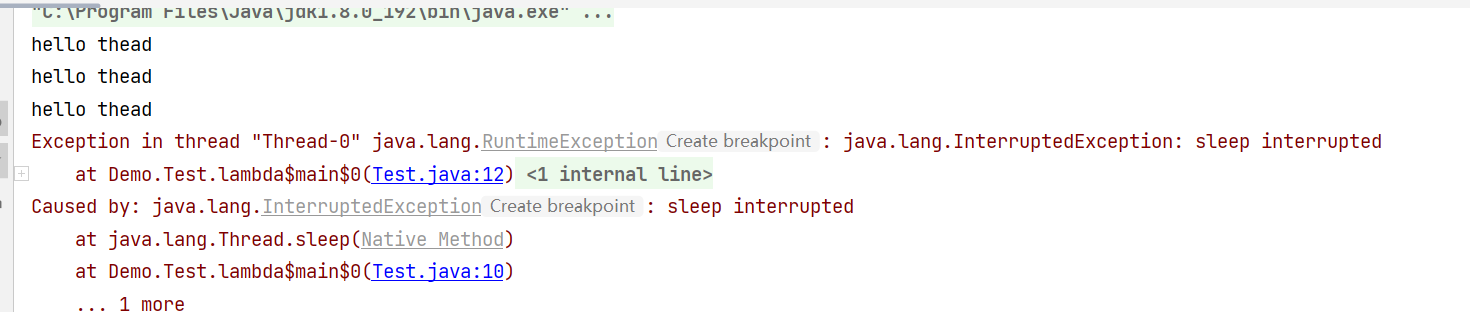
这样会使结果不那么美观。那么接下来就要解决这样的问题。
解决方法
我们不抛出异常,而是打印出异常。
继续运行,看看结果是怎样的。

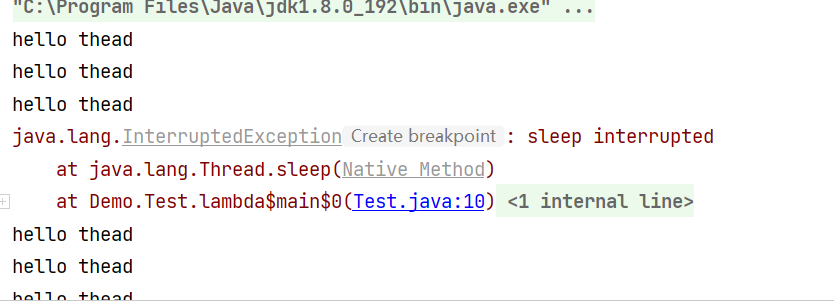
我们可以看到结果中,打印出了异常,而线程并没有结束
我们确确实实使用了interrupt方法,使标志位修改成了true了,那为什么线程还会继续执行呢?


🍆线程等待
因为线程是随机调度的,为了解决这样的问题,从而引入了线程等待。
使用join()
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("hello t1");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("hello t2");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();//加入条件t2.join();//System.out.println("end main");}
运行结果如下
main线程调用t1.join() t2.join(),t1 t2 继续执行 main线程等待
t1和t2谁先结束,这是未知的
而t1 和 t2 比main先结束,这是已知的。
如果想要定义t1和t2的先后结束顺序
就在对应的t1或t2线程内调用join()方法

join还有一个带参数的方法
不带参数的join方法就是所谓的“死等”

✍线程休眠
线程休眠sleep控制的是“线程休眠的时间”,而是不是“两个代码执行的间隔时间”
举例
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());}
由打印结果可以看出,这里并不是精准的1000,
此处sleep是指线程阻塞的时间,在这个时间段内是无法抢占CPU的执行权的
而时间结束,线程由阻塞状态变为就绪状态
但这并不意味着它立即就能到CPU上去执行。
以上就是本文所有内容,如果对你有帮助的话,点赞收藏支持一下吧!💞💞💞
