对AOP的理解
目录
- 一、为何需要AOP?
- 1、从实际需求出发
- 2、现有的技术能解决吗?
- 3、AOP可以解决
- 二、如何实现AOP?
- 1、基本使用
- 2、更推荐的做法
- 2.1 “基本使用”存在的隐患
- 2.2 最佳实践
- 2.2.1 参考@Transactional(通过AOP实现事务管理)
- 2.2.2 自定义注解
- 3、后言
一、为何需要AOP?
1、从实际需求出发
public class Book {......
}public interface IBookService {int insertBook(Book book);int deleteBookById(Long id);int updateBook(Book book);Book selectBookById(Long id);
}public class BookServiceImpl implements IBookService {@Overridepublic int insertBook(Book book) {// 入参检查// 日志记录// 事务处理// 业务逻辑return 0;}@Overridepublic int deleteBookById(Long id) {// 入参检查// 日志记录// 事务处理// 业务逻辑return 0;}@Overridepublic int updateBook(Book book) {// 入参检查// 日志记录// 事务处理// 业务逻辑return 0;}@Overridepublic Book selectBookById(Long id) {// 入参检查// 日志记录// 事务处理// 业务逻辑return null;}
}
- 上述代码的问题:
- (1)业务逻辑代码和非业务逻辑代码耦合
- (2)非业务逻辑的代码重复度高,却没有复用
2、现有的技术能解决吗?
- 方案1:模板模式
public abstract class BookServiceTemplate {public <T, E> T execute(E e) {// 入参检查// 日志记录// 事务处理return doProcess(e);}protected abstract <T, E> T doProcess(E e);
}public class BookServiceImpl implements IBookService {@Overridepublic int insertBook(Book book) {return new BookServiceTemplate() {@Overrideprotected <T, E> T doProcess(E e) {return null;}}.doProcess(book);}...
}
- 在需求初期,BookServiceImpl的4个方法的入参检查、日志记录、事务处理都比较一致时,上面的写法还行得通。
- 可一旦其中一个方法(如insertBook)需要改变入参检查、日志记录、事务处理时,事情就变得麻烦了。改模板吧,影响了其他方法(如updateBook)。去掉insertBook方法的模板吧,随着需求的发展,模板模式彻底腐化或被抛弃了。
- 方案2:代理模式
public class BookServiceProxyImpl implements IBookService {private final IBookService bookService;public BookServiceProxyImpl(IBookService bookService) {this.bookService = bookService;}@Overridepublic int insertBook(Book book) {// 入参检查boolean pass = checkParams(book);// 日志记录// 事务处理// 业务逻辑return bookService.insertBook(book);}...// 入参检查private boolean checkParams(Book book) {...}
}
- 挺不错的,其中一个方法(如insertBook)需要改变入参检查、日志记录、事务处理时,改变这个方法即可,对其他方法没影响。
- 但这个代理类不太“干净”,又能看到业务代码逻辑的入口(如insertBook),又能看到非业务逻辑代码(如checkParams)。
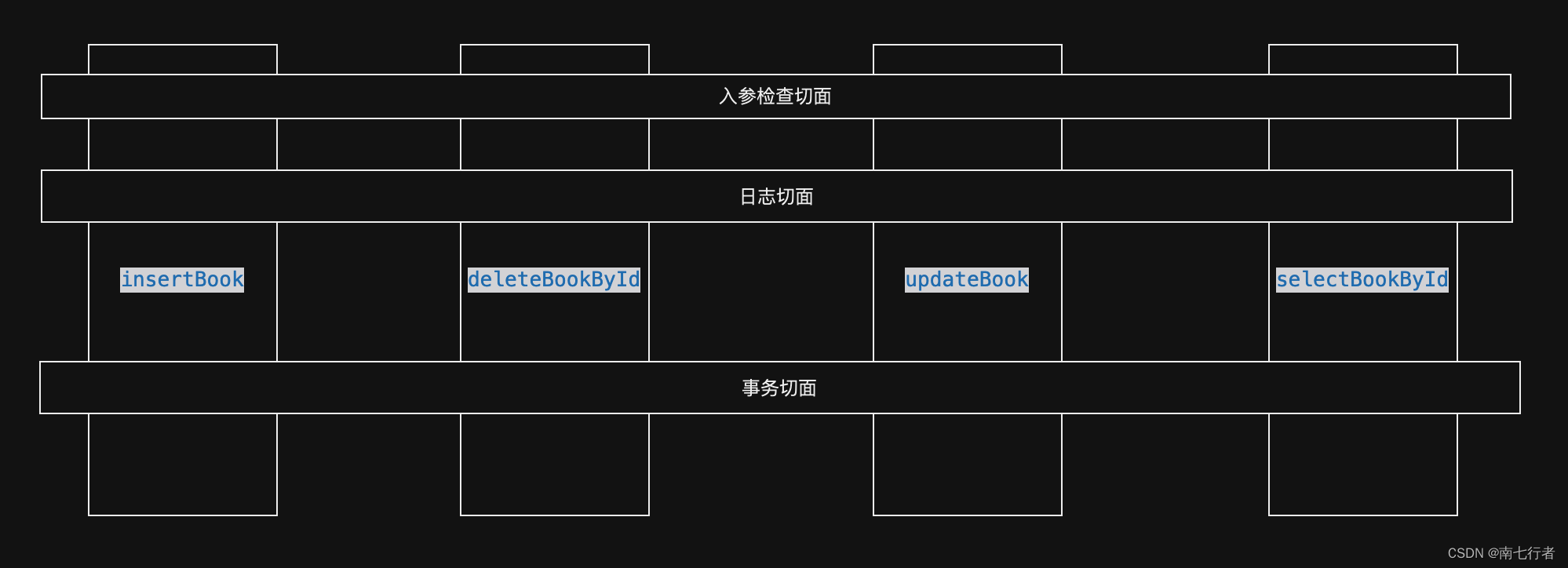
3、AOP可以解决
- 将业务逻辑代码和非业务逻辑代码解耦
- 业务逻辑代码在对象A,非业务逻辑代码在对象B
- Spring管理了对象A和对象B,在逻辑执行中,交织对象A的业务逻辑和对象B的非业务逻辑
- 这是我对AOP的简单理解。(AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming,即面向切面编程)
- 面向对象编程(OOP):通过将系统的大功能点拆分为一个一个小功能点,分别交给不同的类/对象负责(封装),并利用类的继承、多态构建系统的结构,让类相互配合,从而让系统运作起来。
- AOP本质还是OOP,是对OOP的补充。
二、如何实现AOP?
1、基本使用
- 示例【来源】:
public class User {
}public interface IUserService {int insertUser(User user);int deleteUserById(Long id);
}@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {@Overridepublic int insertUser(User user) {return 0;}@Overridepublic int deleteUserById(Long id) {return 0;}
}
public class Mail {
}public interface IMailService {int insert(Mail mail);
}@Service
public class MailServiceImpl implements IMailService {@Overridepublic int insert(Mail mail) {return 0;}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {/*** com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2.user.service.impl.UserServiceImpl类的所有public xxx 方法(yyy)在执行前都会被拦截,<br>* 并执行这个方法*/@Before("execution(public * com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2.user.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")public void doAccessCheck() {System.out.println("[Before] do access check...");}/*** com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2.mail.service.impl.MailServiceImpl类的所有public xxx 方法(yyy)在执行前都会被拦截,<br>* 并执行这个方法*/@Around("execution(public * com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2.mail.service.impl.MailServiceImpl.*(..))")public Object doLogging(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {System.out.println("[Around] start " + pjp.getSignature());Object retVal = pjp.proceed();System.out.println("[Around] end " + pjp.getSignature());return retVal;}
}
- 如果不加:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();Arrays.stream(beanDefinitionNames).forEach(System.out::println);}
}/**
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
application
loggingAspect
mailServiceImpl
userServiceImpl
*/
- LoggingAspect因为被打上了@Component注解,因此也被加载成bean了。
- 但实际上,loggingAspect没有起任何作用(什么都没输出):
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class);userService.insertUser(new User());}
}
- 加上@EnableAspectJAutoProxy后:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class);userService.insertUser(new User());}
}
- 多了一个bean:org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator
- 但报错:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2.user.service.impl.UserServiceImpl' available
- 这就诡异了,明明在Spring容器中看到了userServiceImpl,Spring咋说没有呢?!
- 很可能是因为:使用代理对象作为容器中的实际Bean
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceImpl");System.out.println(bean instanceof Advised); // 带上@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,则为true;否则为fasle。}
}
- 这么改就对了:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class);userService.insertUser(new User());}
}
- 或者:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example2")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);IUserService userService = (IUserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceImpl");userService.insertUser(new User());}
}
- 输出:
[Before] do access check...
2、更推荐的做法
2.1 “基本使用”存在的隐患
- 目标代码(如
userService.insertUser(new User());)无法感知到自己会被拦截。
2.2 最佳实践
2.2.1 参考@Transactional(通过AOP实现事务管理)
- 对于一个bean,我希望这个bean的insertUser方法开启事务,可以这么写:
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {@Override@Transactionalpublic int insertUser(User user) {return 0;}......
}// 需要依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId><version>5.2.25.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- 通过注解,可以“自主”告知Spring,代理“我”吧,我需要AOP。
2.2.2 自定义注解
跟着廖雪峰老师,实现:对计算方法执行的耗时。
public class User {
}public interface IUserService {User register(String email, String password, String name);
}@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {@Override@MetricTime("register")public User register(String email, String password, String name) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return new User();}
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MetricTime {String value();
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class MetricAspect {@Around("@annotation(metricTime)")public Object metric(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, MetricTime metricTime) throws Throwable {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();try {return pjp.proceed();} finally {long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("[Metric] [" + metricTime.value() + "] time cost: " + (end - start));}}
}
@annotation(xxx)中的xxx和MetricTime xxx要一一对应。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan("com.forrest.learnspring.aop.example4.user")
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Application.class);IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class);userService.register("forrest@gmail.com", "123456", "forrest");}
}/**
[Metric] [register] time cost: 1001
*/
3、后言
- 实际开发中,写AOP代码比较少,主要是业务代码本身难以完全拨离非业务代码。
- (1)例如,打日志。不可能只在方法的前后打日志,在方法执行中,也需要加一些日志。
- (2)例如,参数检查。在方法执行前做参数检查,只是一些基本的检查。另外,有些参数的校验本身就属于业务逻辑的一部分。抛开业务本身,是没法判断参数是否正确的。
- (3)例如,事务处理。可以用Spring提供的@Transactional注解。即使要自己定义注解通过AOP实现事务,在写方法体时也要格外注意,别带一些没必要参与事务的逻辑。
- 不过,真需要在执行某些方法时,做一些拦截处理,AOP还是不错的选择。
