结构体变量
C语言允许用户自己建立由不同类型数据组成的组合型的数据结构,它称为结构体(structre)。 在程序中建立一个结构体类型:
1.结构体
建立结构体
struct Student
{ int num; //学号为整型 char name[20]; //姓名为字符串 char sex; //性别为字符型 int age; //年龄为整型float score; //成绩为实型 char addr[30]; //地址为字符串
}; //注意最后有一个分号
同时定义变量
struct Student
{ int num; char name[20];char sex; int age;float score;char addr[30];
}student1, student2;
定义变量
struct Student student1, student2;
输出变量
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ struct Student //声明结构体类型struct Student{ long int num; //以下4行为结构体的成员char name[20];char sex;char addr[20];}a={10101,"Li Lin",'M',"123 Beijing Road"}; //定义结构体变量a并初始化printf("NO.:%ld\nname:%s\nsex:%c\naddress:%s\n",a.num,a.name,a.sex,a.addr);return 0;
}
结构体变量的初始化和引用
//结构体变量的初始化和引用
student1.num=10010;
/*已定义了student1为student类型的结构体变量,
则student1.num表示student1变量中的num成员,即student1的num(学号)成员*/
对结构体变量的成员可以像普通变量一样进行各种运算
同类的结构体变量可以互相赋值。
student1=student2; //假设student1和student2已定义为同类型的结构体变量
例题:输入两个学生的学号、姓名和成绩,输出成绩较高的学生的学号、姓名和成绩。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ struct Student //声明结构体类型struct Student { int num;char name[20];float score;}student1,student2; //定义两个结构体变量student1,student2 scanf("%d%s%f",&student1.num,student1.name,&student1.score); //输入学生1的数据scanf("%d%s%f",&student2.num,student2.name,&student2.score); //输入学生1的数据printf("The higher score is:\n");if(student1.score>student2.score)printf("%d %s %6.2f\n",student1.num,student1.name,student1.score);else if(student1.score<student2.score)printf("%d %s %6.2f\n",student2.num,student2.name,student2.score);else{ printf("%d %s %6.2f\n",student1.num,student1.name,student1.score);printf("%d %s %6.2f\n",student2.num,student2.name,student2.score);}return 0;
}
2.使用结构体数组
struct 结构体名 {成员表列} 数组名[数组长度];
struct Person
{ char name[20];int count;
}
struct Person leader[3]; //leader是结构体数组名 例题:有3个候选人,每个选民只能投票选一人,要求编一个统计选票的程序,先后输入被选人的名字,最后输出各人得票结果。
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
struct Person //声明结构体类型struct Person
{ char name[20]; //候选人姓名int count; //候选人得票数
}leader[3]={"Li",0,"Zhang",0,"Sun",0}; //定义结构体数组并初始化int main()
{ int i,j;char leader_name[20]; //定义字符数组 for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ scanf("%s",leader_name); //输入所选的候选人姓名for(j=0;j<3;j++)if(strcmp(leader_name,leader[j].name)==0) leader[j].count++;}printf("\nResult:\n");for(i=0;i<3;i++)printf("%5s:%d\n",leader[i].name,leader[i].count);return 0;
}
3.结构体指针
通过指向结构体变量的指针变量输出结构体变量中成员的信息。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{ struct Student //声明结构体类型struct Student{ long num;char name[20];char sex;float score;};struct Student stu_1; //定义struct Student类型的变量stu_1 struct Student *p; //定义指向struct Student 类型数据的指针变量p p=&stu_1; //p指向stu_1 stu_1.num=10101; //对结构体变量的成员赋值 strcpy(stu_1.name,"Li Lin"); //用字符串复制函数给stu_1.name赋值stu_1.sex='M';stu_1.score=89.5;printf("No.:%ld\nname:%s\nsex:%c\nscore:%5.1f\n",stu_1.num,stu_1.name,stu_1.sex,stu_1.score); //输出结果 printf("\nNo.:%ld\nname:%s\nsex:%c\nscore:%5.1f\n",(*p).num,(*p).name,(*p).sex, (*p).score); return 0;
}
4.链表
4.1what is "linked list"
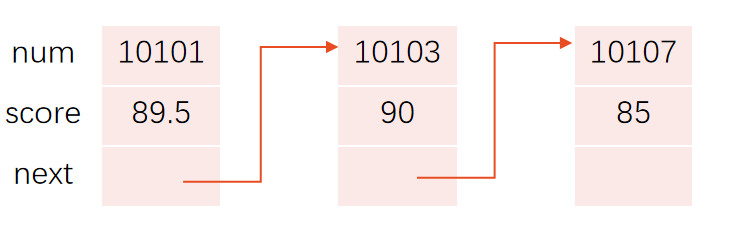
链表有一个“头指针”变量,图中以head表示,它存放一个地址,该地址指向一个元素。 链表中每一个元素称为“结点”,每个结点都应包括两个部分:
(1) 用户需要用的实际数据;
(2) 下一个结点的地址。
head指向第1个元素,第1个元素又指向第2个元素……直到最后一个元素,该元素不再指向其他元素,它称为“表尾”,它的地址部分放一个“NULL”(表示“空地址”),链表到此结束。

struct Student
{ int num;float score;struct Student *next; //next是指针变量,指向结构体变量
};
4.2建立简单的静态链表
Build a static linked list——"p"
#include <stdio.h>
struct Student //声明结构体类型struct Student
{ int num;float score;struct Student*next;
};
int main()
{ struct Student a,b,c,*head,*p; //定义3个结构体变量a,b,c作为链表的结点a.num=10101; a.score=89.5; //对结点a的num和score成员赋值b.num=10103; b.score=90; //对结点b的num和score成员赋值c.num=10107; c.score=85; //对结点c的num和score成员赋值head=&a; //将结点a的起始地址赋给头指针heada.next=&b; //将结点b的起始地址赋给a结点的next成员b.next=&c; //将结点c的起始地址赋给a结点的next成员c.next=NULL; //c结点的next成员不存放其他结点地址p=head; //使p指向a结点do{ printf("%ld %5.1f\n",p->num,p->score); //输出p指向的结点的数据p=p->next; //使p指向下一结点}while(p!=NULL); //输出完c结点后p的值为NULL,循环终止return 0;
}
-> 代表指针指向结点数据
4.3建立简单的动态链表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct Student)
struct Student
{ long num;float score;struct Student*next;
};
int n; //n为全局变量,本文件模块中各函数均可使用它
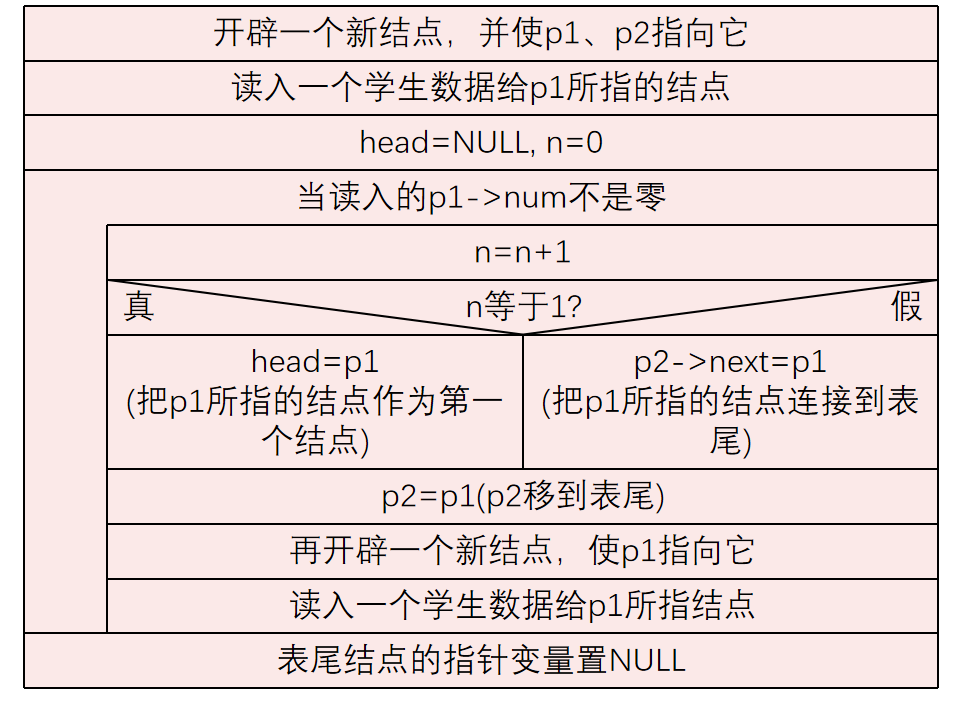
struct Student *creat(void)
//定义函数。此函数返回一个指向链表头的指针
{ struct Student *head;struct Student *p1,*p2;n=0;p1=p2=(struct Student*) malloc(LEN); //开辟一个新单元scanf("%ld,%f",&p1->num,&p1->score);//输入第1个学生的学号和成绩head=NULL;while(p1->num!=0){ n=n+1;if(n==1) head=p1;else p2->next=p1;p2=p1;p1=(struct Student*)malloc(LEN);//开辟动态存储区,把起始地址赋给p1scanf("%ld,%f",&p1->num,&p1->score);//输入其他学生的学号和成绩}p2->next=NULL;return(head);
}
int main()
{ struct Student *pt;pt=creat(); //函数返回链表第一个结点的地址 printf("\nnum:%ld\nscore:%5.1f\n",pt->num,pt->score);//输出第1个结点的成员值return 0;
};
4.4 输出链表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct Student)
struct Student //声明结构体类型struct Student
{ long num;float score;struct Student *next;
};
int n; //全局变量n
void print(struct Student*head) //定义print函数
{ struct Student*p; //在函数中定义struct Student类型的变量pprintf("\nNow,These %d records are:\n",n);p=head; //使p指向第1个结点if(head!=NULL) //若不是空表do{ printf("%ld %5.1f\n",p->num,p->score); //输出一个结点中的学号与成绩p=p->next; //p指向下一个结点}while(p!=NULL); //当p不是"空地址"
}
