oneMKL--FFT 基本使用
oneMKL–FFT 基本使用
本人基于官方文档的摘录与理解
oneMKL--FFT基本使用
- oneMKL--FFT 基本使用
- 1. Both FFT and Cluster FFT functions compute an FFT in five steps
- 2 Computing an FFT
- 2.1 缺省值
- 2.2 Fourier Transform Funcions Code Examples
- 2.2.1 One_dimentional In-place FFT(一维的原地的FFT,原地指输出覆盖原始数据)
- 2.2.2 One_dimentional Out-of-place FFT(一维的异地的FFT,异地指输出在准备好的地方) and Changing default setting
- 2.2.3 Two-dimentional FFT
- 2.2.4 Changing Default Settings
- 3 Using Status Checking Functions
- 4 Computing 2D FFT by One-Dimensional Transforms
- 5 Examples of Using OpenMP* Threading for FFT Computation
- 6 oneMKL 中 FFT 的所有函数
- 7 参数解释
- Configuration settings
1. Both FFT and Cluster FFT functions compute an FFT in five steps
-
为计算分配一个全新的描述器,通过调用DftiCreateDescriptor or DftiCreateDescriptorDM
- 这个描述器定义了快速傅里叶变换中的参数,比如 维度(dimensionality)、大小(sizes)、转换次数(number of transforms)、输入输出数据的存储布局(指layout,行优先还是列优先)、比例因子(scaling factors)。这些配置参数很多都分配了默认值,有需要的话要再程序中修改。
-
需要时,选择性的调整描述器的配置,通过调用DftiSetValue or DftiSetValueDM
- 通常,你必须仔细定义用于FFT的数据存储布局(指layout)或 用于Cluster FFT过程中的数据分布。描述器的配置参数,比如默认值,可以通过DftiGetValue or DftiGetValueDM 函数来获得
-
提交描述器,通过调用DfticommitDescriptor or DftiCommitDescriptorDM
- 这使描述器ready for transform computation。
- 一旦提交了描述器,变换(transform)的参数就会被冻结于描述器中,比如变换的类型和数值(type and number of transforms)、步幅(strides)和距离(distances)、数据的类型和存储布局(layout)等等。
-
开始计算变换,通过调用DfticomputeForward/DftiComputeBackward or DftiComputeForwardDM/DftiComputeBackwardDM,根据需要来设置运算次数
- 因为描述器是分开定义和提交的,计算函数做的所有工作就是接受输入和输出并且按照定义来计算变换。
- 想要修改另一个计算函数的调用的任何配置参数,就使用DftiSetValue后面跟着DftiCommitDescriptor(DftiSetValueDM后面就跟着DftiCommitDescriptorDM)来修改,或者 创建并提交另一个描述器。
-
释放描述器,通过调用DftiFreeDescriptor or DftiFreeDescriptorDM
- 描述器内部消耗的内存将被释放掉
上述所有方法都会返回一个整形的状态值(status value),该值在操作成功完成时为0。
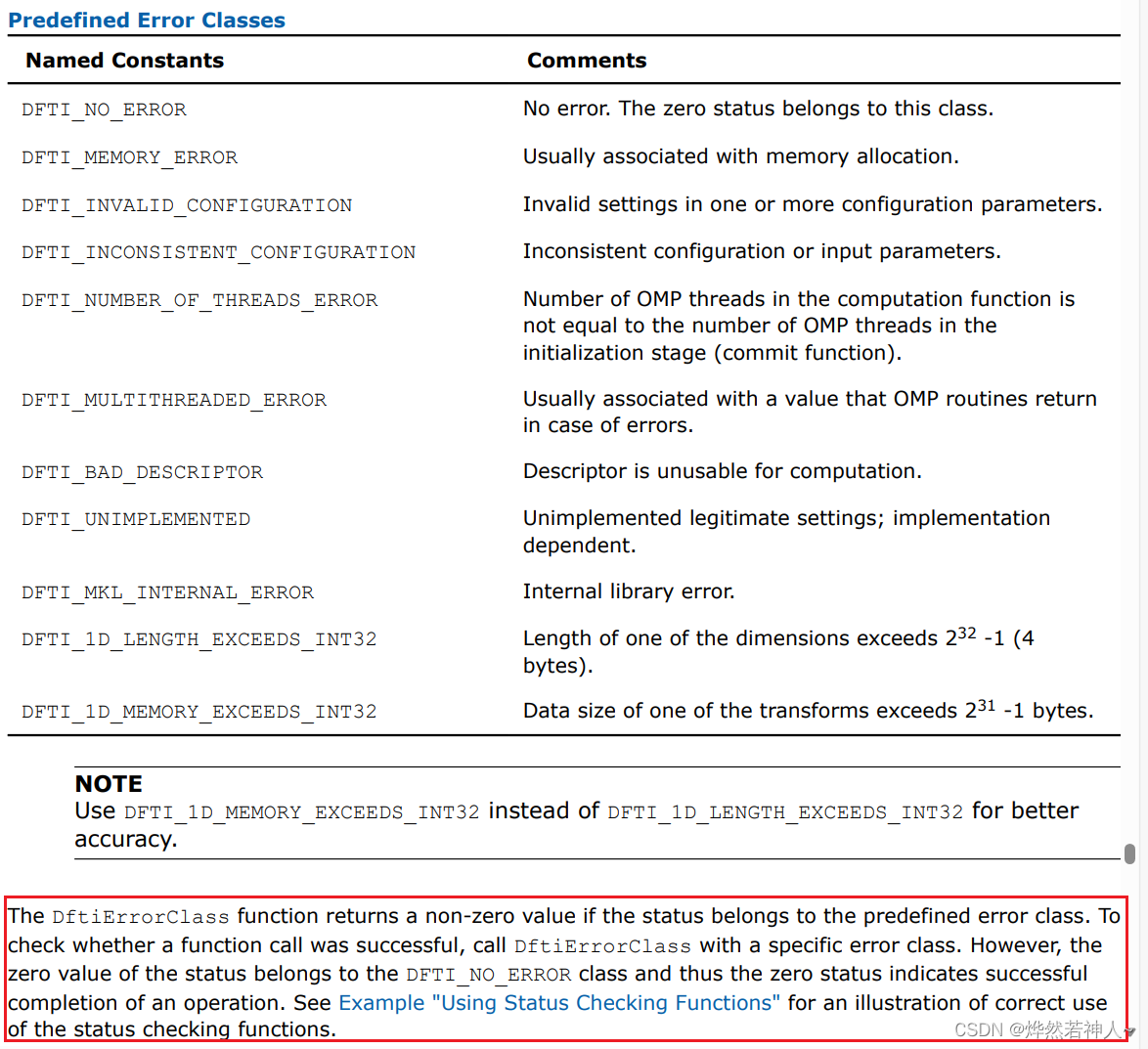
你可以通过DftiErrorClass or DftiErrorMessage 来了解非0状态的意义。
2 Computing an FFT
2.1 缺省值
描述器的数据结构在创建时就包含了FFT的长度和域(domain,复数或实数)的信息,也包含了一些配置参数。这些参数的一些缺省值如下:
- Scale factor :none (that is, σ=1)
- Number of data sets:one (数据集数量)
- Data storage: contiguous(连续的)
- Placement of results: in-place(the computed result overwrites the input data,计算出来的结果覆盖输入数据)
这些默认设置想要改变可以通过 DftiSetValue
2.2 Fourier Transform Funcions Code Examples
2.2.1 One_dimentional In-place FFT(一维的原地的FFT,原地指输出覆盖原始数据)
complex<float> c2c_data[32];
//float _Complex c2c_data[32]; //c风格写法,vs识别有问题
float r2c_data[34];
DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc1_handle = NULL;
DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc2_handle = NULL;
MKL_LONG status;
for (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) c2c_data[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) r2c_data[i] = i;//complex operation
status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_COMPLEX, 1, 32);
status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc1_handle);
status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc1_handle, c2c_data);
status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle);//reall operation
status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc2_handle, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_REAL, 1, 32);
status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc2_handle);
status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc2_handle, r2c_data);cout << "c2c:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {cout << c2c_data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl << endl;cout << "r2c:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 34; i++) {cout << r2c_data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;}
输出:
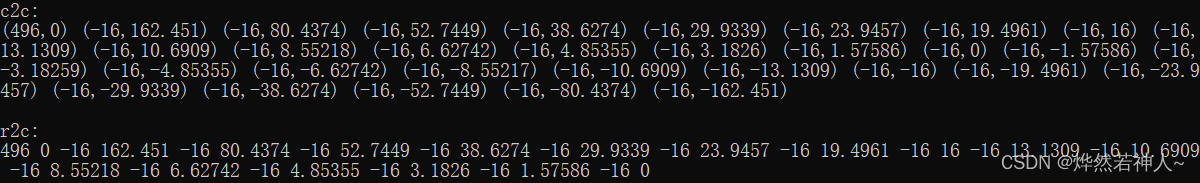
总结: example中一个数据类型是复数类型complex,一个数据类型是float。输出结果的不同应该是受fft算法的影响,不是很懂。
2.2.2 One_dimentional Out-of-place FFT(一维的异地的FFT,异地指输出在准备好的地方) and Changing default setting
#include <iostream>
#include <mkl_dfti.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;void main() {complex<float> c2c_input[32];complex<float> c2c_output[32];float r2c_input[32];float r2c_output[32];DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc1_handle = NULL;DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc2_handle = NULL;MKL_LONG status;//store the number of command execution status. MKL_LONG is long int.//assign values to arraysfor (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) c2c_input[i] = i;for (int i = 0; i <= 31; i++) r2c_input[i] = i;// real operation/*create a descriptorsynax:status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&desc_handle, precision, forward_domain, dimension,length);the first parameter &desc_handle is the operation handle of a descriptorthe second parameter DFTI_PRECSION is the precision of FFT operation. DFTI_PRECESION has two enumeration types:DFTI_SINGLE、DFTI_DOUBLE the third parameter DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN is the domain of FFT operation. It means the type of fft.DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN has two enumeration types:DFTI_COMPLEX、DFTI_REALthe fourth parameter dimention is the dimension of FFT operationthe fifth parameter length is the length of the transform for a one-dimensional transform.the lengths of each dimension for a multi-dimensional transform.*/status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle,DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_COMPLEX, 1, 32);//create a descriptor/*FFT Descriptor Configuration FunctionSyntax: status = DftiSetValue(desc_handle, config_param, config_val);The desc_handle's type is DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE. The previous commande had initialized the DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE.The DFTI_PlACEMENT is the config_param.The function only can set one particular parameter with a specified configuration value.*/status = DftiSetValue(my_desc1_handle, DFTI_PLACEMENT, DFTI_NOT_INPLACE);status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc1_handle);/*Syntax:status = DftiComputeForward(desc_handle, x_inout);status = DftiComputeForward(desc_handle, x_in, y_out);status = DftiComputeForward(desc_handle, xre_inout, xim_inout);status = DftiComputeForward(desc_handle, xre_in, xim_in, yre_out, yim_out);x_inout,x_in: array of type float or double depending on the precision of the transformData to be transformed in case of a real forward domain or, in the case of a complex forwarddomain in association with FTI_COMPLEX_COMPLEX, set for DFTI_COMPLEX_STORAGE.xre_inout,xim_inout,xre_in, xim_in:Real and imaginary parts of the data tobe transformed in the case of acomplex forward domain.*/status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc1_handle, c2c_input, c2c_output);status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle);//complex operationstatus = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc2_handle, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_REAL, 1, 32);status = DftiSetValue(my_desc2_handle,DFTI_PLACEMENT,DFTI_NOT_INPLACE);status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc2_handle);status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc2_handle, r2c_input, r2c_output);status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc2_handle);cout << "c2c:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {cout << c2c_output[i] << " ";}cout << endl << endl;cout << "r2c:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {cout << r2c_output[i] << " ";}//cout << endl;
}
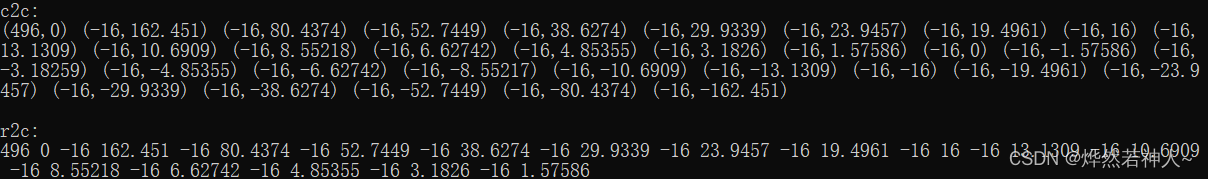
输出:
2.2.3 Two-dimentional FFT
#include "mkl_dfti.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
using namespace std;void main() {complex<float> c2c_data[32][100];float r2c_data[34][102];DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc1_handle = NULL;DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc2_handle = NULL;MKL_LONG status;MKL_LONG dim_sizes[2] = { 32,100 };for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {c2c_data[i][j] = i * 100 + j;}}for (int i = 0; i < 34; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 102; j++) {r2c_data[i][j] = i * 100 + j;}}status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_COMPLEX, 2, dim_sizes);status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc1_handle);status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc1_handle, c2c_data);status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc1_handle);status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc2_handle, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_REAL, 2, dim_sizes);status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc2_handle);status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc2_handle, r2c_data);status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc2_handle);for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {cout << r2c_data[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {cout << c2c_data[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}
}2.2.4 Changing Default Settings
/* C99 example */
#include "mkl_dfti.h"
float _Complex x_in[32], x_out[32];
DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE my_desc_handle = NULL;
MKL_LONG status;
/* ...put values into x_in[i] 0<=i<=31 */
status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&my_desc_handle, DFTI_SINGLE,DFTI_COMPLEX, 1, 32);
status = DftiSetValue(my_desc_handle, DFTI_PLACEMENT, DFTI_NOT_INPLACE);
status = DftiCommitDescriptor(my_desc_handle);
status = DftiComputeForward(my_desc_handle, x_in, x_out);
status = DftiFreeDescriptor(&my_desc_handle);
/* result is the complex value x_out[i], 0<=i<=31 */3 Using Status Checking Functions
This example illustrates the use of status checking functions described in “Fourier Transform Functions”
#include "mkl_dfti.h"
#include <complex>
//#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
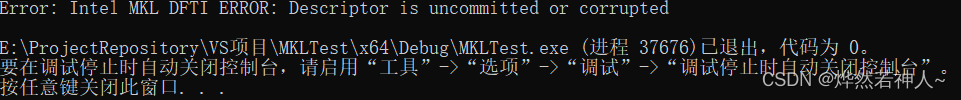
using namespace std;void main() {complex<float> c2c_data[32];DFTI_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE desc = NULL;MKL_LONG status;//status = DftiCreateDescriptor(&desc, DFTI_SINGLE, DFTI_COMPLEX, 1, 32);status = DftiCommitDescriptor(desc);/*predicate = DftiErrorClass(status, error_class);error_class: predefined error class which type is MKL_LONGpredicate : result of checking which type is MKL_LONG*/if (status && !DftiErrorClass(status, DFTI_NO_ERROR)) {cout << "Error: " << DftiErrorMessage(status) << endl;}
}
4 Computing 2D FFT by One-Dimensional Transforms
略
5 Examples of Using OpenMP* Threading for FFT Computation
略
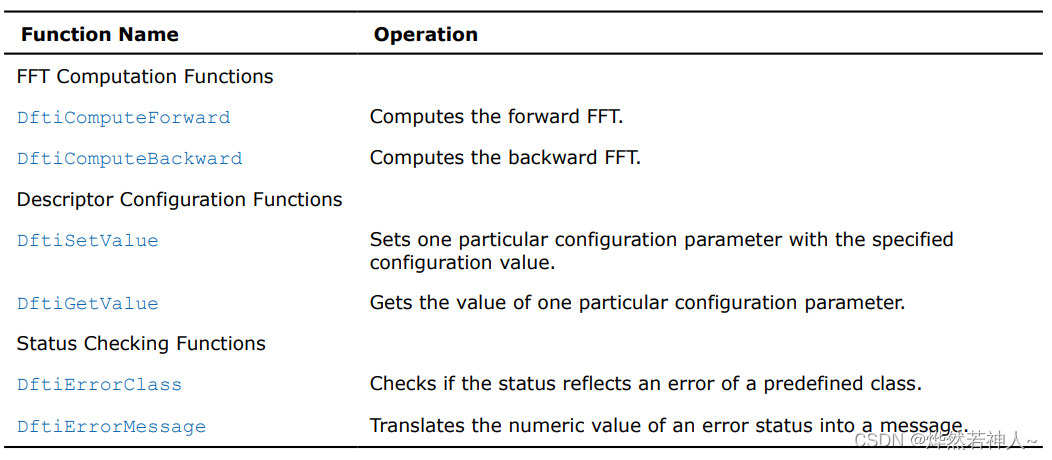
6 oneMKL 中 FFT 的所有函数
FFT函数的头文件是mkl_dfti.h

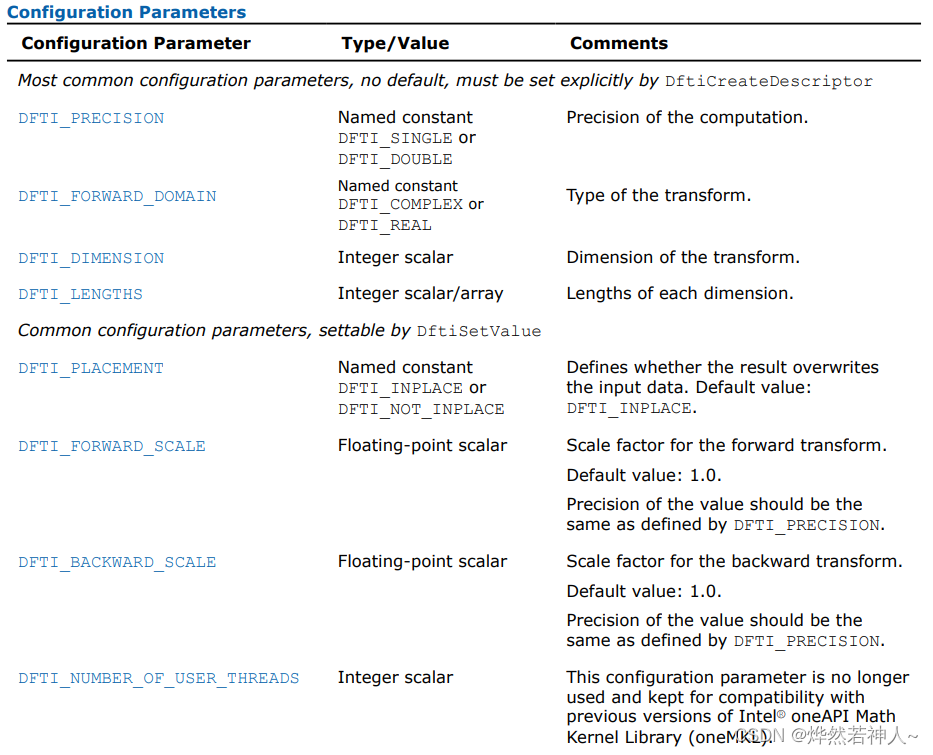
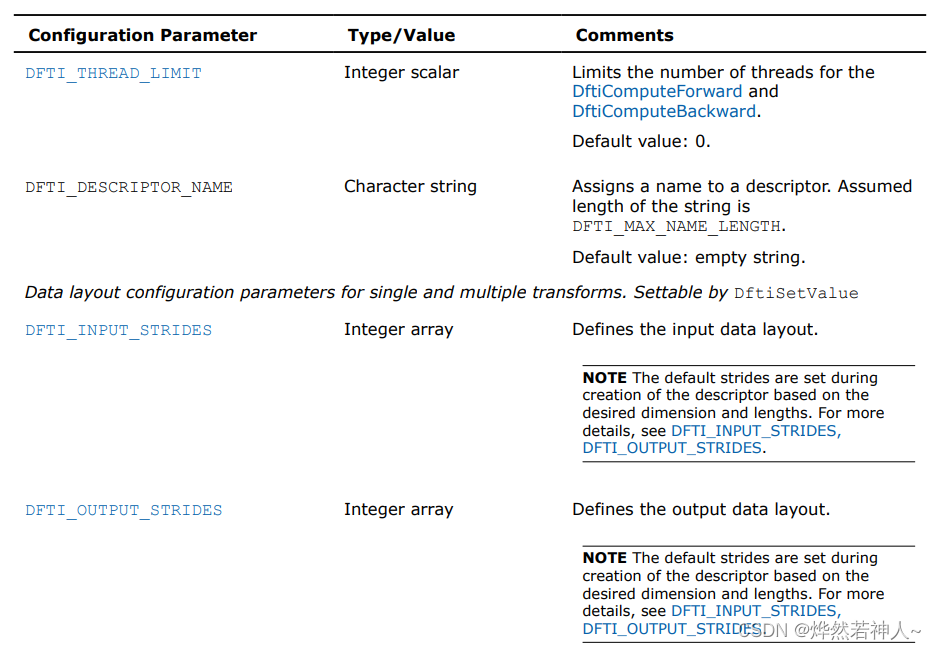
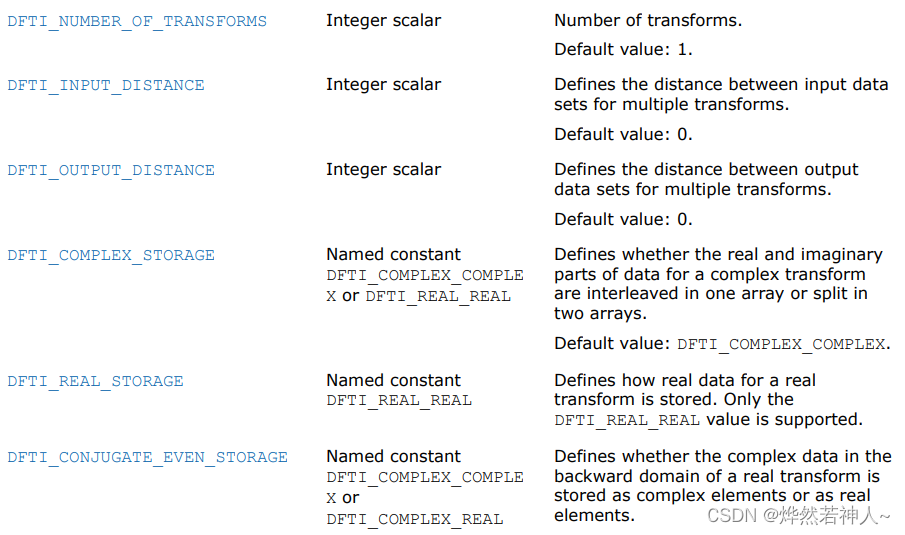
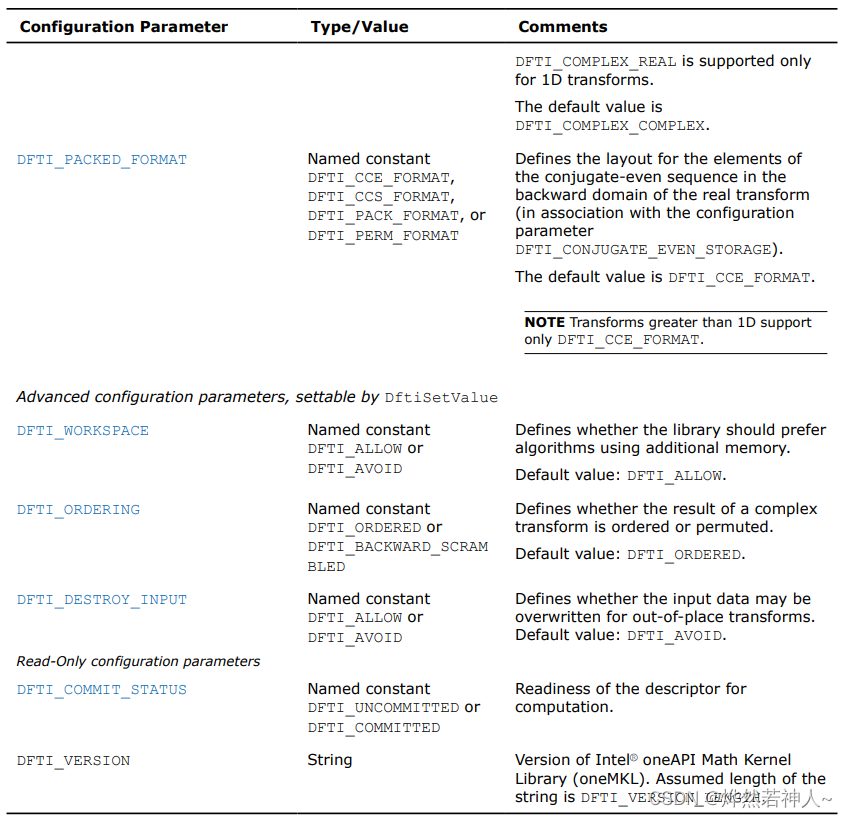
7 参数解释
Configuration settings
在MKL_DFTI模型中,每一个配置参数都由一个命名了的常量(named constant)所确定。这些常量都有一个枚举类型(enumeration type)DFTI_CONFIG_PARAM 并且被定义在mkl_dfti.h头文件中。