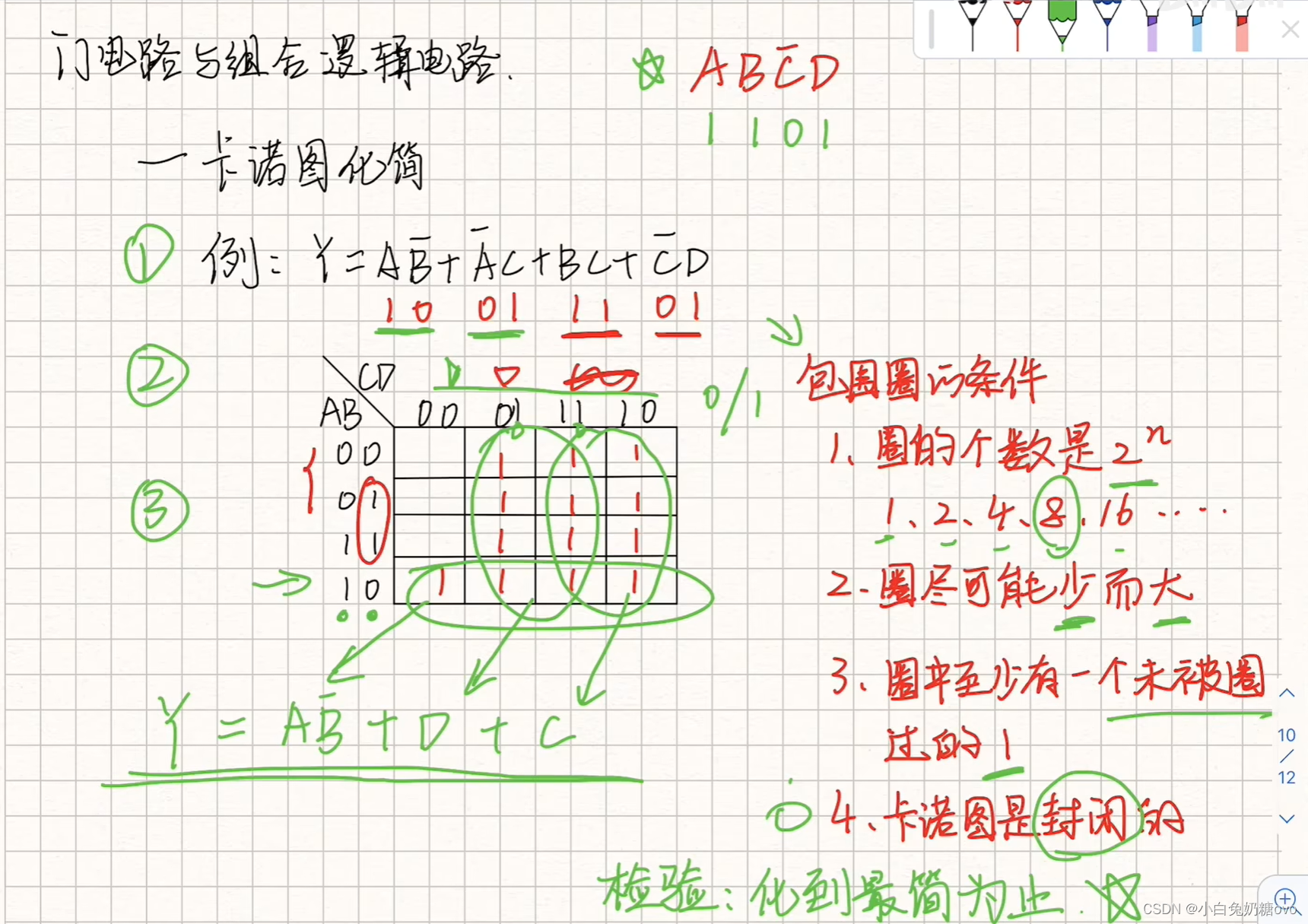
Karnaugh map (卡诺图)
【Leetcode】 289. Game of Life
According to Wikipedia’s article: “The Game of Life, also known simply as Life, is a cellular automaton devised by the British mathematician John Horton Conway in 1970.”
The board is made up of an m x n grid of cells, where each cell has an initial state: live (represented by a 1) or dead (represented by a 0). Each cell interacts with its eight neighbors (horizontal, vertical, diagonal) using the following four rules (taken from the above Wikipedia article):
- Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbors dies as if caused by under-population.
- Any live cell with two or three live neighbors lives on to the next generation.
- Any live cell with more than three live neighbors dies, as if by over-population.
- Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbors becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction.
The next state is created by applying the above rules simultaneously to every cell in the current state, where births and deaths occur simultaneously. Given the current state of the m x n grid board, return the next state.
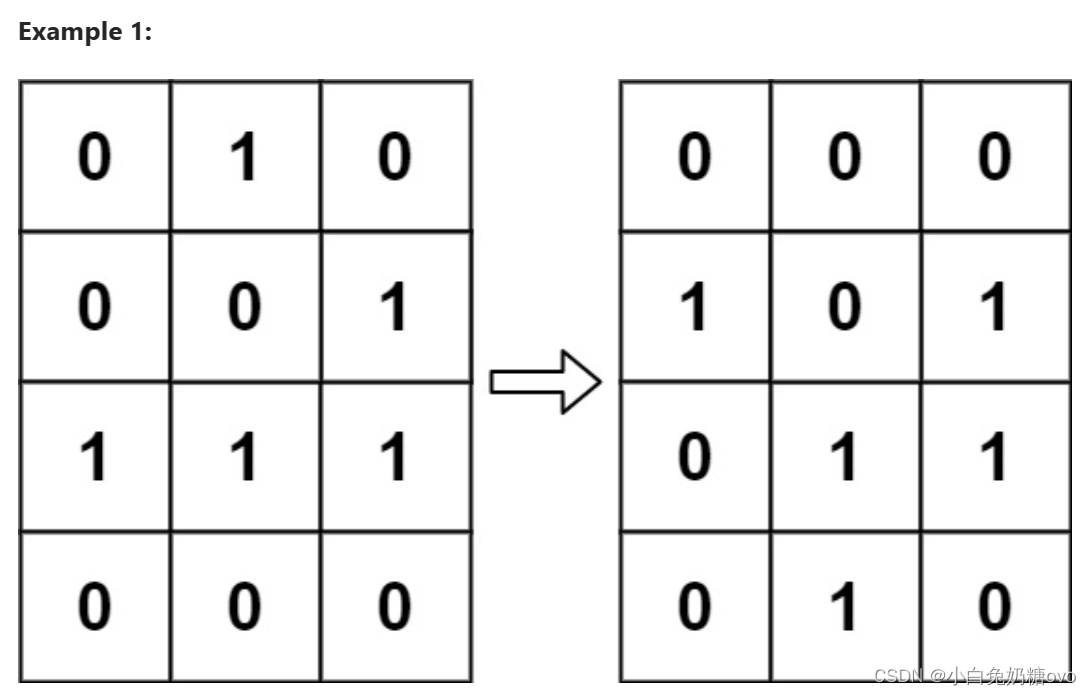
Input: board = [[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,1,1],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,1,0]]
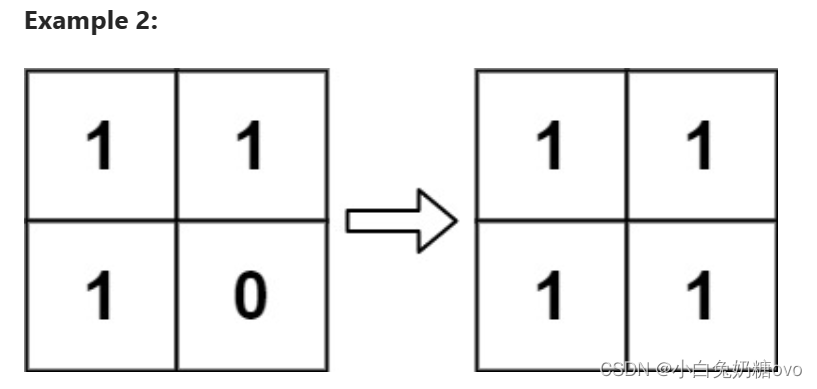
Input: board = [[1,1],[1,0]]
Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Constraints:
m == board.length
n == board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 25
board[i][j] is 0 or 1.
Follow up:
- Could you solve it in-place? Remember that the board needs to be updated simultaneously: You cannot update some cells first and then use their updated values to update other cells.
- In this question, we represent the board using a 2D array. In principle, the board is infinite, which would cause problems when the active area encroaches upon the border of the array (i.e., live cells reach the border). How would you address these problems?
AC:
/** @lc app=leetcode.cn id=289 lang=cpp** [289] 生命游戏*/// @lc code=start
class Solution {
public:void gameOfLife(vector<vector<int>>& board) {int neighbors[3] = {0, 1, -1};int rows = board.size();int cols = board[0].size();vector<vector<int>> copyBoard(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0));for(int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {for(int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {copyBoard[row][col] = board[row][col];}}for(int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {for(int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {int liveNeighbors = 0;for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {if(!(neighbors[i] == 0 && neighbors[j] == 0)) {int r = (row + neighbors[i]);int c = (col + neighbors[j]);if((r < rows && r >= 0) && (c < cols && c >= 0) && (copyBoard[r][c] == 1)) {liveNeighbors += 1;}}}}// 规则 1 || 规则 3if((copyBoard[row][col] == 1) && (liveNeighbors < 2 || liveNeighbors > 3)) {board[row][col] = 0;}//规则 4if(copyBoard[row][col] == 0 && liveNeighbors == 3) {board[row][col] = 1;}}}}
};
// @lc code=end
老规矩,附上官方题解链接
就该题而言,设计了诸多的逻辑判断语句,为了简化这些语句,使得代码看上去更加简洁。遂学习了卡诺图!
卡诺图(Karnaugh Map)是一种图形化的方法,用于简化逻辑函数或表达式。它是通过将逻辑函数的真值表可视化为一个方格图,然后根据特定的规则来识别和合并相邻的真值表项来进行简化的。
以下是在逻辑语句化简中使用卡诺图的步骤:
-
根据逻辑函数建立真值表:根据逻辑函数的输入和输出,创建一个真值表,列出所有可能的输入组合和相应的输出。
-
确定卡诺图的维度:根据逻辑函数的输入变量的数量,确定卡诺图的维度。如果有n个输入变量,则卡诺图的维度将是2^n。
-
绘制卡诺图:根据卡诺图的维度,在一个方格图中标出所有可能的输入组合,并将对应的输出值填入每个输入组合的方格中。
-
合并相邻项:根据特定的规则,合并卡诺图中相邻的真值表项。相邻的项是指它们的输入组合只有一个变量的不同。合并的目的是将多个项合并为更简单的表达式。
-
转换为逻辑表达式:根据合并后的卡诺图,将每个合并的区域转换为逻辑表达式。每个合并区域代表一个逻辑条件,可以通过将每个变量的值取反或保持不变来表示。最终的逻辑表达式是由所有合并区域的逻辑表达式组成的。
-
检查和验证:使用得到的简化表达式来验证原始逻辑函数。将原始逻辑函数和简化表达式的输出进行比较,确保它们在所有输入组合上都产生相同的结果。
通过使用卡诺图,可以更容易地理解和简化复杂的逻辑函数。它提供了一种可视化的方式来识别和合并相似的逻辑项,从而减少逻辑表达式的复杂性。
案例如下: