【数据结构】每天五分钟,快速入门数据结构(一)——数组
目录
一.初始化语法
二.特点
三.数组中的元素默认值
四.时间复杂度
五.Java中的ArrayList类 可变长度数组
1 使用
2 注意事项
3 实现原理
4 ArrayList源码
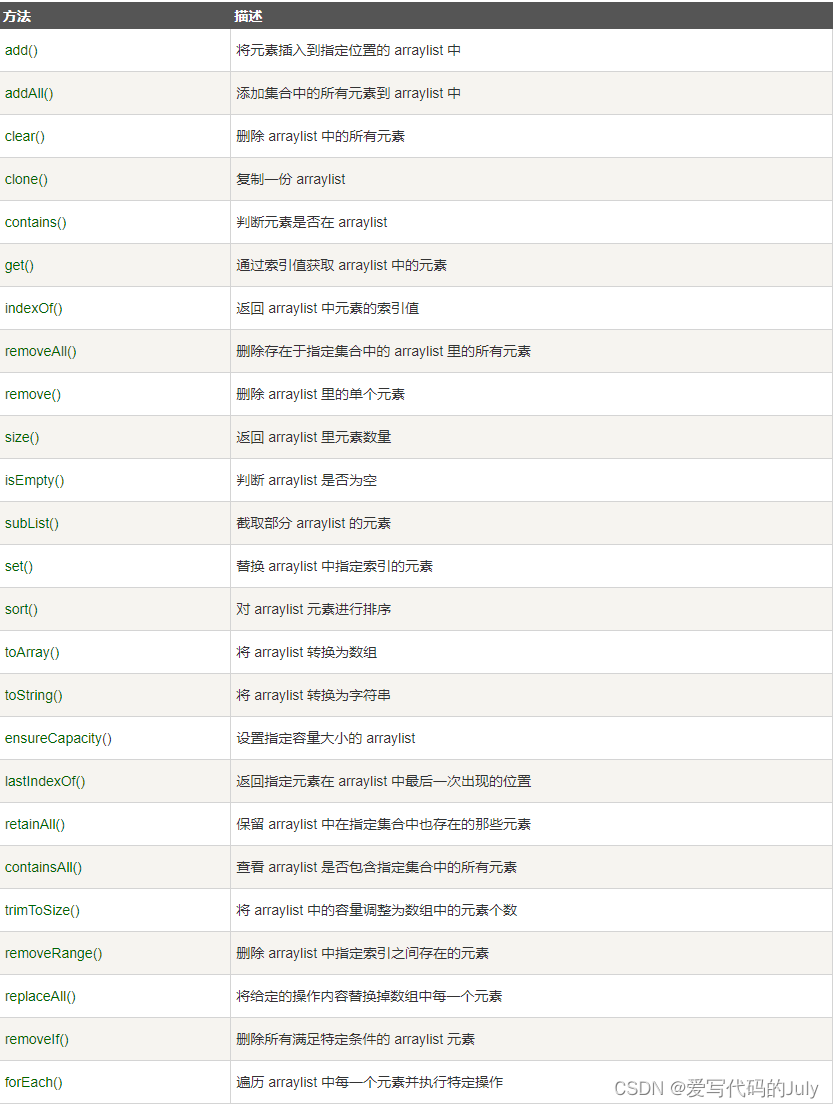
5 ArrayList方法
一.初始化语法
// 数组动态初始化(先定义数组,指定数组长度,后续再进行赋值)
int[] arr = new int[7];
arr[0] = 1;
// 数组静态初始化(在创建数组时直接赋值)
String[] names = new String[]{"张三","李四","王五"};
int[] nums = {0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4};
//遍历数组中的元素
for( int i = 0;i < arr.length; i++){System.out.println(arr[i]);
}二.特点
-
数组下标从0开始
-
随机访问能力:可以通过索引进行o(1)时间复杂度的访问
-
一旦初始化就不能改变长度
-
物理上和逻辑上都是连续的
三.数组中的元素默认值
int :0;
char: 空;
boolean: false;
double: 0.0;
引用类型:null
四.时间复杂度
在数组中的任意位置插入:O(n) 通过索引值访问数组元素:O(1)
查找数组中某个值所在的索引值:O(n)或者O(log n)(有序数组二分查找) 删除数组中的某个元素:O(n)
五.Java中的ArrayList类 可变长度数组
1 使用
ArrayList<String> sites = new ArrayList<String>(); // 创建一个可变长数组sites.add("张三"); // 添加元素sites.add("李四");sites.add("王五");System.out.println(sites); // 打印输出数组元素System.out.println(sites.get(1)); // 访问第二个元素sites.set(1, "柳柳"); // 修改元素内容,第一个参数为索引位置,第二个为要修改的值sites.remove(3); // 删除元素sites.size(); // 获取数组长度2 注意事项
-
数组下标从0开始
-
数组中存储的元素类型只能为引用类型,因此需要使用基本类型的包装类
3 实现原理
自动创建一个长度为n的数组,当存放的数据量超过n时,就重新创建一个更长的数组,再将原数组内容复制到新数组中,更改数组名指向地址。
4 ArrayList源码
package java.util;public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{// 序列版本号private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;// 默认容量大小private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;// 空数组private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};// 用于保存ArrayList中数据的数组private transient Object[] elementData;// ArrayList中所包含元素的个数private int size;// 带初始容量参数的构造函数public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {super();if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];}// 默认构造函数,其默认初始容量为10public ArrayList() {super();this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}// 带Collection参数的构造函数public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();size = elementData.length;// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);}// 将此 ArrayList 实例的容量调整为列表的当前大小(实际元素个数)public void trimToSize() {modCount++;if (size < elementData.length) {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}}// 如有必要,增加此 ArrayList 实例的容量,以确保它至少能够容纳最小容量参数所// 指定的元素数public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {int minExpand = (elementData != EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)// any size if real element table? 0// larger than default for empty table. It's already supposed to be// at default size.: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;if (minCapacity > minExpand) {ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}// 返回ArrayList中的元素个数public int size() {return size;}// 判断ArrayList是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}// 判断ArrayList是否包含Object(o)public boolean contains(Object o) {return indexOf(o) >= 0;}// 返回ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 -1public int indexOf(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)if (elementData[i]==null)return i;} else {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)if (o.equals(elementData[i]))return i;}return -1;}// 返回ArrayList中最后一次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含索引,则返回 -1public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)if (elementData[i]==null)return i;} else {for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)if (o.equals(elementData[i]))return i;}return -1;}// 返回此 ArrayList 实例的浅表副本public Object clone() {try {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")ArrayList<E> v = (ArrayList<E>) super.clone();// 将当前ArrayList的全部元素拷贝到v中v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);v.modCount = 0;return v;} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneablethrow new InternalError();}}// 按适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组public Object[] toArray() {return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);}// 返回ArrayList的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {if (a.length < size)// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);if (a.length > size)a[size] = null;return a;}// 位置访问操作 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E elementData(int index) {return (E) elementData[index];}// 返回ArrayList中指定位置上的元素public E get(int index) {rangeCheck(index);return elementData(index);}// 用指定的元素替代ArrayList中指定位置上的元素,并返回替代前的元素public E set(int index, E element) {rangeCheck(index);E oldValue = elementData(index);elementData[index] = element;return oldValue;}// 将指定的元素添加到ArrayList的尾部public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}// 将指定的元素插入ArrayList中的指定位置public void add(int index, E element) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index);elementData[index] = element;size++;}// 移除ArrayList中指定位置上的元素,并返回该位置上的元素public E remove(int index) {rangeCheck(index);modCount++;E oldValue = elementData(index);int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its workreturn oldValue;}// 移除ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在则移除并返回true,否则返回false)public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)if (elementData[index] == null) {fastRemove(index);return true;}} else {for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {fastRemove(index);return true;}}return false;}// 私有方法,用于快速移除private void fastRemove(int index) {modCount++;int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work}// 移除ArrayList中的所有元素public void clear() {modCount++;// clear to let GC do its workfor (int i = 0; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;size = 0;}// 按照指定 collection 的迭代器所返回的元素顺序,// 将该 collection 中的所有元素添加到ArrayList的尾部public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountSystem.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}// 从指定的位置开始,将指定 collection 中的所有元素插入到ArrayList中public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCountint numMoved = size - index;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,numMoved);System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);size += numNew;return numNew != 0;}// 移除列表中索引在 fromIndex(包括)和 toIndex(不包括)之间的所有元素protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {modCount++;int numMoved = size - toIndex;System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,numMoved);// clear to let GC do its workint newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {elementData[i] = null;}size = newSize;}// 私有方法,用于范围检测private void rangeCheck(int index) {if (index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}// 私有方法,用于add和addAllprivate void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {if (index > size || index < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;}// 移除ArrayList中Collection所包含的所有元素public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return batchRemove(c, false);}// 保留所有ArrayList和Collection共有的元素public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return batchRemove(c, true);}private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;int r = 0, w = 0;boolean modified = false;try {for (; r < size; r++)if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)elementData[w++] = elementData[r];} finally {// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection,// even if c.contains() throws.if (r != size) {System.arraycopy(elementData, r,elementData, w,size - r);w += size - r;}if (w != size) {// clear to let GC do its workfor (int i = w; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;modCount += size - w;size = w;modified = true;}}return modified;}// java.io.Serializable的写入函数// 将ArrayList的“容量,所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException{// Write out element count, and any hidden stuffint expectedModCount = modCount;s.defaultWriteObject();// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()s.writeInt(size);// Write out all elements in the proper order.for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {s.writeObject(elementData[i]);}if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}// java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出// 先将ArrayList的“容量”读出,然后将“所有的元素值”读出private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;// Read in size, and any hidden stuffs.defaultReadObject();// Read in capacitys.readInt(); // ignoredif (size > 0) {// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacityensureCapacityInternal(size);Object[] a = elementData;// Read in all elements in the proper order.for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {a[i] = s.readObject();}}}// 返回一个从指定位置开始遍历的ListIterator迭代器public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {if (index < 0 || index > size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);return new ListItr(index);}// 返回一个ListIterator迭代器public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {return new ListItr(0);}// 返回一个Iterator迭代器public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Itr();}// 返回一个指定范围的子List列表public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);}
}5 ArrayList方法